Abstract
Background
The incidence of type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has quadruplicated in the recent decades and Prevention of T2DM cases is possible by changing lifestyle practices. The process of diagnosis of diabetes is a tedious one. The advent and advancement in (AI) techniques presents a probable solution to this critical problem.
Objective
The study aims to assess the diverse attributes of the test sample population across Assam and enhance the early prediction of Type II Diabetes Mellitus by employing artificial neural networks.
Methods
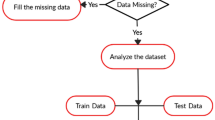
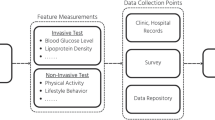
The aim of this study is to design a suitable AI model that prognosticates the likelihood of diabetes in individuals with maximum accuracy based on the levels of liver enzymes. This work also analyzes the effect of fast food intake, sleeping patterns, and consumption of alcohol on healthy controls and contemplates their susceptibility to contract T2DM.
Results
The AI model accurately predicted T2DM likelihood and revealed significant links between unhealthy behaviors and increased T2DM risk among healthy individuals.
Conclusions
The study underscores lifestyle modifications for T2DM prevention, highlighting AI’s potential in diagnosis and the impact of unhealthy habits on T2DM susceptibility.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Rafaqat S, Sattar A, Khalid A, Rafaqat S. Role of liver parameters in diabetes mellitus - a narrative review. Endocr Regul. 2023;57(1):200–20.
Li Y, Wang J, Han X, Hu H, Wang F, Yu C, Yuan J, Yao P, Li X, Yang K, Miao X, Wei S, Wang Y, Chen W, Liang Y, Zhang X, Guo H, Yang H, Wu T, He M. Serum alanine transaminase levels predict type 2 diabetes risk among a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population. Ann Hepatol. 2019;18:298–303.
Abdu Y, Naja S, Mohamed Ibrahim MI, Abdou M, Ahmed R, Elhag S, Saleh AO, Yassin M, Bougmiza I. Sleep quality among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus during COVID-19 pandemic: evidence from Qatar’s National Diabetes Center. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes: Targets Ther. 2023;16:2803–12.
Charan J, Biswas T. How to calculate sample size for different study designs in medical research? Indian J Psychol Med. 2013;35(2):121–6.
Yang J, Zhang K, Xi Z, et al. Short sleep duration and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic associated fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2023;27:1985–96.
Fakhari S, Waszkiewicz N. Old and new biomarkers of alcohol abuse: narrative review. J Clin Med. 2023;12(6):2124.
Gu X, Drouin-Chartier J-P, Sacks FM, Hu FB, Rosner B, Willett WC. Red meat intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in a prospective cohort study of United States females and males. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023;118(6):1153–63.
Zhang Y, Meng Y, Wang J. Higher adherence to plant-based diet lowers type 2 diabetes risk among high and non-high cardiovascular risk populations: a cross-sectional study in Shanxi, China. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):786.
Mathur S, Mehta DK, Kapoor S, Yadav S. Liver function in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Sci Stud. 2016;3:43–7.
Byrne TJ, Parish JM, Somers V, Aqel BA, Rakela J. Evidence for liver injury in the setting of obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Hepatol. 2012;11:228–31.
Prati D, Taioli E, Zanella A. Updated definitions of healthy ranges for serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:1–10.
Li J, Sun C, Liu S, Li Y. Dietary Protein Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Among Women and Men in Northeast China. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37604. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37604
Das SJ, Dutta S, Tiwari D, Basumatary TK, Kashyap N, Kalita MP, Bose S, Bose PD. Prognostic value of myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 in type II diabetes mellitus in non-obese NAFLD: a case-control study from Assam. Hum Gene. 2024;39:201246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humgen.2023.201246.
Haykin S. Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation. New Jersey: Prentice Hall PTR; 1998.
Gonem S, Wall A, De P. Prevalence of abnormal liver function tests in patients with diabetes mellitus. Endocrine Abstr. 2007;13:175.
Clark JM, Brancati FL, Diehl AM. The prevalence and etiology of elevated aminotransferase levels in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:960–7.
Friedman LS, Dienstag JL, Watkins E. Evaluation of blood donors with elevated serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Ann Intern Med. 1987;107:137–44.
Erbey JR, Silberman C, Lydick E. Prevalence of abnormal serum alanine aminotransferase levels in obese patients and patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Med. 2000;109:588–90.
Lebovitz H, Kreider M, Freed M. Evaluation of liver function in type 2 diabetic patients during clinical trials: evidence that rosiglitazone does not cause hepatic dysfunction. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:815–21.
Ioja S, Weir ID, Rennert NJ. Relationship between sleep disorders and the risk for developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Postgrad Med. 2012;124:119–29.
Feng SZ, Tian JL, Zhang Q, Wang H, Sun N, et al. An experimental research on chronic intermittent hypoxia leading to liver injury. Sleep Breath. 2011;15:493–502.
Duffey KJ, Popkin BM. Adults with healthier dietary patterns have healthier beverage patterns. J Nutr. 2006;136:2901–7.
Pamidi S, Tasali E. Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes: is there a link? Front Neurol. 2012;3:126. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2012.00126
Acknowledgments
We sincerely acknowledge the Department of Medicine, Assam Medical College, Dibrugarh, Assam, India, for providing us the data sets pertaining to this study. The data was acquired under the supervision of registered medical practitioners with informed consent of the patients and will be produced if required/asked.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee of Gauhati Medical College and Cotton University has been taken and will be provided if required.
Patient consent
Required consent has been duly taken and will be provided if required.
IEC number for Gauhati Medical College and Hospital: MCI/190/2007/Pt-II/Oct.2022/44
IEC number for Cotton University: CU/ACA/ETHICS/2022/1
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, P.P., Das, S.J. Prediction of type II diabetes mellitus based on demographic features by the use of machine learning classification algorithms — a study across Assam, India. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-024-01334-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-024-01334-4