Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to evaluate the nutritional status of individuals with and without diabetes over the age of 65 and its effects on the quality of life.
Materials and methods
A total of 188 subjects, 94 diabetic individuals and 94 non-diabetic individuals as the control group, were included in the study. Both groups were surveyed using the mini nutritional assessment short form (MNA-SF) scale, Europen quality of life 5 dimensions-3 level version (EQ-5D-3L) quality of life scale and socio-demographic data questionnaire. Height, weight, and body mass index (BMI) were taken for anthropometric measurements. The levels of biochemical parameters were measured.
Results
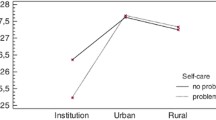
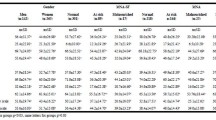
The mean age of the participants was 70.34 ± 4.63 years, and 64.9% were female. In total, 4.3% of patients with diabetes had malnutrition and 37.2% were at risk of malnutrition. While malnutrition was not detected in patients without diabetes, 26.6% were at risk. In terms of malnutrition, a statistically significant difference was found between the two groups (p = 0.027). The EQ-5D-3L quality of life index score was lower in patients with diabetes (p = 0.025).
Conclusion
Identifying and following up on malnutrition status in elderly diabetes patients are of importance with regard to disease control and quality of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Population Data (2018) http://www.worldpopdata.org/
Sanz-París A, García-Almeida JM, Gomez-Candela C, Burgos-Pelaez R, Martín-Palmero A, Matía-Martin P, et al. Malnütrition prevalance in hospitalized elderly diabetic patients. Nutr Hosp. 2013;28(3):592–9.
Rakicioğlu N. The approaches of medıcal nutrıtıonal therapy for dıabetıc elderly. Turk J Geriatr. 2006;9(1):52–9.
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018 Diabetes Care 2018 Jan; 41(Supplement 1): S1-S2.https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-Sint01
Saintrain MVL, Sandrin RLSP, Bezerra CB, Lima AOP, Nobre MA, Braga DRA. Nutritional assessment of older adults with diabetes mellitus. Diab Res Clin Pract. 2019;155:107819.
Bakker MH, Vissink A, Spoorenberg SLW, Jager-Wittenaar H, Wynia K, Visser A. Are edentulousness, oral health problems and poor health-related quality of life associated with malnutrition in community-dwelling elderly (aged 75 years and over)? A cross-sectional study. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):E1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121965.
Grandy S, Fox KM, SHIELD Study Group. Change in health status (EQ-5D) over 5 years among individuals with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus in the SHIELD longitudinal study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2012;10:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-10-99.
Rubenstein LZ, Harker JO, Salvà A, et al. Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice: developing the short-form mini-nutritional assessment (MNA-SF). J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(6):M366–72.
Kaiser MJ, Bauer JM, Ramsch C, Uter W, Guigoz Y, Cederholm T, et al. Validation of the mini nutritional assessment short form (MNA-SF): a practical tool for identification of nutritional status. J Nutr Health Aging. 2009;13:782–8.
Guigoz Y. The mini nutritional assessment (MNA) review of the literature-what does it tell us? J Nutr Health Aging. 2006;10:466–85 Discussion 485-467.
The EuroQol group. EQ-5D ınstruments. https://euroqol.org/eq-5d-instruments/eq-5d-5l-about/
Sut KH, Unsal S. Is EQ-5D a valid quality of life instrument in patients with acute coronary syndrome? The Anatolion. J Cardiol. 2011;1:156–62.
Baysal A, Aksoy M, Besler HT, Bozkurt N, Keçecioğlu S, Kutluay Merdol T, Pekcan G, Mercanlıgil SM, Yıldız (Haz.) E (2008) Diyet El Kitabı (yenilenmiş 5. bs.) (s67-141). Ankara: Hatipoğlu Yayınevi
Global Database on Body Mass Index. http://apps.who.int/bmi/index.jsp
Sanz-París A, Gomez-Candela C, Martín-Palmero A, García-Almeida JM, Burgos-Pelaez R, Matía-Martin P, et al. Application of the new ESPEN definition of malnutrition in geriatric diabetic patients during hospitalization: a multicentric study. Clinical Nutr. 2016;35(6):1564–7.
Liu G-X, Chen Y, Yang Y-X, Yang K, Liang J, Wang S, et al. Pilot study of the mini nutritional assessment on predicting outcomes in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17:2485–92.
Alfonso-Rosa RM, Del Pozo-Cruz B, Del Pozo-Cruz J, Del Pozo-Cruz JT, Sañudo B. The relatıonshıp between nutrıtıonal status, functıonal capacıty, and health-related qualıty of lıfe in older adults with type 2 dıabetes: a pılot explanatory study. J Nutr, Health Aging. 2013;17(4):315–21.
Kanwa S, Qidwai W, Nanji K. Relationship of nutritional status and functional capacity in elderly patients visiting outpatient clinics of a tertiary care hospital. J Coll Phys Surg Pak. 2018;28(7):509–13.
Yildirim ZG, Mehmet UM, Ozge Telci Caklili OT, Hasan Huseyin Mutlu HH, Oguz A. Malnutrition rate among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Progr Nutr. 2018;20(2):183–8.
Ulger Z, Halil M, Kalan I, Yavuz BB, Cankurtaran M, Gungor E, et al. Comprehensive assessment of malnutrition risk and related factors in a large group of community-dwelling older adults. Clin Nutr. 2010;29(4):507–11.
Turnbull PJ, Sinclair AJ. Evaluation of nutritional status and its relationship with functional status in older citizens with diabetes mellitus using the mini nutritional assessment (MNA) tool-a preliminary investigation. J Nutr Health Aging. 2002;6(3):185–9.
Ellinger V, Carbonell A. More to look into the nutrition of elderly diabetic patients. J Diab Metab Disord Control. 2014;1(3):47.
Ayman A, Hayek A, Robert AA, Al Saeed A, Alzaid AA, Al Sabaan FS. Factors associated with health-related quality of life among Saudi patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional survey. Diab Metab J. 2014;38:220–9.
Saleh F, Ara F, Mumu SJ, Hafez MA. Assessment of health-related quality of life of Bangladeshi patients with type 2 diabetes using the EQ-5D: a cross-sectional study. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:497.
Funding
The study was funded by the İzmir Katip Çelebi University Scientific Research Projects Unit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The İzmir Katip Çelebi University Non-Interventional Clinical Research Ethics Committee granted the ethics committee approval with the approval date 17.11.2016 and number 122.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pamuk, G., Kaner, G., Koc, E.M. et al. Assessment of nutritional status and quality of life in individuals with and without diabetes over 65 years of age. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 41, 141–147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-020-00855-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-020-00855-y