Abstract
Objective
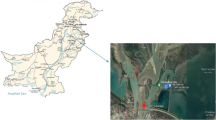
The present study aims to demonstrate whether there is a simultaneous seasonal (wet season and dry season) variation in different bacterial counts and detection of heavy metals in shrimp and water of the Karnaphuli River which is one of the major rivers of Bangladesh.
Methods
We collected water and shrimp samples from the river and studied the physicochemical parameters (for water only), different bacterial counts and detection level of heavy metals of both sample types. We analysed our data among and within the samples.
Results
We found that some of the physicochemical parameters of water of the river are significantly varied seasonally. We did not find the bacteriological count to vary significantly in both shrimp and water samples, except the total viable bacterial (TVB) count during the wet and dry seasons for water samples. We found that lead (Pb) significantly increased during the dry season in water samples. Also, there was a slight increment of Pb in shrimp samples during the dry season. However, in other analysis, we also found a seasonal variation in heavy metals individually for shrimp and water samples but not both.
Conclusion
The present study failed to identify a simultaneous increase or decrease in bacterial counts and detection of heavy metals in water and shrimp samples of the Karnaphuli River. Further large-scale analysis would be required to understand an association of pollution between shrimp and water of the river.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hossen M, Rafiq F, Kabir M, Morshed M (2019) Assessment of water quality scenario of Karnaphuli River in terms of water quality index, South-Eastern Bangladesh. Am J Water Resour 7(3):106–110
Bhuyan MS, Islam MS (2017) Status and impacts of industrial pollution on the Karna fully river in Bangladesh: a review. Int J Mar Sci 7:16
Islam MR, Das NG, Barua P, Hossain MB, Venkatramanan S, Chung SY (2017) Environmental assessment of water and soil contamination in Rajakhali Canal of Karnaphuli River (Bangladesh) impacted by anthropogenic influences: a preliminary case study. Appl Water Sci 7(2):997–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0310-2
Wang A-J, Kawser A, Xu Y-H, Ye X, Rani S, Chen K-l (2016) Heavy metal accumulation during the last 30 years in the Karnaphuli River estuary, Chittagong, Bangladesh. SpringerPlus 5(1):2079. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3749-1
Islam MM, Karim MR, Zheng X, Li X (2018) Heavy metal and metalloid pollution of soil, water and foods in Bangladesh: a critical review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(12):20181211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122825
Alam K, Rabbi F, Ahsan DC, Sultana DS (2022) Seasonal variation and molecular characterization of vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from Karnaphuni river and Estuary of Chittagong, Bangladesh. Biores Commun (BRC) 6(2):904–913
Ali MM, Ali ML, Proshad R, Islam S, Rahman Z, Tusher TR et al (2020) Heavy metal concentrations in commercially valuable fishes with health hazard inference from Karnaphuli river, Bangladesh. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 26(10):2646–2662. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1676635
Uddin MR, Hossain MM, Akter S, Ali ME, Ahsan MA (2020) Assessment of some physicochemical parameters and determining the corrosive characteristics of the Karnaphuli estuarine water, Chittagong, Bangladesh. Water Sci 34(1):164–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/11104929.2020.1803662
Sarwar MI, Majumder AK, Islam MN (2010) Water quality parameters: a case study of Karnafully river Chittagong, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Sci Ind Res 45(2):177–181
Uddin MJ, Jeong Y-K (2021) Urban river pollution in Bangladesh during last 40 years: potential public health and ecological risk, present policy, and future prospects toward smart water management. Heliyon 7(2):06107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06107
Siddiquee NA, Parween S, Quddus M, Barua P (2012) Heavy metal pollution in sediments at ship breaking area of Bangladesh. Coastal environments: focus on Asian regions. Springer, pp 78–87
Wang A-J, Kawser A, Xu Y-H, Ye X, Rani S, Chen K-l (2016) Heavy metal accumulation during the last 30 years in the Karnaphuli River estuary, Chittagong Bangladesh. Springerplus 5(1):1–14
Alam MW, Zafar M (2012) Occurrences of Salmonella spp. in water and soil sample of the Karnafuli river estuary. Microbes Health 1(2):41–45
Dey S, Uddin MS, Manchur MA (2017) Physicochemical and bacteriological assessment of surface water quality of the Karnaphuli River in Bangladesh. J Pure Appl Microbiol 11(4):1721–1728
Ling T-Y, Gerunsin N, Soo C-L, Nyanti L, Sim S-F, Grinang J (2017) Seasonal changes and spatial variation in water quality of a large young tropical reservoir and its downstream river. J Chem 2017:8153246. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8153246
Alam M, Uddin M, Satter M, Majed N (2020) Seasonal variation of water quality and waste loads in Buriganga river with GIS visualization. Bangladesh J Sci Ind Res 55(2):113–130
Patel V, Parikh P (2013) Assessment of seasonal variation in water quality of River Mini, at Sindhrot, Vadodara. Int J Environ Sci 3(5):1424–1436
Ren X, Wang Q, Shao H, Xu Y, Liu P, Li J (2021) Effects of low temperature on shrimp and crab physiology, behavior, and growth: a review. Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.746177
Ahmed ASS, Sultana S, Habib A, Ullah H, Musa N, Hossain MB et al (2019) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some commercially important fishes from a tropical river estuary suggests higher potential health risk in children than adults. PLoS One 14(10):0219336. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219336
Ezemonye LI, Adebayo PO, Enuneku AA, Tongo I, Ogbomida E (2019) Potential health risk consequences of heavy metal concentrations in surface water, shrimp (Macrobrachium macrobrachion) and fish (Brycinus longipinnis) from Benin River, Nigeria. Toxicol Rep 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.11.010
Maurya PK, Malik DS, Yadav KK, Kumar A, Kumar S, Kamyab H (2019) Bioaccumulation and potential sources of heavy metal contamination in fish species in River Ganga basin: possible human health risks evaluation. Toxicol Rep 6:472–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.05.012
Hossain MB, Bhuiyan NZ, Kasem A, Hossain MK, Sultana S, Nur AU et al (2022) Heavy metals in four marine fish and shrimp species from a subtropical coastal area: accumulation and consumer health risk assessment. Biology (Basel) 11(12):20221207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121780
Jeyachandran S, Kiyun P, Ihn-Sil K, Vaseeharan B (2021) Bacterial Disease Control Methods in Shrimp (Penaeus) Farming Sector in Asian Countries. In: Ramón ERR (ed) Arthropods. IntechOpen
Li J, Jiang H, Li L, Zhang X, Chen J (2019) The effect of disease and season to hepatopancreas and intestinal mycobiota of litopenaeus vannamei. Front Microbiol 10:889. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00889
Oudainia SE, Derbal F, Alik O, Bourehail N (2022) Seasonal and sexual variations of trace-metal elements (Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, Fe) in muscle and eggs of the deep-water Pandalid Shrimp Plesionika edwardsii (Brandt 1851) from Northeast Algeria. Thalassas Int J Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-022-00512-7
Alam SMN (2023) Advancing quality and health management practices in extensive shrimp (Penaeus monodon) farming in Bangladesh. Aquacult Int 31(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-022-00961-0
Alam MS, Liu Q, Schneider P, Mozumder MMH, Uddin MM, Monwar MM et al (2022) Stock assessment and rebuilding of two major shrimp fisheries (Penaeus monodon and Metapenaeus monoceros) from the industrial fishing zone of Bangladesh. J Mar Sci Eng 10(2):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020201
Rahman IMM, Barua S, Barua R, Mutsuddi R, Alamgir M, Islam F et al (2017) Quality assessment of the non-carbonated bottled drinking water marketed in Bangladesh and comparison with tap water. Food Control 73:1149–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.10.032
Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (1974) Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology
Mallick D, Shafiqul IM, Talukder A, Mandol S, Al Imran M, Biswas S (2016) Seasonal variability in water chemistry and sediment characteristics of intertidal zone at Karnafully estuary, Bangladesh
Bhuyan MS, Bakar M (2017) Assessment of water quality in Halda River (the Major carp breeding ground) of Bangladesh
Rahman MH, Ferdouse J, Ullah AKMA, Hossain MT (2022) Water quality assessment and identification of novel bacterial strains in the Halda river water of Bangladesh. Air Soil Water Res 15:11786221221135164. https://doi.org/10.1177/11786221221135164
Sikdar MSS, Abony M, Zerin T, Banik A, Datta S (2018) Seasonal variation of bacterial load in river and lake waters of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Microbiol 35(2):116–121
Yousuf AHM, Ahmed MK, Yeasmin S, Ahsan N, Rahman MM, Islam MM (2008) Prevalence of microbial load in shrimp, Penaeus monodon and prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii from Bangladesh. World J Agric Sci 4(5):852–855
Møretrø T, Moen B, Heir E, Hansen AÅ, Langsrud S (2016) Contamination of salmon fillets and processing plants with spoilage bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 237:98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.08.016
Rondón-Espinoza J, Gavidia CM, González R, Ramos D (2022) Water quality and microbiological contamination across the fish marketing chain: a case study in the Peruvian Amazon (Lagoon Yarinacocha). Water 14(9):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091465
Haque MA, Jewel MAS, Al Masud A, Rahman MS, Hasan J (2018) Assessment of bacterial pollution in sediment of padma river, Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Curr World Environ 13(1):66
Hossain MN, Rahaman A, Hasan MJ, Uddin MM, Khatun N, Shamsuddin SM (2021) Comparative seasonal assessment of pollution and health risks associated with heavy metals in water, sediment and Fish of Buriganga and Turag river in Dhaka city, Bangladesh. SN Appl Sci 3(4):509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04464-0
Ahmad M, Islam S, Rahman S, Haque M, Islam M (2010) Heavy metals in water, sediment and some fishes of Buriganga River, Bangladesh
Ali MM, Ali ML, Islam MS, Rahman MZ (2016) Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 5:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.01.002
Aytekin T, Kargın D, Çoğun HY, Temiz Ö, Varkal HS, Kargın F (2019) Accumulation and health risk assessment of heavy metals in tissues of the shrimp and fish species from the Yumurtalik coast of Iskenderun Gulf, Turkey. Heliyon 5(8):02131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02131
Deniz A, Köşker AR, Durmuş M, Bakan M (2016) Determination of seasonal changes on some heavy metal (Cd, Pb, Cr) levels of shrimp and prawn species from north-eastern Mediterranean sea, Gulf of Mersin, Turkey. J Aquac Eng Fish Res 2(2):42–49
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the Department of Microbiology, University of Chittagong, Samuda Chemical Complex Limited, and Atomic Energy Centre, Chattogram, Bangladesh, for providing the laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Sayonthoni Das Tuhi, Rasel Barua, Rajesh Mutsuddi, Nipa Deb, Md. Rezaul Karim, Shahadat Hossain, and Mohammed Abul Manchur declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Animal Ethical Review Board, Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of Chittagong, approved the shrimp associated experimental issues in this study.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tuhi, S.D., Barua, R., Mutsuddi, R. et al. An analysis of simultaneous seasonal variation in different bacterial counts and detection of heavy metals in water and shrimp of the Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 15, 239–247 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-023-00177-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-023-00177-6