Abstract
Objective and methods
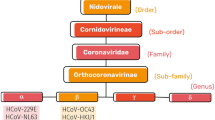
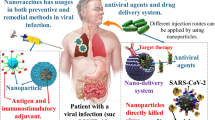
SARS-COV2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) has become life-threatening and emerged as a global pandemic in recent years. Although the understanding of coronaviruses has become the focus in almost every research field, efficient early diagnosis and treatment techniques still need improvement. Nanotechnology has presented various solutions to fighting SARS-CoV-2 through infection control measures, detection, therapeutics, and vaccines. More specifically, metallic nanoparticles such as gold, silver, iron, and others made a lot of effort to translate the products for real-time applications to control the pandemic.
Results and conclusion
Owing to their unique characteristics, such as high surface area volume ratio, non-toxic and excellent antiviral properties, metallic nanoparticles are extensively used in developing nanotechnology-based products like disinfection systems, nano-based masks, and other protecting equipment, diagnostic kits, effective therapeutic agents, and vaccines. In this review, we will discuss different metallic nanoparticles, their characteristics, and different approaches of their use to combat SARS-COV2. Thus, this review is highly instructive and helpful in developing strategies based on nanostructures to combat COVID-19.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashok G, Paul JJ, Thusnavis MB, Packiavathy SV, Gautam S (2023) Internet of Things (IoT) based automated sanitizer dispenser and COVID-19 statistics reporter in a post-pandemic world. Health Technol 13(2):327–341
Liu W, Liu L, Kou G, Zheng Y, Ding Y et al (2020) Evaluation of nucleocapsid and spike protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. J Clin Microbiol 6:e00461-e520
Gautam S (2020) The influence of COVID-19 on air quality in India: a boon or inutile. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104(6):724–726
Singh A, Gaud B, Jaybhaye S (2020) Optimization of synthesis parameters of silver nanoparticles and its antimicrobial activity. Mater Sci Energy Technol 3:232–236
Jayakumar, J, Ebanesar A, Gautam S (2023) Predictive analysis, diagnosis of COVID-19 through computational screening and validation with spectro photometrical approach. Toxicol Environ Health Sci 1–9.
Zhao Z, Cui H, Song W, Ru X, Zhou W, et al (2020) A simple magnetic nanoparticles-based viral RNA extraction method for efficient detection of SARS-CoV-2. Mol Biol
Kampf G, Todt D, Pfaender S, Steinmann E (2020) Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and their inactivation with biocidal agents. J Hosp Infect 3:246–251
Guan Y, Zheng BJ, He YQ, Liu XL, Zhuang ZX et al (2003) Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in Southern China. Science 5643:276–278
Zou L, Ruan F, Huang M, Liang L, Huang H et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. N Engl J Med 12:1177–1179
Onofrio L, Caraglia M, Facchini G, Margherita V, Placido SD et al (2020) Toll-like receptors and COVID-19: a two-faced story with an exciting ending. Future Sci OA 8:FSO605
Salata O (2004) No title found. J Nanobiotechnol 1:3
Khurana A, Allawadhi P, Khurana I, Allwadhi S, Weiskirchen R et al (2021) Role of nanotechnology behind the success of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19. Nano Today 38:101142
Nel AE, Miller JF (2021) Nano-enabled COVID-19 vaccines: meeting the challenges of durable antibody plus cellular immunity and immune escape. ACS Nano 4:5793–5818
Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S et al (2021) Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med 5:403–416
Hayashi Y, Matsuzawa M, Yamaguchi J, Yonehara S, Matsumoto Y et al (2006) Large nonlinear effect observed in the enantiomeric excess of proline in solution and that in the solid state. Angew Chem 28:4709–4713
Mody VV, Nounou MI, Bikram M (2009) Novel nanomedicine-based MRI contrast agents for gynecological malignancies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 10:795–807
Praetorius N, Mandal T (2007) Engineered nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul 1:37–51
Isaacoff BP, Brown KA (2017) Progress in top-down control of bottom-up assembly. Nano Lett 11:6508–6510
Khoshnevisan K, Maleki H, Baharifar H (2021) Nanobiocide based-silver nanomaterials upon coronaviruses: approaches for preventing viral infections. Nanoscale Res Lett 1:100
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C et al (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 6:2064–2110
Chandrakala V, Aruna V, Angajala G (2022) Review on metal nanoparticles as nanocarriers: current challenges and perspectives in drug delivery systems. Emergent Mater 6:1593–1615
Khan JA, Kudgus RA, Szabolcs A, Dutta S, Wang E et al (2011) Designing nanoconjugates to effectively target pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 6:e20347
Li W-R, Xie X-B, Shi Q-S, Zeng H-Y, Ou-Yang Y-S et al (2010) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 4:1115–1122
Yıldırım ÖA, Durucan C (2010) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles elaborated by microemulsion method. J Alloys Compd 2:944–949
Calderón L, Harris R, Cordoba-Diaz M, Elorza M, Elorza B et al (2013) Nano and microparticulate chitosan-based systems for antiviral topical delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci 1–2:216–222
Yeh Y-C, Creran B, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles: preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 6:1871–1880
Li C, Shuford KL, Park Q-H, Cai W, Li Y et al (2007) High-yield synthesis of single-crystalline gold nano-octahedra. Angew Chem Int Ed 18:3264–3268
Darroudi M, Ahmad MB, Zamiri R, Abdullah AH, Ibrahim NA et al (2011) Preparation and characterization of gelatin mediated silver nanoparticles by laser ablation. J Alloys Compd 4:1301–1304
Li M, Cushing SK, Wu N (2015) Plasmon-enhanced optical sensors: a review. Analyst 2:386–406
Tapasztó L, Dobrik G, Lambin P, Biró LP (2008) Tailoring the atomic structure of graphene nanoribbons by scanning tunnelling microscope lithography. Nat Nanotechnol 7:397–401
Nikbakht H, Gill P, Tabarraei A, Niazi A (2014) Nanomolecular detection of human influenza virus type A using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assisted with rod-Shaped gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv 26:13575
Manawi Y, Ihsanullah SA, Al-Ansari T, Atieh M (2018) A review of carbon nanomaterials’ synthesis via the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method. Materials 5:822
Komarneni S, Katsuki H (2002) Nanophase materials by a novel microwave-hydrothermal process. Pure Appl Chem 9:1537–1543
Sreekanth TVM, Nagajyothi PC, Muthuraman P, Enkhtaivan G, Vattikuti SVP et al (2018) Ultra-sonication-assisted silver nanoparticles using panax ginseng root extract and their anti-cancer and antiviral activities. J Photochem Photobiol B 188:6–11
Nissinen T, Ikonen T, Lama M, Riikonen J, Lehto V-P (2016) Improved production efficiency of mesoporous silicon nanoparticles by pulsed electrochemical etching. Powder Technol 288:360–365
Salleh A, Naomi R, Utami ND, Mohammad AW, Mahmoudi E et al (2020) The potential of silver nanoparticles for antiviral and antibacterial applications: a mechanism of action. Nanomaterials 8:1566
Vahedifard F, Chakravarthy K (2021) Nanomedicine for COVID-19: the role of nanotechnology in the treatment and diagnosis of COVID-19. Emergent Mater 1:75–99
Al-Hatamleh MAI, Hatmal MM, Alshaer W, Rahman ENSEA, Mohd-Zahid MH et al (2021) COVID-19 infection and nanomedicine applications for development of vaccines and therapeutics: an overview and future perspectives based on polymersomes. Eur J Pharmacol 896:173930
Gutierrez L, Li X, Wang J, Nangmenyi G, Economy J et al (2009) Adsorption of rotavirus and bacteriophage MS2 using glass fiber coated with hematite nanoparticles. Water Res 20:5198–5208
Koohi SR, Derakhshan MA, Faridani F, Muhammad Nejad S, Amanpour S et al (2018) Plasmonic photothermal therapy of colon cancer cells utilising gold nanoshells: an in vitro study. IET Nanobiotechnol 2:196–200
Kubo R (1962) Electronic properties of metallic fine particles. I J Phys Soc Jpn 6:975–986
Zhou J, Kroll AV, Holay M, Fang RH, Zhang L (2020) Biomimetic nanotechnology toward personalized vaccines. Adv Mater 13:1901255
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2006) Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B 14:7238–7248
Link S, El-Sayed MA (1999) Spectral properties and relaxation dynamics of surface plasmon electronic oscillations in gold and silver nanodots and nanorods. J Phys Chem B 40:8410–8426
Kneipp K, Wang Y, Kneipp H, Perelman LT, Itzkan I et al (1997) Single molecule detection using surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS). Phys Rev Lett 9:1667–1670
Talebian S, Wallace GG, Schroeder A, Stellacci F, Conde J (2020) Nanotechnology-based disinfectants and sensors for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Nanotechnol 8:618–621
Clem AL, Sims J, Telang S, Eaton JW, Chesney J (2007) Virus detection and identification using random multiplex (RT)-PCR with 3’-locked random primers. Virol J 1:65
Jung JY, Yoon HK, An S, Lee JW, Ahn E-R et al (2018) Rapid oral bacteria detection based on real-time PCR for the forensic identification of saliva. Sci Rep 1:10852
Xiang J, Yan M, Li H, Liu T, Lin C, et al (2020) Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunoassay and colloidal gold-immunochromatographic assay kit for detection of novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) causing an outbreak of pneumonia (COVID-19). Epidemiology
Santiago I (2020) Trends and innovations in biosensors for COVID-19 mass testing. ChemBioChem 20:2880–2889
Carter LJ, Garner LV, Smoot JW, Li Y, Zhou Q et al (2020) Assay techniques and test development for COVID-19 diagnosis. ACS Cent Sci 5:591–605
Huang X, Zhao Z, Fan J, Tan Y, Zheng N (2011) Amine-assisted synthesis of concave polyhedral platinum nanocrystals having 411 high-index facets. J Am Chem Soc 13:4718–4721
Gao Y, Yan L, Huang Y, Liu F, Zhao Y et al (2020) Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science 6492:779–782
Glynou K, Ioannou PC, Christopoulos TK, Syriopoulou V (2003) Oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticles as probes in a dry-reagent strip biosensor for DNA analysis by hybridization. Anal Chem 16:4155–4160
Ventura BD, Cennamo M, Minopoli A, Campanile R, Censi SB et al (2020) Colorimetric test for fast detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasal and throat swabs. ACS Sens 10:3043–3048
Udugama B, Kadhiresan P, Kozlowski HN, Malekjahani A, Osborne M et al (2020) Diagnosing COVID-19: the disease and tools for detection. ACS Nano 4:3822–3835
Loynachan CN, Thomas MR, Gray ER, Richards DA, Kim J et al (2018) Platinum nanocatalyst amplification: redefining the gold standard for lateral flow immunoassays with ultrabroad dynamic range. ACS Nano 1:279–288
Khan J, Rasmi Y, Kırboğa KK, Ali A, Rudrapal M et al (2022) Development of gold nanoparticle-based biosensors for COVID-19 diagnosis. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 1:111
Moitra P, Alafeef M, Dighe K, Frieman MB, Pan D (2020) Selective naked-eye detection of SARS-CoV-2 mediated by N gene targeted antisense oligonucleotide capped plasmonic nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6:7617–7627
Pramanik A, Gao Y, Patibandla S, Mitra D, McCandless MG et al (2021) The rapid diagnosis and effective inhibition of coronavirus using spike antibody attached gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv 6:1588–1596
Dykman LA, Staroverov SA, Fomin AS, Gabalov KP (2021) The potential of gold nanoparticles for coronavirus diagnosis and prophylaxis. In: Tuchin VV, Genina EA, eds. Saratov fall meeting 2020: optical and nanotechnologies for biology and medicine. SPIE, Saratov, Russian Federation, p 40
Barcikowski S, Devesa F, Moldenhauer K (2009) Impact and structure of literature on nanoparticle generation by laser ablation in liquids. J Nanoparticle Res 8:1883–1893
Gurunathan S, Park JH, Han JW, Kim J-H (2015) Comparative assessment of the apoptotic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Bacillus tequilensis and Calocybe indica in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells: targeting p53 for anticancer therapy. Int J Nanomed 10:4203
Mukherjee P, Ahmad A, Mandal D, Senapati S, Sainkar SR et al (2001) Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their immobilization in the mycelial matrix: a novel biological approach to nanoparticle synthesis. Nano Lett 10:515–519
Chernousova S, Epple M (2013) Silver as Antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Ed 6:1636–1653
Galdiero S, Falanga A, Vitiello M, Cantisani M, Marra V et al (2011) Silver nanoparticles as potential antiviral agents. Molecules 10:8894–8918
Wong KKY, Cheung SOF, Huang L, Niu J, Tao C et al (2009) Further evidence of the anti-inflammatory effects of silver nanoparticles. ChemMedChem 7:1129–1135
Cohen J (2020) Lab’s scramble to spot hidden coronavirus infections. Science
Marimuthu S, Antonisamy AJ, Malayandi S, Rajendran K, Tsai P-C et al (2020) Silver nanoparticles in dye effluent treatment: a review on synthesis, treatment methods, mechanisms, photocatalytic degradation, toxic effects and mitigation of toxicity. J Photochem Photobiol B 205:111823
Chen Y-N, Hsueh Y-H, Hsieh C-T, Tzou D-Y, Chang P-L (2016) Antiviral activity of graphene-silver nanocomposites against non-enveloped and enveloped viruses. Int J Environ Res Public Health 4:430
AbdEllah NH, Gad SF, Muhammad K, E Batiha G, Hetta HF (2020) Nanomedicine as a promising approach for diagnosis, treatment, and prophylaxis against COVID-19. Nanomedicine 21:2085–2102
Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Soc Rev 3:209–217
Karagoz S, Kiremitler NB, Sarp G, Pekdemir S, Salem S et al (2021) Antibacterial, antiviral, and self-cleaning mats with sensing capabilities based on electrospun nanofibers decorated with ZnO nanorods and Ag nanoparticles for protective clothing applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:5678–5690
Pilaquinga F, Morey J, Torres M, Seqqat R, Piña MDLN (2021) Silver nanoparticles as a potential treatment against SARS-COV-2: a review. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 13(5):e1707
Jeremiah SS, Miyakawa K, Morita T, Yamaoka Y, Ryo A (2020) Potent antiviral effect of silver nanoparticles on SARS-CoV-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1:195–200
He Q, Lu J, Liu N, Lu W, Li Y et al (2022) Antiviral properties of silver nanoparticles against SARS-CoV-2: effects of surface coating and particle size. Nanomaterials 6:990
Allawadhi P, Singh V, Khurana A, Khurana I, Allwadhi S et al (2021) Silver nanoparticle based multifunctional approach for combating COVID-19. Sens Int 2:100101
Huber D (2005) Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 5:482–501
Fernández-Remolar DC (2015) Iron oxides, hydroxides and oxy-hydroxides. In: Gargaud M, Irvine WM, Amils R, Cleaves HJ, Pinti DL, et al., (eds.) Encyclopedia of astrobiology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 1268–1270.
Crist RM, Grossman JH, Patri AK, Stern ST, Dobrovolskaia MA et al (2013) Common pitfalls in nanotechnology: lessons learned from NCI’s nanotechnology characterization laboratory. Integr Biol 1:66–73
Fortin J-P, Wilhelm C, Servais J, Ménager C, Bacri J-C et al (2007) Size-sorted anionic iron oxide nanomagnets as colloidal mediators for magnetic hyperthermia. J Am Chem Soc 9:2628–2635
Murugan K, Wei J, Alsalhi MS, Nicoletti M, Paulpandi M et al (2017) Magnetic nanoparticles are highly toxic to chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum, dengue virus (DEN-2), and their mosquito vectors. Parasitol Res 2:495–502
Roy A, Bulut O, Some S, Mandal AK, Yilmaz MD (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv 5:2673–2702
Kumar R, Nayak M, Sahoo GC, Pandey K, Sarkar MC et al (2019) Iron oxide nanoparticles based antiviral activity of H1N1 influenza A virus. J Infect Chemother 5:325–329
Wiehe A, O’Brien JM, Senge MO (2019) Trends and targets in antiviral phototherapy. Photochem Photobiol Sci 11:2565–2612
Maisch T (2007) Anti-microbial photodynamic therapy: useful in the future? Lasers Med Sci 2:83–91
Coyne DW (2009) Ferumoxytol for treatment of iron deficiency anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother 15:2563–2568
Weiss C, Carriere M, Fusco L, Capua I, Regla-Nava JA et al (2020) Toward nanotechnology-enabled approaches against the COVID-19 pandemic. ACS Nano 6:6383–6406
Nicola M, Alsafi Z, Sohrabi C, Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A et al (2020) The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): a review. Int J Surg 78:185–193
Russell P, Esser L, Hagemeyer CE, Voelcker NH (2023) The potential impact of nanomedicine on COVID-19-induced thrombosis. Nat Nanotechnol 1:11–22
Johnstone TC, Suntharalingam K, Lippard SJ (2016) The next generation of platinum drugs: targeted Pt(II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt(IV) prodrugs. Chem Rev 5:3436–3486
Wang Z, Chen L, Huang C, Huang Y, Jia N (2017) Albumin-mediated platinum nanocrystals for in vivo enhanced computed tomography imaging. J Mater Chem B 19:3498–3510
Doherty RE, Sazanovich IV, McKenzie LK, Stasheuski AS, Coyle R et al (2016) Photodynamic killing of cancer cells by a Platinum(II) complex with cyclometallating ligand. Sci Rep 1:22668
Liu Y, Chen S, Zhong L, Wu G (2009) Preparation of high-stable silver nanoparticle dispersion by using sodium alginate as a stabilizer under gamma radiation. Radiat Phys Chem 4:251–255
Madsen AT, Ahmed EH, Christensen CH, Fehrmann R, Riisager A (2011) Hydrodeoxygenation of waste fat for diesel production: study on model feed with Pt/alumina catalyst. Fuel 11:3433–3438
Kasem KK (2012) Role of platinum in photoelectrochemical studies related to solar energy harvesting. Platin Met Rev 4:221–228
Popok VN, Stepanov AL, Odzhaev VB (2005) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by the ion implantation method and investigation of their optical properties. J Appl Spectrosc 2:229–234
Wani IA, Ganguly A, Ahmed J, Ahmad T (2011) Silver nanoparticles: ultrasonic wave assisted synthesis, optical characterization and surface area studies. Mater Lett 3:520–522
Shim I-K, Lee YI, Lee KJ, Joung J (2008) An organometallic route to highly monodispersed silver nanoparticles and their application to ink-jet printing. Mater Chem Phys 2–3:316–321
Dong C, Zhang X, Cai H (2014) Green synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles using hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose. J Alloys Compd 583:267–271
Poon W-L, Alenius H, Ndika J, Fortino V, Kolhinen V et al (2017) Nano-sized zinc oxide and silver, but not titanium dioxide, induce innate and adaptive immunity and antiviral response in differentiated THP-1 cells. Nanotoxicology 7:936–951
Miyako E, Nagata H, Hirano K, Sakamoto K, Makita Y et al (2008) Photoinduced antiviral carbon nanohorns. Nanotechnology 7:075106
Cuevas-Ferrando E, Randazzo W, Pérez-Cataluña A, Falcó I, Navarro D et al (2021) Platinum chloride-based viability RT-qPCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection in complex samples. Sci Rep 1:18120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Istuti Saraswat, Sarmistha Saha, Anuja Mishra declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saraswat, I., Saha, S. & Mishra, A. A review of metallic nanostructures against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 15, 315–324 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-023-00182-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-023-00182-9