Abstract
Background
Diabetes and related peripheral neuropathy result in various sensory and motor complications. Such changes are documented early and more precisely in nerve conduction studies than in clinical evaluation and quantitative sensory testing. Different exercises and mobilization also affect the same differently.
Objective
This review aimed to compile the current evidence on the effectiveness of exercises and manual therapy on nerve conduction studies of lower limbs in patients with diabetes and diabetic peripheral neuropathy and to evaluate the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
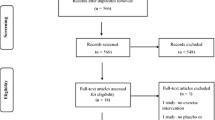
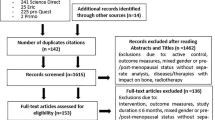
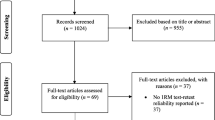
Studies that examined the effects of different exercises and manual therapy on nerve conduction studies of lower limbs in patients with diabetes mellitus and diabetic peripheral neuropathy were searched on available databases. The PRISMA statement was followed. Quality check was done using the Pedro scale.
Results
Thirteen studies matched the inclusion criteria. Interventions included moderate-intensity aerobic exercises, resistance exercises, tai chi exercises, sensorimotor and gait training, neurodynamic mobilization, and a combination of aerobics and resistance training.
Conclusion
The present systematic review suggests that 8 to 12 weeks of physical exercise improves nerve conduction velocity of the motor tibial, peroneal nerve, and sensory sural nerve in diabetes with or without peripheral neuropathy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CMAP:
-
Compound muscle action potential
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DPN:
-
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- IENFD:
-
Intra epidermal nerve fiber density
- NAPA:
-
Nerve action potential amplitude
- NCS:
-
Nerve conduction studies
- NCV:
-
Nerve conduction velocity
- SNAP:
-
Sensory nerve action potential
- PEDRO:
-
Physiotherapy evidence database
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis
- PICOS:
-
Population, intervention, comparison, outcomes, study design
- TENS:
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
- ADA:
-
American diabetes association
- HbA1c:
-
Hemoglobin A1c
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- QST:
-
Quantitative sensory testing
References
Aldana -yovera M, Velasquez-Rimachi V, Huerta-Rosario A, More-Yupanqui MD, Osores-Flores M, Espinoza R, et al. Prevalence and incidence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Latin America and the Caribbean: a systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:1–29.
Edwards JL, Vincent AM, Cheng HT, Feldman EL. Diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms to management. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;120(1):1–34.
Ahmad I, Noohu MM, Verma S, Singla D, Hussain ME. Effect of sensorimotor training on balance measures and proprioception among middle and older age adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Gait Posture. 2019;74:114–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2019.08.018.
Feldman EL, Callaghan BC, Pop-Busui R, Zochodne DW, Wright DE, Bennett DL, et al. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0092-1.
Janghorbani M, Rezvanian H, Kachooei A, Ghorbani A, Chitsaz A, Izadi F, et al. Peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in Isfahan, Iran: prevalence and risk factors. Acta Neurol Scand. 2006;114(6):384–91.
Sloan G, Selvarajah D, Tesfaye S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(7):400–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-021-00496-z.
Pai YW, Tang CL, Lin CH, Lin SY, Lee IT, Chang MH. Glycaemic control for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy is more than fasting plasma glucose and glycated haemoglobin. Diabetes Metab. 2021;47(1):101158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2020.04.004.
Amato Nesbit S, Sharma R, Waldfogel JM, Zhang A, Bennett WL, Yeh HC, et al. Non-pharmacologic treatments for symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019;35(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/03007995.2018.1497958.
Andreassen CS, Jakobsen J, Ringgaard S, Ejskjaer N, Andersen H. Accelerated atrophy of lower leg and foot muscles-a follow-up study of long-term diabetic polyneuropathy using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Diabetologia. 2009;52(6):1182–91.
Allen MD, Kimpinski K, Doherty TJ, Rice CL. Length dependent loss of motor axons and altered motor unit properties in human diabetic polyneuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(4):836–43.
Parasoglou P, Rao S, Slade JM. Declining skeletal muscle function in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Clin Ther. 2017;39(6):1085–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.05.001.
Rosenberger DC, Blechschmidt V, Timmerman H, Wolff A, Treede RD. Challenges of neuropathic pain: focus on diabetic neuropathy. J Neural Transm. 2020;127(4):589–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-020-02145-7.
Yagihashi S, Yamagishi SI, Wada R. Pathology and pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic neuropathy: correlation with clinical signs and symptoms. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77(3 SUPPL.):184–9.
van Dam PS. Oxidative stress and diabetic neuropathy: pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment perspectives. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18(3):176–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.287.
Alam U, Fawwad A, Shaheen F, Tahir B, Basit A, Malik RA. Improvement in neuropathy specific quality of life in patients with diabetes after vitamin D supplementation. J Diabetes Res. 2017;7928083. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7928083
Khan KS, Andersen H. The impact of diabetic neuropathy on activities of daily living, postural balance and risk of falls - a systematic review. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2022;16(2):289–94.
Ghanavati T, ShaterzadehYazdi MJ, Goharpey S, Arastoo AA. Functional balance in elderly with diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;96(1):24–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2011.10.041.
Boulton AJM. The diabetic foot. Medicine. 2019;47(2):100–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpmed.2018.11.001.
Van Schie CH. Neuropathy: mobility and quality of life. Diabetes/Metab Res Rev. 2008;24(Suppl 1):S45–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.856.
Selvarajah D, Kar D, Khunti K, Davies MJ, Scott AR, Walker J, Tesfaye S. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: advances in diagnosis and strategies for screening and early intervention. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(12):938–48.
Mscot PH, Deshpande N. Falls and balance impairments in older adults with type diabetes thinking beyond diabetic peripheral neuropathy. 2016;40(1):6–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.08.005.
Pop-Busui R, Boulton AJM, Feldman EL, Bril V, Freeman R, Malik RA, et al. Diabetic neuropathy: a position statement by the American diabetes association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):136–54.
García-Molina L, Lewis-Mikhael AM, Riquelme-Gallego B, Cano-Ibáñez N, Oliveras-López MJ, Bueno-Cavanillas A. Improving type 2 diabetes mellitus glycaemic control through lifestyle modification implementing diet intervention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Nutr. 2020;59(4):1313–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02147-6.
Chiles NS, Phillips CL, Volpato S, Bandinelli S. Diabetes, peripheral neuropathy, and lower extremity function. NIH Public Access. 2015;61(6):515–25.
Galiero R, Ricciardi D, Pafundi PC, Todisco V, Tedeschi G, Cirillo G, et al. Whole plantar nerve conduction study: a new tool for early diagnosis of peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021;176:108856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108856.
Kohara N, Kimura J, Kaji R, Goto Y, Ishii J, Takiguchi M, et al. F-wave latency serves as the most reproducible measure in nerve conduction studies of diabetic polyneuropathy: Multicentre analysis in healthy subjects and patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetologia. 2000;43(7):915–21.
Weisman A, Bril V, Ngo M, Lovblom LE, Halpern EM, Orszag A, et al. Identification and prediction of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy using individual and simple combinations of nerve conduction study parameters. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(3):1–9.
Mackel R, Brink E. Conduction of neural impulses in diabetic neuropathy. Chem Biol. 2003;10:161–8.
Hung JW, Liou CW, Wang PW, Yeh SH, Lin LW, Lo SK, et al. Effect of 12-week tai chi chuan exercise on peripheral nerve modulation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Rehabil Med. 2009;41(11):924–9.
Hogikyan RV, Wald JJ, Feldman EL, Greene DA, Halter JB, Supiano MA. Acute effects of adrenergic-mediated ischemia on nerve conduction in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism. 1999;48(4):495–500.
De Souza RJ, De Souza A, Nagvekar MD. Nerve conduction studies in diabetics presymptomatic and symptomatic for diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2015;29(6):811–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.05.009.
Balducci S, Iacobellis G, Parisi L, Di Biase N, Calandriello E, Leonetti F, et al. Exercise training can modify the natural history of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2006;20(4):216–23.
Dixit S, Maiya AG, Shastry BA. Effect of aerobic exercise on peripheral nerve functions of population with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: A single blind, parallel group randomized controlled trial. J Diabetes Complications. 2014;28(3):332–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2013.12.006.
Serry ZMH, Mossa G, Elhabashy H, Elsayed S, Elhadidy R, Azmy RM, et al. Transcutaneous nerve stimulation versus aerobic exercise in diabetic neuropathy. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2016;53(2):124–9.
Gholami F, Nikookheslat S, Salekzamani Y, Boule N, Jafari A. Effect of aerobic training on nerve conduction in men with type 2 diabetes and peripheral neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Neurophysiol Clin. 2018;48(4):195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2018.03.001.
Ahmad I, Verma S, Noohu MM, Shareef MY, Ejaz HM. Sensorimotor and gait training improves proprioception, nerve function, and muscular activation in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized control trial. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(2):234–48.
Stubbs EB, Fisher MA, Miller CM, Jelinek C, Butler J, McBurney C, et al. Randomized controlled trial of physical exercise in diabetic veterans with length-dependent distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.0005.
Gholami F, Khaki R, Mirzaei B, Howatson G. Resistance training improves nerve conduction and arterial stiffness in older adults with diabetic distal symmetrical polyneuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2021;153:111481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2021.111481.
Singleton JR, Marcus RL, Jackson JE, Lessard M, Graham TE, Smith AG. Exercise increases cutaneous nerve density in diabetic patients without neuropathy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2014;1(10):844–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.125.
Alsubiheen A, Petrofsky J, Daher N, Lohman E, Balbas E, Lee H. Tai chi with mental imagery theory improves soleus H-reflex and nerve conduction velocity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2017.01.005.
Azizi S, Najafi S, Rezasoltani Z, Sanati E, Zamani N, Dadarkhah A. Effects of aerobic exercise on electrophysiological features of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: single-blind clinical trial. Top Geriatr Rehabil. 2019;35(2):164–9.
Doshi MK, Singarvelan RM. Effect of tibial nerve mobilization on nerve conduction velocity in diabetic neuropathy patient. Int J Heal Sci Res. 2019;9(5):218–24.
Kluding PM, Pasnoor M, Singh R, Jernigan S, Farmer K, Rucker J, et al. The effect of exercise on neuropathic symptoms, nerve function, and cutaneous innervation in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2012;26(5):424–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2012.05.007.
Kakrani AL, Gokhale VS, Vohra KV, Chaudhary N. Clinical and nerve conduction study correlation in patients of diabetic neuropathy. J Assoc Physicians India. 2014;62(1):24–7.
Dyck PJ, Overland CJ, Low PA, Litchy WJ, Davies JL, Dyck PJB, et al. Signs and symptoms versus nerve conduction studies to diagnose diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy: CI vs. NPhys trial Muscle and Nerve. 2010;42(2):157–64.
Malik RA, Tesfaye S, Newrick PG, Walker D, Rajbhandari SM, Siddique I, et al. Sural nerve pathology in diabetic patients with minimal but progressive neuropathy. Diabetologia. 2005;48(3):578–85.
Perkins BA, Bril V. Diabetic neuropathy: a review emphasizing diagnostic methods. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114(7):1167–75.
Fuller AA, Singleton JR, Smith AG, Marcus RL. Exercise in type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Curr Geriatr Reports. 2016;5(3):150–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13670-016-0177-6.
Valls-Canals J, Povedano M, Montero J, Pradas J. Diabetic polyneuropathy. Axonal or demyelinating? Electromyography and clinical neurophysiology. 2002;42(1):3–6.
Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, Freeman R, Malik RA, Maser RE, Sosenko JM, Ziegler D. Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(4):956–62.
Cameron NE, Eaton SEM, Cotter MA, Tesfaye S. Vascular factors and metabolic interactions in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia. 2001;44(11):1973–88.
Fuchsjäger-Mayrl G, Pleiner J, Wiesingen GF, Sieder AE, Quittan M, Nuhr MJ, et al. Endothelial function in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(10):1795–801.
Orlando G, Balducci S, Bazzucchi I, Pugliese G, Sacchetti M. Neuromuscular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: underlying mechanisms and effect of resistance training. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(1):40–50.
Sylantiev C, Schwartz R, Chapman J, Buchman AS. Medial plantar nerve testing facilitates identification of polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2008;38(6):1595–8.
Løseth S, Nebuchennykh M, Stålberg E, Mellgren SI. Medial plantar nerve conduction studies in healthy controls and diabetics. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118(5):1155–61.
Frigeni B, Cacciavillani M, Ermani M, Briani C, Alberti P, Ferrarese C, et al. Neurophysiological examination of dorsal sural nerve. Muscle Nerve. 2012;46(6):891–4.
Kural MA, Karlsson P, Pugdahl K, Isak B, Fuglsang-Frederiksen A, Tankisi H. Diagnostic utility of distal nerve conduction studies and sural near-nerve needle recording in polyneuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(9):1590–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.031.
Boulé NG, Haddad E, Kenny GP, Wells GA, Sigal RJ. Effects of exercise on glycemic control and body mass in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. JAMA. 2001;286(10):1218–27.
Lee JH, Lee R, Hwang MH, Hamilton MT, Park Y. The effects of exercise on vascular endothelial function in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis Fred DiMenna. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2018;10(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-018-0316-7.
Gustafsson T, Puntschart A, Kaijser L, Jansson E, Sundberg CJ. Exercise-induced expression of angiogenesis-related transcription and growth factors in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Hear Circ Physiol. 1999;276(45–2):679–85.
Griffin JW, Thompson WJ. Biology and pathology of nonmyelinating schwann cells. Glia. 2008;56(14):1518–31.
Tesfaye S, Boulton AJM, Dyck PJ, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(10):2285–93. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-1303.
Hortobágyi T, Granacher U, Fernandez-del-Olmo M, Howatson G, Manca A, Deriu F, et al. Functional relevance of resistance training-induced neuroplasticity in health and disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;2021(122):79–91.
Yarrow JF, White LJ, McCoy SC, Borst SE. Training augments resistance exercise induced elevation of circulating brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Neurosci Lett. 2010;479(2):161–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.05.058.
Posadzki P, Jacques S. Tai chi and meditation: a conceptual (re)synthesis? J Holist Nurs. 2009;27(2):103–14.
Lan C, Lai JS, Chen SY. Tai chi chuan: an ancient wisdom on exercise and health promotion. Sport Med. 2002;32(4):217–24.
Dickstein R, Deutsch JE. Motor imagery in physical therapist practice. Phys Ther. 2007;87(7):942–53.
Santana HS, Fernandes de Oliveira IA, Lima ÊM, Medrado ARAP, Nunes Sa K, Martinez AMB, et al. Neurodynamic mobilization and peripheral nerve regeneration: a narrative review. Int J Neurorehabilitation. 2015;02:2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2376-0281.1000163
Da Silva JT, Dos Santos FM, Giardini AC, De Oliveira MD, De Oliveira ME, Ciena AP, et al. Neural mobilization promotes nerve regeneration by nerve growth factor and myelin protein zero increased after sciatic nerve injury. Growth Factors. 2015;33(1):8–13.
Singh PP, Bindra S, Singh S, Aggarwal R, Singh J. Effect of nerve mobilization on vibration perception threshold in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Indian J Physiother Occup Ther. 2012;6(3):195–201.
Kumar PS, Adhikari P, Prabhu MM. Efficacy of tibial nerve neurodynamic mobilization for neuropathic pain in type II diabetes mellitus-a randomized controlled trial. Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy. 2011;5(4):189–92.
Gilbert KK, Roger James C, Apte G, Brown C, Sizer PS, Brismeé JM, et al. Effects of simulated neural mobilization on fluid movement in cadaveric peripheral nerve sections: implications for the treatment of neuropathic pain and dysfunction. J Man Manip Ther. 2015;23(4):219–25. https://doi.org/10.1179/2042618614Y.0000000094.
Gilbert KK, Smith MP, Sobczak S, James CR, Sizer PS, Brismée J-M. Effects of lower limb neurodynamic mobilization on intraneural fluid dispersion of the fourth lumbar nerve root: an unembalmed cadaveric investigation. J Man Manip Ther. 2015;23(5):239–45.
Zhu GC, Tsai KL, Chen YW, Hung CH. Neural mobilization attenuates mechanical allodynia and decreases proinflammatory cytokine concentrations in rats with painful diabetic neuropathy. Physical Therapy & Rehabilitation Journal. 2018;98(4):214–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzx124.
Page P. Sensorimotor training: A “global” approach for balance training. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2006;10(1):77–84.
Abdelbasset WK, Elsayed SH, Nambi G, Tantawy SA, Kamel DM, Eid MM, et al. Response to Letter to the Editor on “Potential efficacy of sensorimotor exercise program on pain, proprioception, mobility, and quality of life in diabetic patients with foot burns: A 12-week randomized control study.” Burns. 2021;47(5):1204–5.
Ahmad I, Verma S, Noohu MM, Hussain ME. Effect of sensorimotor training on spatiotemporal parameters of gait among middle and older age adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Somatosens Mot Res. 2021;38(3):230–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/08990220.2021.1955671.
Hohman TC, Cotter MA, Cameron NE. ATP-sensitive K+ channel effects on nerve function, Na+, K+ ATPase, and glutathione in diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;397(2–3):335–41.
Colberg SR, Sigal RJ, Yardley JE, Riddell MC, Dunstan DW, Dempsey PC, et al. Physical activity/exercise and diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(11):2065–79.
Callaghan BC, Cheng HT, Stables CL, Smith AL, Feldman EL. Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(6):521–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70065-0.
Vincent AM, Russell JW, Low P, Feldman EVAL, Arbor A. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. 2004;25(4):612–28.
Asensio-Pinilla E, Udina E, Jaramillo J, Navarro X. Electrical stimulation combined with exercise increase axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Exp Neurol. 2009;219(1):258–65.
Vaynman S, Gomez-pinilla F. License to run: exercise impacts functional plasticity in the Intact and Injured Central Nervous System by Using Neurotrophins. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2005;19(4):283–95. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968305280753.
Wilhelm JC, Xu M, Cucoranu D, Chmielewski S, Holmes T, Lau KS, et al. Cooperative roles of BDNF expression in neurons and Schwann cells are modulated by exercise to facilitate nerve regeneration. J Neurosci. 2012;32(14):5002–9. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1411-11.2012.
Park JS, Höke A. Treadmill exercise induced functional recovery after peripheral nerve repair is associated with increased levels of neurotrophic factors. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(3):1–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, J., Ahmad, I. & Singh, A.K.C. Effects of exercises and manual therapy on nerve conduction studies of lower limb in patients with diabetes and diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-023-01258-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-023-01258-5