Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that carries substantial implications for health, social well-being, and economic factors. Stanniocalcin-1 STC-1 is a polypeptide hormone that was initially distinguished as a controller of calcium/phosphate homeostasis in the fish. There is a growing evidence that human STC-1, an autocrine/paracrine factor, plays a role in both inflammation and carcinogenesis. The stable fragment proenkephalin-A (PENKA) is a novel biomarker derived from the precursor enkephalin, which is involved in multiple biological pathways.
Objective
The objective of this study was to assess the significance of two newly discovered biomarkers, stanniocalcin-1 and proenkephalin-A, in patients recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
The study consisted of 90 participants, who were divided into two groups. The first group comprised 60 patients with recently diagnosed T2DM, while the second group consisted of 30 healthy individuals serving as controls. The age range of the participants spanned from 35 to 65 years.
Result
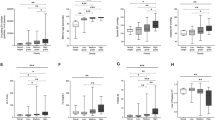
The study found a significant increase in body mass index (BMI), fasting blood glucose (FBG), HbA1c, C-peptide, HOMA-IR, total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), LDL, VLDL, stanniocalcin-1, and proenkephalin-A in patients with newly DM when compared with those in the control group. Also, there was a significant increase in HDL levels in the control group compared to the newly diagnosed diabetic group.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the results of our study indicate that stanniocalcin-1 and proenkephalin-A could potentially be used as indicators of glucose homeostasis. Consequently, these biomarkers may offer an alternative to conventional markers in predicting risk factors for diabetes mellitus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishii H, Shuichi S, Williams P, Demiya S, Aranishi T, Treuer T. Cross-sectional survey in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes to understand mealtime insulin unmet needs in Japan: the MINUTES-J study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;162:108076.
Asiimwe D, Mauti GO, Kiconco R. Prevalence and risk factors associated with type 2 diabetes in elderly patients aged 45–80 years at Kanungu District. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:1–5.
Cassano V, Leo A, Tallarico M, Nesci V, Cimellaro A, Fiorentino TV, Citraro R, Hribal ML, De Sarro G, Perticone F. Metabolic and cognitive effects of ranolazine in type 2 diabetes mellitus: data from an in vivo model. Nutrients. 2020;12:382.
Chen F, Zhang Z, Pu F. Role of stanniocalcin-1 in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18:3946–53.
Leung CCT, Wong CKC. Effects of STC1 overexpression on tumorigenicity and metabolism of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2018;9:6852.
López JJ, Jardín I, Cantonero Chamorro C, Duran ML, Tarancon Rubio MJ, Reyes Panadero M, Jiménez F, Montero R, González MJ, Martínez M. Involvement of stanniocalcins in the deregulation of glycaemia in obese mice and type 2 diabetic patients. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:684–94.
Beunders R, Struck J, Wu AHB, Zarbock A, Di Somma S, Mehta RL, Koyner JL, Nadim MK, Maisel AS, Murray PT. Proenkephalin (PENK) as a novel biomarker for kidney function. J Appl Lab Med. 2017;2:400–12.
Mohammed NUG, Khaleel FM, Gorial FI. The role of serum chitinase-3-like 1 protein (YKL-40) level and its correlation with proinflammatory cytokine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Baghdad Sci J. 2022;19:1014.
Ernst A, Köhrle J, Bergmann A. Proenkephalin A 119–159, a stable proenkephalin A precursor fragment identified in human circulation. Peptides. 2006;27:1835–40.
Taha EM, Mohialdeen Taha M, Al-Obaidy SK, Faris Hasan B, Rahim SM. Association between atherogenic index and cholesterol to HDL ratio in COVID-19 patients during the initial phase of infection. Arch Razi Inst. 2022;77:1303–10.
Green IC, Perrin D, Pedley KC, Leslie RDG, Pyke DA. Effect of enkephalins and morphine on insulin secretion from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia. 1980;19:158–61.
Schulz C-A, Christensson A, Ericson U, Almgren P, Hindy G, Nilsson PM, Struck J, Bergmann A, Melander O, Orho-Melander M. High level of fasting plasma proenkephalin-A predicts deterioration of kidney function and incidence of CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN. 2017;28:291.
Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, Benson G, Brown FM, Freeman R. G. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 15. Management of diabetes in pregnancy: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45:S60–82.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9.
Elghoneimy YF, Nashy MR, Othman SA, Almarri NM, Alruwaili AA, Alotaibi AR, Alshammari FA. Which level of preoperative glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) affect early morbidity and mortality after cardiac surgery? Australas Med J. 2020;13:32–40.
Farhan LO, Taha EM, Farhan AM. A Case control study to determine Macrophage migration inhibitor, and N-telopeptides of type I bone collagen Levels in the sera of osteoporosis patients. Baghdad Sci J. 2022;19(4):848–54.
d’Emden M. Glycated haemoglobin for the diagnosis of diabetes. Aust Prescr. 2014;37(3):98–100.
Salih JM, Abdulateef DS. Detection of C-peptide in human hair and nail: a comparison between healthy persons and persons with type 1 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8:e001297.
Kashtl GJ, Abed BA, Farhan LO, Noori I, Salman ASD. A Comparative study to determine LDH enzyme levels in serum samples of women with breast cancer and women with breast cancer and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Chem Sci. 2023;6:883–90.
Araujo DB, Dantas JR, Silva KR, Souto DL, Pereira M de FC, Moreira JP, Luiz RR, Claudio-Da-Silva CS, Gabbay MAL, Dib SA. Allogenic adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells and vitamin D supplementation in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus: a 3-month follow-up pilot study. Front Immunol. 2020;11:993.
Yan S-T, Sun J, Gu Z-Y, Miao X-Y, Ma L-C, Sun B-R, Fu X-M, Liu H-Z, Yang G, Fang F-S. The bidirectional association of C-peptide with cardiovascular risk in nondiabetic adults and patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21:201.
Abed BA, Al-AAraji SB, Salman IN. Estimation of Galanin hormone in patients with newly thyroid dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biochem Cell Arch. 2021;21:1317–21.
Farhan LO, Abed BA, Dawood A. Comparison study between adipsin levels in sera of Iraqi patients with diabetes and neuropathy. Baghdad Sci J. 2023;20:726.
Abed BA, Hamid GS. Evaluation of lipocalin-2 and vaspin levels in in Iraqi women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Iraqi J Sci. 2022;63:4650–8.
Khatun M, Arffman RK, Lavogina D, Kangasniemi M, Laru J, Ahtikoski A, Lehtonen S, Paulson M, Hirschberg AL, Salumets A. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome present with altered endometrial expression of stanniocalcin-1. Biol Reprod. 2020;102:306–15.
Roddy GW, Rinkoski TA, Monson KJ, Chowdhury UR, Fautsch MP. Stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1), a downstream effector molecule in latanoprost signaling, acts independent of the FP receptor for intraocular pressure reduction. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0232591.
Shi M, Yuan Y, Liu J, Chen Y, Li L, Liu S, An X, Luo R, Long D, Chen B. MSCs protect endothelial cells from inflammatory injury partially by secreting STC1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:109–18.
Huang L, Belousova T, Chen M, DiMattia G, Liu D, Sheikh-Hamad D. Overexpression of stanniocalcin-1 inhibits reactive oxygen species and renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2012;82:867–77.
Mohammed NUG, Gorial FI, Khaleel FM, Abed BA, Mutar SA, Farhan LO, Salman IN. Role of human β-defensin-3 in rheumatoid arthritis: an observational single-center study. Al-Rafidain J Med Sci (ISSN 2789-3219). 2023;5:S71-75.
Ishibashi K, Imai M. Prospect of a stanniocalcin endocrine/paracrine system in mammals. Am J Physiol Physiol. 2002;282:F367–75.
Zaidi D, Turner JK, Durst MA, Wagner GF. Stanniocalcin-1 co-localizes with insulin in the pancreatic islets. ISRN Endocrinol. 2012;2012:834359.
Ellard JP, McCudden CR, Tanega C, James KA, Ratkovic S, Staples JF, Wagner GF. The respiratory effects of stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) on intact mitochondria and cells: STC-1 uncouples oxidative phosphorylation and its actions are modulated by nucleotide triphosphates. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;264:90–101.
Sarapio E, De Souza SK, Model JFA, Trapp M, Da Silva RSM. Stanniocalcin-1 and-2 effects on glucose and lipid metabolism in white adipose tissue from fed and fasted rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;97:916–23.
Schein V, Kucharski LC, Guerreiro PMG, Martins TL, Morgado I, Power DM, Canario AVM, da Silva RSM. Stanniocalcin 1 effects on the renal gluconeogenesis pathway in rat and fish. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;414:1–8.
Khorashadi M, Beunders R, Pickkers P, Legrand M. Proenkephalin: a new biomarker for glomerular filtration rate and acute kidney injury. Nephron. 2020;144:655–61.
Holm H, Nägga K, Nilsson ED, Ricci F, Melander O, Hansson O, Bachus E, Fedorowski A, Magnusson M. High circulating levels of midregional proenkephalin A predict vascular dementia: a population-based prospective study. Sci Rep. 2020;10:8027.
Tang D, Lin T, Wang Y, Cao H. High expression of proenkephalin is associated with favorable outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:6681–90.
Mohammed NUG, Khaleel FM, Gorial FI. Cystatin D as a new diagnostic marker in rheumatoid arthritis. Gene Reports. 2021;23:101027.
Le Merrer J, Becker JA, Befort K, Kieffer BL. Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:1379–412.
Vuong C, Van Uum SHM, O’Dell LE, Lutfy K, Friedman TC. The effects of opioids and opioid analogs on animal and human endocrine systems. Endocr Rev. 2010;31:98–132.
van Hateren KJJ, Landman GWD, Arnold JFH, Joosten H, Groenier KH, Navis GJ, Sparwasser A, Bakker SJL, Bilo HJG, Kleefstra N. Serum proenkephalin A levels and mortality after long-term follow-up in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (ZODIAC-32). PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0133065.
Khawaja XZ, Green IC, Thorpe JR, Bailey CJ. Increased sensitivity to insulin-releasing and glucoregulatory effects of dynorphin A 1–13 and U 50488h in ob/ob versus lean mice. Diabetes. 1990;39:1289–97.
Gupta A, Gullapalli S, Pan H, Ramos-Ortolaza DL, Hayward MD, Low MJ, Pintar JE, Devi LA, Gomes I. Regulation of opioid receptors by their endogenous opioid peptides. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41:1103–18.
Marino R, Struck J, Hartmann O, Maisel AS, Rehfeldt M, Magrini L, Melander O, Bergmann A, Di Somma S. Diagnostic and short-term prognostic utility of plasma pro-enkephalin (pro-ENK) for acute kidney injury in patients admitted with sepsis in the emergency department. J Nephrol. 2015;28:717–24.
Shah KS, Taub P, Patel M, Rehfeldt M, Struck J, Clopton P, Mehta RL, Maisel AS. Proenkephalin predicts acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery patients. Clin Nephrol. 2015;83:29–35.
Hollinger A, Wittebole X, François B, Pickkers P, Antonelli M, Gayat E, Chousterman BG, Lascarrou J-B, Dugernier T, Di Somma S. Proenkephalin A 119–159 (Penkid) is an early biomarker of septic acute kidney injury: the kidney in sepsis and septic shock (Kid-SSS) study. Kidney Int Rep. 2018;3:1424–33.
Beunders R, van Groenendael R, Leijte GP, Kox M, Pickkers P. Proenkephalin compared to conventional methods to assess kidney function in critically ill sepsis patients. Shock. 2020;54:308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The research was conducted in line with the Helsinki Declaration. Obtained informed consent from all participants prior to their involvement. Furthermore, the study received ethical approval from the ethics committee of the national diabetes center.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abed, B.A., Salman, I.N., Hassan, E.A. et al. Role of stanniocalcin-1 and proenkephalin-A as novel biomarkers in prediction of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-024-01353-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-024-01353-1