Abstract
Objective
Thorium-232 is a natural radionuclide from the actinide family, is abundantly present in monazite and other ores after thorium occupational or accidental exposures it deposited in many organs. The object of the study is to investigate thorium shortterm hazards effects on the male albino rate and study the alginate mitigation effect on thorium hazards.
Methods
Rats were grouped into control, Thorium (Th) and Th+Alginate(Alg) groups. The 54 rats of the different groups were decapitated (6 rats for each decapitation) after the 1st, 3rd, and 7th day during the treatment. Parameters of hematological (Hb, RBCs, indices, granular, lymphocytes), liver (GOT, GPT, Alb.), lipid (chol., trig.) kidney (creat., urea, uric acid) were determined after the determination of thorium distribution and accumulation in different organs.
Results
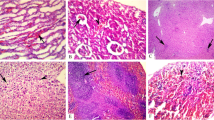
The results showed that the IP administration of 13.6 mg/kg b.wt. thorium nitrate (Th) for seven days produced an organs distribution of Th and accumulated in liver>brain>lipid>Kidney>heart>testes at the end of the experiment, also it induced a hematological, hepatic and lipid dysfunction with no effect on renal function. On the other hand, the oral administration of 5% alginate in the drinking water in parallel with Th injection could slightly reduce Th hazardous effects which may be due to alginate ability to inhibit many inflammatory factors that reduce the hemolysis in erythrocyte, reduce hepatocellular apoptosis, enhance the cholesterol excretion into the feces and also due to the antioxidant and chelating capacity of alginate to Th ions.
Conclusion
So, alginate administration could ameliorate Th short-term hazards effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Veado, M. A. R. V. et al. Metal pollution in the environment of Minas Gerais State–Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 117, 157–172 (2006).
Peng, C. et al. Influence of Speciation of Thorium on Toxic Effects to Green Algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, doi: 10.3390/ijms18040795 (2017).
Sheppard, S. C., Sheppard, M. I., Gallerand, M. O. & Sanipellia, B. Derivation of ecotoxicity thresholds for uranium. J. Environ. Radioact. 79, 55–83 (2005).
Rezk, M. M. A neuro–comparative study between single/ successive thorium dose intoxication and alginate treatment. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 185, 414–423 (2018).
Correa, L. M., Kochhann, D., Becker, A. G., Pavanato, M. A. & Llesuy, S. F. Biochemistry, cytogenetics and bioaccumulation in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to different thorium concentrations. Aquat. Toxicol. 88, 250–256 (2008).
Kochhann, D., Pavanato, M., Llesuy, S., Correa, L. & Riffel, L. R. Bioaccumulation and oxidative stress parameters in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to different thorium concentrations. Chemospher. 77, 384–391 (2009).
Mernagh, T. P. & Miezitis, Y. A. in Review of the Geochemical Processes Controlling the Distribution of Thorium in the Earth’s Crust and Australia’s Thorium Resources (Geoscience Australia, Australia, 2007).
Davis, T. A., Volesky, B. & Mucci, A. A review of the biochemistry heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 37, 4311–4330 (2003).
Sosnik, A. Alginate particles as a platform for drug delivery by the oral route: state–of–the–Art. ISRN Pharm. 2014, doi.org/10.1155/2014/926157 (2014).
Lee, K. Y. & Mooney, D. J. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 37, 106–126 (2012).
Uno, T., Hattori, M. & Yoshida, T. Oral administration of alginic acid oligosaccharide suppresses IgE production and inhibits the induction of oral tolerance. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem.. 70, 3054–3057 (2006).
Kumar, A., Ali, M. & Pandey, B. Understanding the Biological Effects of Thorium and Developing Efficient Strategies for Its Decorporation and Mitigation. Bark Newsletter. 335, 55–56 (2013).
Kumar, A., Sharma, P., Ali, M., Pandey, B. & Mishra, B. Decorporation and therapeutic efficacy of liposomal–DTPA against thorium–induced toxicity in the Wistar rat. Inte. J. Radiat. Biol. 88, 223–229 (2012).
Kumar, A., Ali, M., Pandey, B., Hassan, P. & Mishra, M. Role of membrane sialic acid and glycophorin protein in thorium induced aggregation and hemolysis of human erythrocytes. Biochimie. 92, 869–879 (2010).
Guyton, A. & Hall, J. E. in Text book of medical physiology (Elsevier Inc., Pennsylvania, 2006)
Du, A. L., Sabatié–Gogova, A, Morgenstern, A. & Montavon, G. Is DTPA a good competing chelating agent for Th(IV) in human serum and suitable for targeted alpha therapy? J. Inorg. Biochem. 109, 882–890 (2012).
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry), ADDENDUM FOR THORIUM Supplement to the 1990 Toxicological Profile for Thorium http:// www.atsdr.cdc.gov (2014).
Larsson, A., Lehtinen, K.–J. & Haux, C. Biochemical and hematological effects of titanium dioxides industrial effluent on fish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25, 427–435 (1980).
Abd–Allah, G. A., Ibrahim, M. S., Bahnsawy, M. H. & Abdel–Baky, T. E. Toxic effects of some water pollutants (gallant and mercury) on blood parameters of catfish Clarias Lazera. J. Egypt. Ger. Soc. Zool. 6A, 201–209 (1991).
Brink, C., Dahlen, S. E., Drazen, J., Evanse J. F. & Haw D. W. International Union of Pharmacology: XXXVII. Nomenclature for leukotriene and lipoxin receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 55, 195–227 (2003).
Oliveira, M. S., Duarte, I. M., Paiva, A. V., Matos, R. S. & Almidia C. E. The role of chemical interactions between thorium, cerium, and lanthanum in lymphocyte toxicity. Arch. Environ. Occup. Healt. 69, 40–5 (2014).
Kyoizumi, S., Umeki, S., Akiyama, M., Hirai, Y. & Mori, T. Frequency of mutant T lymphocytes defective in the expression of the T–cell antigen receptor gene among radiation–exposed people. Mutat. Res. 265, 173–180 (1992).
Zhao, K., Chen, T., Lin, B., Cui, W. & Kan, B. Adsorption and recognition of protein molecular imprinted calcium alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel film with good regeneration performance and high toughness. React. Funct. Polym. 87, 7–14 (2015).
Raguvarana, R., Manujaa, A., Manujaa, B. K., Riyesha, T. & Singha, S. Sodium alginate and gum acacia hydrogels of zinc oxide nanoparticles reduce hemolytic and oxidative stress inflicted by zinc oxide nanoparticles on mammalian cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromo. 101, 967–972 (2017).
Singh, S., Chopra, M., Dilbaghi, N., Manuja, B. K. & Kumar, S. Synthesis and evaluation of isometamidium–alginate nanoparticles on equine mononuclear and red blood cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromo. 92, 788–794 (2016).
Kaul, A. & Muth, H. Thorotrast kinetics and radiation dose. Results from studies in Thorotrast patients and from animal experiments. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 15, 241–259 (1978).
Parr, R. M., Lucas, H. F. Jr. & Griem, M. L. Metabolism of 232Th decay series radionuclides in man and other animals following intravascular administration of Thorotrast. ANL–7615. ANL Rep. 1, 97–115 (1968).
Howell, R. W. Patient exposures and consequent risks from nuclear medicine procedures. Health Phys. 100, 313–317 (2011).
Farid, I. & Conibear, S. A. Hepatic function in previously exposed thorium refinery workers as compared to normal controls from the health and nutrition survey. Health Phys. 44, 221–230 (1983).
Evans, C. H. in Biochemistry of the lanthanides (Plenum Press, New York and London, 1990).
Xu, S. et al. Pretreatment with Propylene Glycol Alginate Sodium Sulfate Ameliorated Concanavalin A–induced Liver Injury by Regulating the PI3K/Akt Pathway in Mice. Life Sci. 185, 103–113 (2017).
Shteyer, E. et al. Reduced liver cell death using a bandage of alginate scaffold: A novel approach for liver reconstruction after extended partial hepatectomy. Acta Biomater. 10, 3209–3216 (2014).
Nakazono, S. et al. Anti–obesity effects of enzymatically–digested alginate oligomer in mice model fed a high–fat–diet. Bioact. Carbohydr. Dietary Fibr. 7, 1–8 (2016).
Sasmaz, A., Ozkan, S., Ferit, M. & Sasmaz, M. The hematological and biochemical changes in rats exposed to britholite mineral. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 131, 185–188 (2017).
Lucas, N., Legrand, R., Breton, J., DE’ Chelotte, P. & Edwards–le, F. Chronic delivery of a–melanocyte–stimulating hormone in rat hypothalamus using albumin–alginate microparticles: effects on food intake and body weight. J. Neurosci. 290, 445–453 (2015).
Kimura, Y., Watanabe, Y. & Okuda, H. Effects of soluble sodium alginate on cholesterol excretion and glucose tolerance in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 54, 47–54 (1996).
Peerce, B. E. & Wright, E. M. Sodium–induced conformational changes in the glucose transporter of intestinal brush borders. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 14105–14112 (1984).
Downs, W. L., Scott, K. J., Maynard, E. A. & Hodge, H. C. in Studies on the toxicity of thorium nitrate (University of Rochester, New York, 1959).
Del Rio, D. et al. Dietary (poly) phenolics in human health: structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 18, 1818–1892 (2013).
Kuzkaya, N., Weissmann, N., Harrison, D. G. & Dikalov, S. Interactions of peroxynitrite with uric acid in the presence of ascorbate and thiols: Implications for uncoupling endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 70, 343–354 (2005).
Mclinton, L. T. & Schubert, J. The toxicity of some zirconium and thorium salt in rate. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 94, 1–6 (1948).
Food Administration Organizationn. Committee for Inland Fisheries of Africa. Report of the third session of the working party on pollution and Fisheries, http:// www.fao.org/3/T0666E00.htm (1992).
Marczenko, Z. in Spectrophotometric determination of elements (Ellis Harwood Ltd, England, 1986).
Britton, C. J. in Disorders of blood. 9th edn (J and A. Churchill, Ltd., London, 1963).
Penington, D. G., Rush, B. & Castaldi, P. A. in Clinical hematology in medical practice 4th edn (The English language book society and Black well scientific publication, London, 1999).
Foster, S. A., Swartzentruber, M. & Roberts, P. Reference interval studies of the Rate–Blanked creatinine/ Jaffe Method on BM/Hitachi system in six U. S. Laboratories. Clin. Chem. Abstract No. 361(1994).
Glicker, M. R., Ryder, K. W. & Jackson, S. A. Graphical Comparisons of interferences in Clinical Chemistry Instrumentation. Clin. Chem. 32, 470–474 (1986).
Bergmeyer, H. U., Horder, M. & Rej, R. Approved recommendation on IFCC method for the measurement of catalytic concentration of enzymes. Part 2. IFCC Method for aspartate amino transferase. J. Clin Chem. Clin. Biochem. 24, 497–508 (1986).
Grant, G. H., Silverman, L. M. & Christenson, R. H. in Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry 3rd edn. (eds Tietz N. W.) 328–330 (Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders, 1987).
Shephard, M. D. S. & Whiting, M. J. Falsely low estimation of triglycerides in lipemic plasma by the enzymatic triglyceride method with modified Trinder’s Chromogen. Clin. Chem. 36, 325–329 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezk, M.M., Mohamed, A.A. & Ammar, A.A. Thorium Harmful Impacts on the Physiological Parameters of the Adult Male Albino Rats and Their Mitigation Using the Alginate. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 10, 253–260 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0373-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0373-1