Abstract
Purpose
The adaptive immune responses induced by radiotherapy has been demonstrated to largely rely on STING-dependent type I interferons (IFNs) production. However, irradiated tumor cells often fail to induce dendritic cells (DCs) to produce type I IFNs. Hence, we aim to uncover the limitation of STING-mediated innate immune sensing following radiation, and identify efficient reagents capable to rescue the failure of type I IFNs induction for facilitating radiotherapy.
Methods
A targeted cell-based phenotypic screening was performed to search for active molecules that could elevate the production of type I IFNs. USP14 knockout or inhibition was assayed for IFN production and the activation of STING signaling in vitro. The mechanisms of USP14 were investigated by western blot and co-immunoprecipitation in vitro. Additionally, combinational treatments with PT33 and radiation in vivo and in vitro models were performed to evaluate type I IFNs responses to radiation.
Results
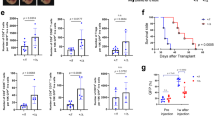
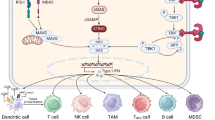
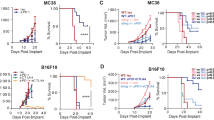
PT33 was identified as an enhancer of STING agonist elicited type I IFNs production to generate an elevated and durable STING activation profile in vitro. Mechanistically, USP14 inhibition or deletion impairs the deubiquitylation of K63-linked IRF3. Furthermore, blockade of USP14 with PT33 enhances DC sensing of irradiated-tumor cells in vitro, and synergizes with radiation to promote systemic antitumor immunity in vivo.
Conclusion
Our findings reveal that USP14 is one of the major IFN production suppressors and impairs the activation of IRF3 by removing the K63-linked ubiquitination of IRF3. Therefore, blockage of USP14 results in the gain of STING signaling activation and radiation-induced adaptive immune responses.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available within the article, supplementary information, or available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- USP14 :
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 14
- IFNs :
-
Interferons
- DCs :
-
Dendritic cells
- STING :
-
Stimulator of interferon genes
- TBK1 :
-
TANK-binding kinase 1
- IRF3 :
-
Interferon regulatory factor 3
- TME :
-
Tumor microenvironment
- cGAMP :
-
Cyclic GMP-AMP
- cGAS :
-
cGAMP synthase
- DUBs :
-
Deubiquitinases
- RIG-I :
-
Retinoic acid-inducible gene I
- USPs :
-
Ubiquitin-specific proteases
- HCV-1 :
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1
- BMDCs :
-
Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells
- CDNs :
-
Cyclic dinucleotides
- KO :
-
Knockout
- OE :
-
Overexpression
References
D.E. Citrin, Recent developments in radiotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 377, 1065–1075 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1608986
E.B. Golden, D. Frances, I. Pellicciotta, S. Demaria, M. Helen Barcellos-Hoff, S.C. Formenti, Radiation fosters dose-dependent and chemotherapy-induced immunogenic cell death. OncoImmunology 3, e28518 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4161/onci.28518
C. Grassberger, S.G. Ellsworth, M.Q. Wilks, F.K. Keane, J.S. Loeffler, Assessing the interactions between radiotherapy and antitumour immunity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 16, 729–745 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0238-9
C. Twyman-Saint Victor, A.J. Rech, A. Maity, R. Rengan, K.E. Pauken, E. Stelekati, J.L. Benci, B. Xu, H. Dada, P.M. Odorizzi, R.S. Herati, K.D. Mansfield, D. Patsch, R.K. Amaravadi, L.M. Schuchter, H. Ishwaran, R. Mick, D.A. Pryma, X. Xu, et al., Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature 520, 373–377 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14292
L. Apetoh, F. Ghiringhelli, A. Tesniere, M. Obeid, C. Ortiz, A. Criollo, G. Mignot, M.C. Maiuri, E. Ullrich, P. Saulnier, H. Yang, S. Amigorena, B. Ryffel, F.J. Barrat, P. Saftig, F. Levi, R. Lidereau, C. Nogues, J.-P. Mira, et al., Toll-like receptor 4–dependent contribution of the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat. Med. 13, 1050–1059 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1622
F. Klug, H. Prakash, P.E. Huber, T. Seibel, N. Bender, N. Halama, C. Pfirschke, R.H. Voss, C. Timke, L. Umansky, K. Klapproth, K. Schäkel, N. Garbi, D. Jäger, J. Weitz, H. Schmitz-Winnenthal, G.J. Hämmerling, P. Beckhove, Low-dose irradiation programs macrophage differentiation to an iNOS(+)M1 phenotype that orchestrates effective T cell immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 24, 589–602 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.09.014
L. Deng, H. Liang, M. Xu, X. Yang, B. Burnette, A. Arina, X.-D. Li, H. Mauceri, M. Beckett, T. Darga, X. Huang, T.F. Gajewski, Z.J. Chen, Y.-X. Fu, R.R. Weichselbaum, STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing promotes radiation-induced type I interferon-dependent antitumor immunity in immunogenic tumors. Immunity 41, 843–852 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.019
B.C. Burnette, H. Liang, Y. Lee, L. Chlewicki, N.N. Khodarev, R.R. Weichselbaum, Y.-X. Fu, S.L. Auh, The efficacy of radiotherapy relies upon induction of type I interferon–dependent innate and adaptive immunity. Cancer Res. 71, 2488–2496 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2820
S.R. Paludan, G. Andrew, Bowie Imm. Sens. DNA Immun. 38, 870–880 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.05.004
Y. Hou, H. Liang, E. Rao, W. Zheng, X. Huang, L. Deng, Y. Zhang, X. Yu, M. Xu, H. Mauceri, A. Arina, R.R. Weichselbaum, Y.-X. Fu, Non-canonical NF-kappaB antagonizes STING sensor-mediated DNA sensing in radiotherapy. Immunity 49, 490–503.e494 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.008
C. Han, Z. Liu, Y. Zhang, A. Shen, C. Dong, A. Zhang, C. Moore, Z. Ren, C. Lu, X. Cao, C.-L. Zhang, J. Qiao, Y.-X. Fu, Tumor cells suppress radiation-induced immunity by hijacking caspase 9 signaling. Nat. Immunol. 21, 546–554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-0641-5
X. Yue, Y. Zuo, H. Ke, J. Luo, L. Lou, W. Qin, Y. Wang, Z. Liu, D. Chen, H. Sun, W. Zheng, C. Zhu, R. Wang, G. Wen, J. Du, B. Zhou, X. Bu, Identification of 4-arylidene curcumin analogues as novel proteasome inhibitors for potential anticancer agents targeting 19S regulatory particle associated deubiquitinase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 137, 29–50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.032
H. Hu, S.-C. Sun, Ubiquitin signaling in immune responses. Cell Res. 26, 457–483 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.40
H. Sun, Q. Zhang, Y.-Y. Jing, M. Zhang, H.-Y. Wang, Z. Cai, T. Liuyu, Z.-D. Zhang, T.-C. Xiong, Y. Wu, Q.-Y. Zhu, J. Yao, H.-B. Shu, D. Lin, B. Zhong, USP13 negatively regulates antiviral responses by deubiquitinating STING. Nat. Commun. 8, 15534 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15534
J. Zhang, Y. Chen, X. Chen, W. Zhang, L. Zhao, L. Weng, H. Tian, Z. Wu, X. Tan, X. Ge, P. Wang, L. Fang, Deubiquitinase USP35 restrains STING-mediated interferon signaling in ovarian cancer. Cell Death Differ. 28, 139–155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0588-y
C. Bodda, L.S. Reinert, S. Fruhwürth, T. Richardo, C. Sun, B.-C. Zhang, M. Kalamvoki, A. Pohlmann, T.H. Mogensen, P. Bergström, L. Agholme, P. O’Hare, B. Sodeik, M. Gyrd-Hansen, H. Zetterberg, S.R. Paludan, HSV1 VP1-2 deubiquitinates STING to block type I interferon expression and promote brain infection. J. Exp. Med. 217, e20191422 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20191422
T. Tsuchida, J. Zou, T. Saitoh, H. Kumar, T. Abe, Y. Matsuura, T. Kawai, S. Akira, The ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 regulates innate immune responses to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Immunity 33, 765–776 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.013
J. Zhang, M.-M. Hu, Y.-Y. Wang, H.-B. Shu, TRIM32 protein modulates type I interferon induction and cellular antiviral response by targeting MITA/STING protein for K63-linked ubiquitination*. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 28646–28655 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.362608
M. Zhang, M.-X. Zhang, Q. Zhang, G.-F. Zhu, L. Yuan, D.-E. Zhang, Q. Zhu, J. Yao, H.-B. Shu, B. Zhong, USP18 recruits USP20 to promote innate antiviral response through deubiquitinating STING/MITA. Cell Res. 26, 1302–1319 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.125
W.-W. Luo, S. Li, C. Li, H. Lian, Q. Yang, B. Zhong, H.-B. Shu, iRhom2 is essential for innate immunity to DNA viruses by mediating trafficking and stability of the adaptor STING. Nat. Immunol. 17, 1057–1066 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3510
Y. Guo, F. Jiang, L. Kong, H. Wu, H. Zhang, X. Chen, J. Zhao, B. Cai, Y. Li, C. Ma, F. Yi, L. Zhang, B. Liu, Y. Zheng, L. Zhang, C. Gao, OTUD5 promotes innate antiviral and antitumor immunity through deubiquitinating and stabilizing STING. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 18, 1945–1955 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-00531-5
B. Zhong, L. Zhang, C. Lei, Y. Li, A.-P. Mao, Y. Yang, Y.-Y. Wang, X.-L. Zhang, H.-B. Shu, The ubiquitin ligase RNF5 regulates antiviral responses by mediating degradation of the adaptor protein MITA. Immunity 30, 397–407 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.01.008
Y. Wang, Q. Lian, B. Yang, S. Yan, H. Zhou, L. He, G. Lin, Z. Lian, Z. Jiang, B. Sun, TRIM30α is a negative-feedback regulator of the intracellular DNA and DNA virus-triggered response by targeting STING. PLoS Pathog. 11, e1005012 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005012
M. Zhang, L. Wang, X. Zhao, K. Zhao, H. Meng, W. Zhao, C. Gao, TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP) negatively regulates IFN-β production and antiviral response by promoting proteasomal degradation of TANK-binding kinase 1. J. Exp. Med. 209, 1703–1711 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20120024
J. Cui, Y. Li, L. Zhu, D. Liu, Z. Songyang, H.Y. Wang, R.-F. Wang, NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting the kinase TBK1 for degradation via the ubiquitin ligase DTX4. Nat. Immunol. 13, 387–395 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2239
Z. Yu, H. Song, M. Jia, J. Zhang, W. Wang, Q. Li, L. Zhang, W. Zhao, USP1–UAF1 deubiquitinase complex stabilizes TBK1 and enhances antiviral responses. J. Exp. Med. 214, 3553–3563 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20170180
M. Lin, Z. Zhao, Z. Yang, Q. Meng, P. Tan, W. Xie, Y. Qin, R.-F. Wang, J. Cui, USP38 inhibits type I interferon signaling by editing TBK1 ubiquitination through NLRP4 signalosome. Mol. Cell 64, 267–281 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.08.029
H. Li, Z. Zhao, J. Ling, L. Pan, X. Zhao, H. Zhu, J. Yu, B. Xie, J. Shen, W. Chen, USP14 promotes K63-linked RIG-I deubiquitination and suppresses antiviral immune responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 49, 42–53 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201847603
H. Li, J. Quan, X. Zhao, J. Ling, W. Chen, USP14 negatively regulates RIG-I-mediated IL-6 and TNF-α production by inhibiting NF-κB activation. Mol. Immunol. 130, 69–76 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2020.12.022
D. Wang, L. Fang, P. Li, L. Sun, J. Fan, Q. Zhang, R. Luo, X. Liu, K. Li, H. Chen, Z. Chen, S. Xiao, The leader proteinase of foot-and-mouth disease virus negatively regulates the type I interferon pathway by acting as a viral Deubiquitinase. J. Virol. 85, 3758–3766 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02589-10
L. Huang, Y. Zhang, J. Zheng, N. Ni, Q. Qin, X. Huang, Y. Huang, Grouper ubiquitin-specific protease 14 promotes iridovirus replication through negatively regulating interferon response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 105, 253–262 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.07.015
M. Chen, Q. Meng, Y. Qin, P. Liang, P. Tan, L. He, Y. Zhou, Y. Chen, J. Huang, R.-F. Wang, J. Cui, TRIM14 inhibits cGAS degradation mediated by selective autophagy receptor p62 to promote innate immune responses. Mol. Cell 64, 105–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.08.025
M.B. Lutz, N. Kukutsch, A.L. Ogilvie, S. Rossner, F. Koch, N. Romani, G. Schuler, An advanced culture method for generating large quantities of highly pure dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow. J. Immunol. Methods 223, 77–92 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1759(98)00204-x
X.-C. Wang, X. Yue, R.-X. Zhang, T.-Y. Liu, Z.-Z. Pan, M.-J. Yang, Z.-H. Lu, Z.-Y. Wang, J.-H. Peng, L.-Y. Le, G.-Y. Wang, Q.-H. Peng, Y. Meng, W. Huang, R.-Y. Liu, Genome-wide RNAi screening identifies RFC4 as a factor that mediates Radioresistance in colorectal Cancer by facilitating nonhomologous end joining repair. Clin. Cancer Res. 25, 4567 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3735
L. Li, R.Y. Liu, J.L. Huang, Q.C. Liu, Y. Li, P.H. Wu, Y.X. Zeng, W. Huang, Adenovirus-mediated intra-tumoral delivery of the human endostatin gene inhibits tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 118, 2064–2071 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21585
W. Zeng, M. Xu, S. Liu, L. Sun, Z.J. Chen, Key role of Ubc5 and Lysine-63 Polyubiquitination in viral activation of IRF3. Mol. Cell 36, 315–325 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.09.037
A. Härtlova, S.F. Erttmann, F.A.M. Raffi, A.M. Schmalz, U. Resch, S. Anugula, S. Lienenklaus, L.M. Nilsson, A. Kröger, J.A. Nilsson, T. Ek, S. Weiss, N.O. Gekara, DNA damage primes the type I interferon system via the cytosolic DNA sensor STING to promote anti-microbial innate immunity. Immunity 42, 332–343 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.012
S.M. Harding, J.L. Benci, J. Irianto, D.E. Discher, A.J. Minn, R.A. Greenberg, Mitotic progression following DNA damage enables pattern recognition within micronuclei. Nature 548, 466–470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23470
C.-L. Kuo, L. Goldberg Alfred, Ubiquitinated proteins promote the association of proteasomes with the deubiquitinating enzyme Usp14 and the ubiquitin ligase Ube3c. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, E3404–E3413 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1701734114
F. Wang, S. Ning, B. Yu, Y. Wang, USP14: Structure, function, and target inhibition. Front. Pharmacol. 12 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.801328
S. Liu, X. Cai, J. Wu, Q. Cong, X. Chen, T. Li, F. Du, J. Ren, Y.-T. Wu, V. Grishin Nick, J. Chen Zhijian, Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 347, aaa2630 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa2630
Funding
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 81803054 and 81973174), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2021A1515012496 and 2022A1515012221).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: X.Y. and X.B.; Performed in vitro functional studies and analyzed data: W.W., H.X., C.L., Y.W., and W.Z.; Performed animal experiments and analyzed data: X.Y. and W.W.; Generated critical cellular tools: H.X., W.W., R.W., C.J. and J.W.; Performed mechanistical studies and analyzed data: X.Y., W.W., Y.L., Y.Z. and H.X.; Statistical analysis: X.Y., X.B.; Supervision of data: X.Y., X.B. and J.Q.; Analysis and interpretation of data and writing of the manuscript: X.B. and X.Y.. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee for Clinical Research and Animal Trials of the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University (SYSUFAH). All the experiments were conducted in the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any potential conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 6616 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Xu, H., Liao, C. et al. Blockade of USP14 potentiates type I interferon signaling and radiation-induced antitumor immunity via preventing IRF3 deubiquitination. Cell Oncol. 45, 1347–1361 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00724-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00724-2