Abstract
Purpose
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide, with dramatically increasing incidence and mortality for decades. However, current therapeutic strategies for CRC, including chemotherapies and immunotherapies, have only demonstrated limited efficacy. Here, we report a novel immune molecule, CD43, that can regulate the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and serves as a promising target for CRC immunotherapy.
Methods
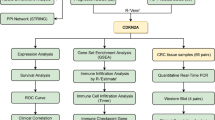
The correlation of CD43 expression with CRC patient prognosis was revealed by public data analysis. CD43 knockout (KO) CRC cell lines were generated by CRISPR-Cas9 technology, and a syngenetic murine CRC model was established to investigate the in vivo function of CD43. The TIME was analyzed via immunohistochemical staining, flow cytometry and RNA-seq. Immune functions were investigated by depletion of immune subsets in vivo and T-cell functional assays in vitro, including T-cell priming, cytotoxicity, and chemotaxis experiments.
Results
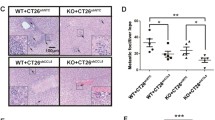
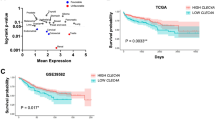
In this study, we found that high expression of CD43 was correlated with poor survival of CRC patients and the limited infiltration of CD8+ T cells in human CRC tissues. Importantly, CD43 expressed on tumor cells, rather than host cells, promoted tumor progression in a syngeneic tumor model. Loss of CD43 facilitated the infiltration of immune cells and immunological memory in the TIME of CRC tumors. Mechanistically, the protumor effect of CD43 depends on T cells, thereby attenuating T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity and cDC1-mediated antigen-specific T-cell activation. Moreover, targeting CD43 synergistically improved PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy for CRC.
Conclusion
Our findings revealed that targeting tumor-intrinsic CD43 could activate the antitumor immune response and provide particular value for optimized cancer immunotherapy by regulating the TIME in CRC patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The analyzed datasets generated during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The transcriptomic data are available in Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) under the accession codes GSE223856.
References
J.Q. Chen, W.H. Zhan, Y.L. He, J.S. Peng, J.P. Wang, S.R. Cai, J.P. Ma, Expression of heparanase gene, CD44v6, MMP-7 and nm23 protein and their relationship with the invasion and metastasis of gastric carcinomas. World J. Gastroenterol. 10, 776–782 (2004)
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, H.E. Fuchs, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 72, 7–33 (2022)
R.M. McQuade, V. Stojanovska, J.C. Bornstein, K. Nurgali, Colorectal Cancer chemotherapy: the evolution of treatment and New Approaches. Curr. Med. Chem. 24, 1537–1557 (2017)
E. Picard, C.P. Verschoor, G.W. Ma, G. Pawelec, Relationships between Immune Landscapes, genetic subtypes and responses to Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 11, 369 (2020)
Y. Jiang, Z. Liu, F. Xu, X. Dong, Y. Cheng, Y. Hu, T. Gao, J. Liu, L. Yang, X. Jia, H. Qian, T. Wen, G. An, Aberrant O-glycosylation contributes to tumorigenesis in human colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 22, 4875–4885 (2018)
T. Gao, T. Du, X. Hu, X. Dong, L. Li, Y. Wang, J. Liu, L. Liu, T. Gu, T. Wen, Cosmc overexpression enhances malignancies in human colon cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24, 362–370 (2020)
N. Very, T. Lefebvre, and I. El Yazidi-Belkoura, Drug resistance related to aberrant glycosylation in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 9, 1380–1402 (2018)
C. Fernandez-Ponce, N. Geribaldi-Doldan, I. Sanchez-Gomar, R.N. Quiroz, L.A. Ibarra, L.G. Escorcia, R. Fernandez-Cisnal, G.A. Martinez, F. Garcia-Cozar, E.N. Quiroz, The role of Glycosyltransferases in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 5822 (2021)
L.A.M. Cornelissen, A. Blanas, A. Zaal, J.C. van der Horst, L.J.W. Kruijssen, T. O’Toole, Y. van Kooyk, S.J. van Vliet, Tn Antigen expression contributes to an Immune Suppressive Microenvironment and Drives Tumor Growth in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 10, 1622 (2020)
E. Remold-O’Donnell, D.M. Kenney, R. Parkman, L. Cairns, B. Savage, F.S. Rosen, Characterization of a human lymphocyte surface sialoglycoprotein that is defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 159, 1705–1723 (1984)
S.R. Carlsson, M. Fukuda, Isolation and characterization of leukosialin, a major sialoglycoprotein on human leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 12779–12786 (1986)
B. Axelsson, P. Perlmann, Persistent superphosphorylation of leukosialin (CD43) in activated T cells and in tumour cell lines. Scand. J. Immunol. 30, 539–547 (1989)
T. Moore, S. Huang, L.W. Terstappen, M. Bennett, V. Kumar, Expression of CD43 on murine and human pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells. J. Immunol. 153, 4978–4987 (1994)
M. Wiken, P. Bjorck, B. Axelsson, P. Perlmann, Induction of CD43 expression during activation and terminal differentiation of human B cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 28, 457–464 (1988)
Y. Rosenstein, J.K. Park, W.C. Hahn, F.S. Rosen, B.E. Bierer, S.J. Burakoff, CD43, a molecule defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, binds ICAM-1. Nature 354, 233–235 (1991)
S. Zheng, K. Huang, W. Xia, J. Shi, Q. Liu, X. Zhang, G. Li, J. Chen, T. Wang, X. Chen, A.P. Xiang, Mesenchymal stromal cells rapidly suppress TCR signaling-mediated cytokine transcription in activated T cells through the ICAM-1/CD43 Interaction. Front. Immunol. 12, 609544 (2021)
R.C. Fuhlbrigge, S.L. King, R. Sackstein, T.S. Kupper, CD43 is a ligand for E-selectin on CLA + human T cells. Blood 107, 1421–1426 (2006)
F. Velazquez, A. Grodecki-Pena, A. Knapp, A.M. Salvador, T. Nevers, K. Croce, P. Alcaide, CD43 functions as an E-Selectin ligand for Th17 cells in Vitro and is required for Rolling on the vascular endothelium and Th17 cell recruitment during inflammation in vivo. J. Immunol. 196, 1305–1316 (2016)
J.D. Hernandez, J.T. Nguyen, J. He, W. Wang, B. Ardman, J.M. Green, M. Fukuda, L.G. Baum, Galectin-1 binds different CD43 glycoforms to cluster CD43 and regulate T cell death. J. Immunol. 177, 5328–5336 (2006)
O. Ramirez-Pliego, D.L. Escobar-Zarate, G.M. Rivera-Martinez, M.G. Cervantes-Badillo, F.R. Esquivel-Guadarrama, G. Rosas-Salgado, Y. Rosenstein, M.A. Santana, CD43 signals induce type one lineage commitment of human CD4 + T cells. BMC Immunol. 8, 30 (2007)
J.L. Cannon, A. Collins, P.D. Mody, D. Balachandran, K.J. Henriksen, C.E. Smith, J. Tong, B.S. Clay, S.D. Miller, A.I. Sperling, CD43 regulates Th2 differentiation and inflammation. J. Immunol. 180, 7385–7393 (2008)
H.F. Zhou, H. Yan, J.L. Cannon, L.E. Springer, J.M. Green, C.T. Pham, CD43-mediated IFN-gamma production by CD8 + T cells promotes abdominal aortic aneurysm in mice. J. Immunol. 190, 5078–5085 (2013)
K.T. Fay, D.B. Chihade, C.W. Chen, N.J. Klingensmith, J.D. Lyons, K. Ramonell, Z. Liang, C.M. Coopersmith, M.L. Ford, Increased mortality in CD43-deficient mice during sepsis. PLoS One 13, e0202656 (2018)
N. Manjunath, M. Correa, M. Ardman, B. Ardman, Negative regulation of T-cell adhesion and activation by CD43. Nature 377, 535–538 (1995)
C. Fratazzi, N. Manjunath, R.D. Arbeit, C. Carini, T.A. Gerken, B. Ardman, E. Remold-O’Donnell and H.G. Remold. A macrophage invasion mechanism for mycobacteria implicating the extracellular domain of CD43. J. Exp. Med. 192, 183–192 (2000)
M. Matsumoto, A. Shigeta, M. Miyasaka, T. Hirata, CD43 plays both antiadhesive and proadhesive roles in neutrophil rolling in a context-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 181, 3628–3635 (2008)
J. Tong, E.J. Allenspach, S.M. Takahashi, P.D. Mody, C. Park, J.K. Burkhardt, A.I. Sperling, CD43 regulation of T cell activation is not through steric inhibition of T cell-APC interactions but through an intracellular mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 199, 1277–1283 (2004)
J.L. Cannon, P.D. Mody, K.M. Blaine, E.J. Chen, A.D. Nelson, L.J. Sayles, T.V. Moore, B.S. Clay, N.O. Dulin, R.A. Shilling, J.K. Burkhardt, A.I. Sperling, CD43 interaction with ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins regulates T-cell trafficking and CD43 phosphorylation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 22, 954–963 (2011)
M. Sorigue, J. Junca, E. Sarrate, J. Grau, Expression of CD43 in chronic lymphoproliferative leukemias. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 94, 136–142 (2018)
Y. Li, X. Tong, L. Huang, L. Li, C. Wang, C. He, S. Liu, Z. Wang, M. Xiao, X. Mao, D. Zhang, A new score including CD43 and CD180: increased diagnostic value for atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Med. 10, 4387–4396 (2021)
X.B. Ma, Y.P. Zhong, Y. Zheng, J. Jiang, Y.P. Wang, Coexpression of CD5 and CD43 predicts worse prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Med. 7, 4284–4295 (2018)
T.K. van den Berg, D. Nath, H.J. Ziltener, D. Vestweber, M. Fukuda, I. van Die, P.R. Crocker, Cutting edge: CD43 functions as a T cell counterreceptor for the macrophage adhesion receptor sialoadhesin (Siglec-1). J. Immunol. 166, 3637–3640 (2001)
S. Wisnovsky, L. Mockl, S.A. Malaker, K. Pedram, G.T. Hess, N.M. Riley, M.A. Gray, B.A.H. Smith, M.C. Bassik, W.E. Moerner, C.R. Bertozzi, Genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal a specific ligand for the glycan-binding immune checkpoint receptor Siglec-7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 118, e2015024118 (2021)
F.M. Tuccillo, C. Palmieri, G. Fiume, A. de Laurentiis, M. Schiavone, C. Falcone, E. Iaccino, R. Galandrini, C. Capuano, A. Santoni, F.P. D’Armiento, C. Arra, A. Barbieri, F. Dal Piaz, D. Venzon, P. Bonelli, F.M. Buonaguro, I. Scala, M. Mallardo, I. Quinto, G. Scala, Cancer-associated CD43 glycoforms as target of immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 13, 752–762 (2014)
K. Hasegawa, S. Tanaka, F. Fujiki, S. Morimoto, K. Nakano, H. Kinoshita, A. Okumura, Y. Fujioka, R. Urakawa, H. Nakajima, N. Tatsumi, J. Nakata, S. Takashima, S. Nishida, A. Tsuboi, Y. Oka, Y. Oji, E. Miyoshi, T. Hirata, A. Kumanogoh, H. Sugiyama, N. Hosen. Glycosylation status of CD43 protein is associated with resistance of leukemia cells to CTL-mediated cytolysis. PLoS One 11, e0152326 (2016)
R.C. Wong, E. Remold-O’Donnell, D. Vercelli, J. Sancho, C. Terhorst, F. Rosen, R. Geha, T. Chatila, Signal transduction via leukocyte antigen CD43 (sialophorin). Feedback regulation by protein kinase C. J. Immunol. 144, 1455–1460 (1990)
D. Baeckstrom, Post-translational fate of a mucin-like leukocyte sialoglycoprotein (CD43) aberrantly expressed in a colon carcinoma cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11503–11509 (1997)
D. Baeckstrom, K. Zhang, N. Asker, U. Ruetschi, M. Ek, G.C. Hansson, Expression of the leukocyte-associated sialoglycoprotein CD43 by a colon carcinoma cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13688–13692 (1995)
J. Fernandez-Rodriguez, C.X. Andersson, S. Laos, D. Baeckstrom, A. Sikut, R. Sikut, G.C. Hansson, The leukocyte antigen CD43 is expressed in different cell lines of nonhematopoietic origin. Tumour Biol. 23, 193–201 (2002)
M. Santamaria, A. Lopez-Beltran, M. Toro, J. Pena, I.J. Molina, Specific monoclonal antibodies against leukocyte-restricted cell surface molecule CD43 react with nonhematopoietic tumor cells. Cancer Res. 56, 3526–3529 (1996)
A. Pimenidou, L.A. Madden, K.P. Topping, K.A. Smith, J.R. Monson, J. Greenman, Novel CD43 specific phage antibodies react with early stage colorectal tumours. Oncol. Rep. 11, 327–331 (2004)
Q. Fu, S.E. Cash, J.J. Andersen, C.R. Kennedy, D.G. Oldenburg, V.B. Zander, G.R. Foley, and C. Simon Shelley, CD43 in the nucleus and cytoplasm of lung cancer is a potential therapeutic target. Int. J. Cancer 132, 1761–1770 (2013)
B.H. Batdorf, S.H. Kroft, P.R. Hosking, A.M. Harrington, A.C. Mackinnon, H. Olteanu, Evaluation of CD43 expression in non-hematopoietic malignancies. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 29, 23–27 (2017)
A. Balikova, K. Jaager, J. Viil, T. Maimets, L. Kadaja-Saarepuu, Leukocyte marker CD43 promotes cell growth in co-operation with beta-catenin in non-hematopoietic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 41, 299–309 (2012)
N. Camacho-Concha, A. Olivos-Ortiz, A. Nunez-Rivera, A. Pedroza-Saavedra, L. Gutierrez-Xicotencatl, Y. Rosenstein, G. Pedraza-Alva, CD43 promotes cells transformation by preventing merlin-mediated contact inhibition of growth. PLoS One 8, e80806 (2013)
B. Ardman, M.A. Sikorski, D.E. Staunton, CD43 interferes with T-lymphocyte adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 89, 5001–5005 (1992)
W.S. Park, H.J. Kim, G.K. Lee, H.S. Son, Y. Bae, Anti-adhesive functions of CD43 expressed on colon carcinoma cells through the modulation of integrins. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 92, 82–89 (2012)
D. Vega-Mendoza, A. Canas-Linares, A. Flores-Alcantar, R. Espinosa-Neira, E. Melchy-Perez, R. Vera-Estrella, C. Auvynet, Y. Rosenstein, CD43 (sialophorin) is involved in the induction of extracellular matrix remodeling and angiogenesis by lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 236, 6643–6656 (2021)
C. Zhong, L. Wang, S. Hu, C. Huang, Z. Xia, J. Liao, W. Yi, J. Chen, Poly(I:C) enhances the efficacy of phagocytosis checkpoint blockade immunotherapy by inducing IL-6 production. J. Leukoc. Biol. 110, 1197–1208 (2021)
F. Heigwer, G. Kerr, M. Boutros, E-CRISP: fast CRISPR target site identification. Nat. Methods 11, 122–123 (2014)
Z. Tang, D. Davidson, R. Li, M.C. Zhong, J. Qian, J. Chen, A. Veillette, Inflammatory macrophages exploit unconventional pro-phagocytic integrins for phagocytosis and anti-tumor immunity. Cell. Rep. 37, 110111 (2021)
J. Chen, M.C. Zhong, H. Guo, D. Davidson, S. Mishel, Y. Lu, I. Rhee, L.A. Perez-Quintero, S. Zhang, M.E. Cruz-Munoz, N. Wu, D.C. Vinh, M. Sinha, V. Calderon, C.A. Lowell, J.S. Danska, A. Veillette, SLAMF7 is critical for phagocytosis of haematopoietic tumour cells via Mac-1 integrin. Nature 544, 493–497 (2017)
Y. Simoni, E. Becht, M. Fehlings, C.Y. Loh, S.L. Koo, K.W.W. Teng, J.P.S. Yeong, R. Nahar, T. Zhang, H. Kared, K. Duan, N. Ang, M. Poidinger, Y.Y. Lee, A. Larbi, A.J. Khng, E. Tan, C. Fu, R. Mathew, M. Teo, W.T. Lim, C.K. Toh, B.H. Ong, T. Koh, A.M. Hillmer, A. Takano, T.K.H. Lim, E.H. Tan, W. Zhai, D.S.W. Tan, I.B. Tan, E.W. Newell, Bystander CD8(+) T cells are abundant and phenotypically distinct in human tumour infiltrates. Nature 557, 575–579 (2018)
V. Brinkmann, A. Billich, T. Baumruker, P. Heining, R. Schmouder, G. Francis, S. Aradhye, P. Burtin, Fingolimod (FTY720): discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 9, 883–897 (2010)
G. Petrova, A. Ferrante, J. Gorski, Cross-reactivity of T cells and its role in the immune system. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 32, 349–372 (2012)
S.H. Shrager, C. Kiel, SnapShot: APC/T cell Immune Checkpoints. Cell 183, 1142–1142.e1141 (2020)
F.M. Tuccillo, A. de Laurentiis, C. Palmieri, G. Fiume, P. Bonelli, A. Borrelli, P. Tassone, I. Scala, F.M. Buonaguro, I. Quinto, G. Scala. Aberrant glycosylation as biomarker for cancer: focus on CD43. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 742831 (2014)
J. Cyster, C. Somoza, N. Killeen, A.F. Williams, Protein sequence and gene structure for mouse leukosialin (CD43), a T lymphocyte mucin without introns in the coding sequence. Eur. J. Immunol. 20, 875–881 (1990)
H. Shi, J. Lan, J. Yang, Mechanisms of resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1248, 83–117 (2020)
G. Bogle, P.R. Dunbar, T cell responses in lymph nodes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2, 107–116 (2010)
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFA0509400 and 2019YFA0110300), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82150117, 82071745 and 82101329), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (202002030069), Guangdong project (2019QN01Y212), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of China (2021A1515012620), Guangzhou Science and Technology Project of China (202201010993 and 105068559019) and a Grant from MOE Key Laboratory of Gene Function and Regulation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.C. and Y.Y.L. wrote the original manuscript. Y.Y.L. and X.Y.W. conceived and conducted most of experiments and data curation. Y.L. participated in the data analysis of the clinical samples. X.M.W., J.L., Y.Z.W. and H.H. assisted with some animal experiments. J.C. and W.Y. supervised the research and authored the final manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript. We thank Figdraw (https://www.figdraw.com) for expert assistance in the pattern drawing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
There is no conflict of interest in our article.
Ethical approval
All of the animal experiments were performed with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Sun Yat-Sen University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yi-yi Li and Xin-yu Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Yy., Wang, Xy., Li, Y. et al. Targeting CD43 optimizes cancer immunotherapy through reinvigorating antitumor immune response in colorectal cancer. Cell Oncol. 46, 777–791 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00794-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00794-w