Abstract
Objective
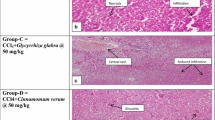
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) toxicity is the model commonly exploited to produce hepatic damage. This model is used to screen drugs with hepatoprotective activity on various experimental animals and to validate their liver protecting property. Carbon tetrachloride gets accumulated in hepatic parenchymal cells and is metabolically activated by cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenases to generate free radicals which covalently bind with tissue macromolecules like carbohydrates and proteins causing disturbances in cellular homeostasis. This may lead to the initiation of lipid peroxidation a sequence of chain reactions in cellular membranes which ultimately may result in steatosis. The present study was an attempt to study the anti-hepatotoxic, hypolipidemic and hypoglycaemic effect of S. nigrum against CCl4 - induced hepatotoxicity in female mice.
Methods
The hypolipidemic, hypoglycaemic and hepatoprotective activity of hydroalcoholic extract of S. nigrum was evaluated by various biochemical parameters and by histopathological examination.
Results
Carbon tetrachloride administration caused a significant increase in liver total lipids, triglyceride (TG), cholesterol and free fatty acid content. Similarly serum low density lipoproteins (LDL-C), very low density lipoprotein levels (VLDL-C) and bilirubin were elevated after toxin administration, while serum high density lipoproteins (HDL-C) was lowered as compared to vehicle control. It was observed that oral administration of the toxin caused a significant increase in blood glucose level, while a significant decrease was observed in the glycogen and protein content of the liver and albumin content of serum as compared to vehicle control.
Conclusion
Oral administration of S. nigrum effectively mitigated the changes induced by CCl4 in a dose - dependent manner. Our results indicated S. nigrum exerts hepatoprotective property by stabilizing tissue macromolecules resulting in maintenance of cellular hemeostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perumpail, B. J. et al. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 23, 8263–8276 (2017).
Recknagel, R. O. Carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol. Rev. 19, 145–208 (1967).
Weber, L. W. D., Boll, M. & Stampfl, A. Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 33, 105–136 (2003).
Patel, A., Biswas, S., Shoja, M. H., Ramalingayya, G. V. & Nandakumar, K. Protective Effects of Aqueous Extract of Solanum nigrum Linn. Leaves in Rat Models of Oral Mucositis. Sci. World J. 2014, doi: 10.1155/ 2014/345939 (2014).
Mushtaq, A. & Ahmad, M. Hepatoprotective Activity of Aqueous–Ethanolic Extract of Solanum nigrum Against Nimesulide Intoxicated Albino rats. Eur. J. Zool. Res. 2, 19–25 (2013).
Sah, A. K., Rambhade, A., Gohate, A., Rambhade, S. K. & Goswami, R. B. Hepatoprotective activity of Phyllanthus Niruri herbs and Solanum nigrum stem bark against paracetamol–induced hepatotoxicity. Am. J. Pharm Tech Res. 2, 1–10 (2012).
Raju, K. et al. Effect of dried fruits of Solanum nigrum Linn. against CCl4–induced hepatic damage in rats. Biol. Pharma. Bull. 26, 1618–1619 (2003).
Lin, H. M. et al. Hepatoprotective effects of Solanum nigrum Linn extract against CCl4–induced oxidative damage in rats. Chem–Biol. Interact. 171, 283–293 (2008).
Arulmozhi, V., Krishnaveni, M., Karthishwaran, K., Dhamodharan, G. & Mirunalini, S. Antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic effect of Solanum nigrum fruit extract on the experimental model against chronic ethanol toxicity. Pharmacogn. Mag. 6, 42–50 (2010).
Lee, S. J., Ko, J. H., Lim, K. & Lim, K. T. 150 kda glycoprotein isolated from Solanum nigrum Linne enhances activities of detoxicant enzymes and lowers plasmic cholesterol in mouse. Pharmacol. Res. 51, 399–408 (2005).
Sohrabipour, S., Kharazmi, F., Soltani, N. & Kamalinejad, M. Effect of the administration of Solanum nigrum fruit on blood glucose, lipid profiles, and sensitivity of the vascular mesenteric bed to phenylephrine in streptozotocin–induced diabetic rats. Med. Sci. Monitor Basic Res. 19, 133–140 (2013).
Fang, H. L. & Lin, W. C. Corn oil enhancing hepatic lipid peroxidation induced by CCl4 does not aggravate liver fibrosis in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 46, 2267–2273 (2008).
Hsieh, C. C., Fang, H. L. & Lina, W. C. Inhibitory effect of Solanum nigrum on thioacetamide–induced liver fibrosis in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 119, 117–121 (2008).
Attia, M. N. T. & Ali, M. A. Hepatoprotective activity of allicin against carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic injury in rats. J. Biol. Sci. 6, 457–468 (2006).
Ploa, G. L. & Hewitt W. R. in Principles and Methods of Toxicology (edn Wallace, H. A.) 599–628 (Raven Press, New York, 1989).
Pappas, Jr. N. J. Source of increased serum aspartate and alanine aminotransferase: cycloheximide effect on carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Clin. Chim. Acta. 154, 181–190 (1986).
Chander, R., Kapoor, N. K. & Dhawan, B. N. Picroliv affects gamma–glutamyl cycle in liver and brain of Mastomys natalensis infected with Plasmodium berghei. Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 32, 324–327 (1994).
Lee, S. J. & Lim, K. T. Glycine–and proline–rich glycoprotein regulates the balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis for ACF formation in 1,2–dimethylhydrazine–treated A/J mice. Mol. Cellular Biochem. 325, 187–197 (2009).
Wang, M. Y., Anderson, G., Nowicki, D. & Jensen, J. Hepatic protection by noni fruit juice against CCl4–induced chronic liver damage in female SDrats. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 63, 141–145 (2008).
Iritani, N. & Fukuda, E. Effect of corn oil feeding on triglyceride synthesis in the rat. J. Nutr. 110, 1138–1143 (1980b).
Boll, M., Weber, L. W. D., Becker, E. & Stampfl, A. Pathogenesis of carbon tetrachloride–induced hepatocyte injury: Bioactivation of CCl4 by cytochrome P450 and effects on lipid homeostasis. Z. Naturforsch. 56, 111–121 (2001).
Subbarao, V. V. & Gupta, M. L. Effect of Liv–52 and carbon tetrachloride on the liver protein and nucleic acids. IRCS Med. Sci. 7, 499–500 (1979).
Gupta, A. K., Ganguly, P., Majumder, U. K. & Ghosal, S. Improvement of lipid and antioxidant status in hyperlipidaemic rats treated with steroidal saponins of Solanium nigrum and Solanum xanthocarpum. PharmacologyOnLin. 1, 1–14 (2009).
Soni, B., Visavadiya, N. P. & Madamwar, D. Ameliorative action of cyanobacterial phycoerythrin on CCl4–induced toxicity in rats. Toxicolog. 248, 59–65 (2008).
Bishayee, A., Sarkar, A. & Chatterjee, M. The hepatoprotective activity of carrot (Daucas carota L.) against carbon tetrachloride intoxication in mouse liver. J. Ethnopharmacol. 47, 69–74 (1995).
Rothschild, M. A., Oratz, M. & Schreiber, S. S. Effects of carbon tetrachloride on albumin synthesis. J. Clin. Invest. 51, 2310–2314 (1972).
Yadav, N. P., Pal, A., Shanker, K., Bawankule, D. U. & Gupta, A. K. Synergistic effect of silymarin and standardized extract of Phyllanthus amarus against CCl4–induced hepatotoxicity in Rattus norvegicus. Phytomedicin. 15, 1053–1061 (2008).
Agbor, G. A., Oben, J. E., Nkegoum, B., Takala, J. P. & Ngogang, J. Y. Hepatoprotective activity of Hibiscus cannabinus (Linn.) against carbon tetrachloride and paracetamol–induced liver damage in rats. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 8, 1397–1401 (2005).
Reitman, S. & Frankel, S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic acid and glutamic pyruvate transaminases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 28, 56–63 (1957).
Fringes, C. S., Fendley, T. W., Dunn, R. T. & Queen, C. A. Improved determination of total serum lipids by the sulpho vanillin reaction. Clin. Chem. 18, 673–674 (1972).
Zlatkis, A., Zak, B. & Boyle, G. J. A new method for the determination of serum cholesterol. Int. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 41, 486–492 (1953).
Folch, J., Lees, M. & Stanley, G. H. S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957).
Foster, L. B. & Dunn, R. T. Stable reagents for determination of serum triglycerides by a colorimetric hantzsch condensation method. Clin. Chem. 19, 338–340 (1973).
Hron, W. T. & Menahan, L. A. A sensitive method for the determination of free fatty acids in plasma. J. Lip. Res. 22, 377–382 (1981).
Friedewald, W. T., Levy, R. I. & Fredrickson, D. S. Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without the use of preparative centrifuge. Clin. Chem. 18, 499–502 (1972).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. & Randall, R. J. Protein measurement with folin–phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Miyada, D. S., Baysinger, V., Notrica, S. & Nakumura, R. M. Albumin quantification by dye binding and salt fractionation techniques. Clin. Chem. 18, 52–56 (1972).
Seifter, S., Dayton, S., Novic, B. & Muntwyler, E. The estimation of glycogen with anthrone reagent. Arch. Biochem. 25, 191–200 (1950).
Dubowski, K. M. An O–toluidine method for body–fluid glucose determination. Clin. Chem. 8, 215–235 (1962).
Malloy, H. T. & Evelyn, K. A. The determination of bilirubin with photoelectric colorimeter. J. Biol. Chem. 119, 481–490 (1937).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krithika, R., Verma, R.J. Hypolipidemic and Hypoglycemic Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Solanum nigrum Linn. in CCl4-induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 10, 268–277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0375-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0375-z