Abstract
Purpose
Heart sounds are basic factors to diagnosis cardiac diseases. To listen to heart sounds clearly, noises from auscultation sounds should be suppressed. Because a stethoscope provides just one channel, the general adaptive noise canceller is not appropriate to enhance heart sounds. Therefore, we proposed a modified adaptive noise canceller with an electrocardiogram to enhance heart sounds using a single stethoscope.
Methods
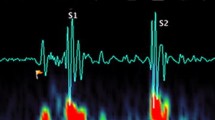
Auscultation sounds can be divided into heart sounds and non-heart sounds. The first heart beat (S1) appears when the R peak occurs on an electrocardiogram. After detecting S1, the second heart beat (S2) can be detected. Then, non-heart sounds are extracted by excluding S1 and S2 from the auscultation sounds. The proposed modified adaptive noise canceller uses the extracted non-heart sounds as reference input and suppresses auscultation sound noise.
Results
Two experiments were conducted to verify the performance of the proposed method. In the simulation, heart sounds were enhanced efficiently. In the experiment using clinical education database, heart sounds were enhanced about 7.7 dB.
Conclusions
Because auscultation sounds consist of various sounds occurring inside the body, heart sounds must be enhanced. We confirmed that the proposed method yielded good results. Therefore, it is expected that the proposed method can be applied to various cardiac diagnosis devices based on a computer system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Bai YW, Lu CL. The embedded digital stethoscope uses the adaptive noise cancellation filter and the type I Chebyshev IIR bandpass filter to reduce the noise of the heart sound. Proc Int Conf. Workshop Enterprise Networking Comput Health Care Industry. 2005; 278–281.
Tinati MA, Bouzerdoum A, Mazumdar J. Modified adaptive line enhancement filter and its application to heart sound noise cancellation. Proc Int Symposium Signal Process Appl Vol 2. 1996; 815–818.
Xiu-min Z, Gui-tao C. A novel de-noising method for heart sound signal using improved thresholding function in wavelet domain. Bio-Med Inform Eng. Int Conf Future. 2009; 65–68.
Bickley LS. Guide to physical examination & history taking. lippincott; 2002.
Carr JJ, Brown JM. Introduction to biomedical equipment technology third edition. Prentice hall; 1998.
Maried EN. Essentials of human anatomy & physiology seventh edition. Benjamin Cummings; 2002.
Widrow B, Stearns SD. Adaptive signal processing. Prentice Hall; 1985.
Tillkian AG. Understanding heart sounds and murmurs with an introduction to lung sounds fourth edition. Saunders; 2001.
http://www.e-mediworld.com/modules/cardioHMS/category/patients/ctscdc.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, P.U., Lee, Y., Cho, J.H. et al. Modified adaptive noise canceller with an electrocardiogram to enhance heart sounds in the auscultation sounds. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 1, 194–198 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-011-0032-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-011-0032-9