Abstract
Purpose
Although EGFR activation is a hallmark of glioblastoma (GBM), anti-EGFR therapy has so far not yielded the desired effects. Targeting PI3K/Akt has been proposed as a strategy to increase the cellular sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors. Here we evaluated the contribution of FOXO3a, a key Akt target, in the response of GBM cells to EGFR inhibition.
Methods
FOXO3a activation was assessed by immunofluorescence and gene reporter assays, and by evaluating target gene expression using Western blotting and qRT-PCR. Cellular effects were evaluated using cell viability and apoptosis assays, i.e., Annexin V/PI staining and caspase 3/7 activity measurements. Drug synergism was evaluated by performing isobolographic analyses. Gene silencing experiments were performed using stable shRNA transfections.
Results
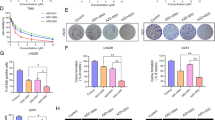
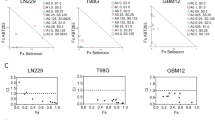
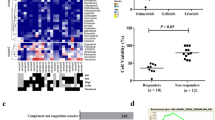
We found that EGFR inhibition in GBM cells led to FOXO3a activation and to transcriptional modulation of its key targets, including repression of the oncogene FOXM1. In addition, we found that specific FOXO3a activation recapitulated the molecular effects of EGFR inhibition, and that the FOXO3a activator trifluoperazine, a FDA-approved antipsychotic agent, reduced GBM cell growth. Subsequent isobolographic analyses of combination experiments indicated that trifluoperazine and erlotinib cooperated synergistically and that their concomitant treatment induced a robust activation of FOXO3a, leading to apoptosis in GBM cells. Using gene silencing, we found that FOXO3a is essential for the response of GBM cells to EGFR inhibition.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that FOXO3a activation is a crucial event in the response of GBM cells to EGFR inhibition, suggesting that FOXO3a may serve as an actionable therapeutic target that can be modulated using FDA-approved drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.P. Dunn, M.L. Rinne, J. Wykosky, G. Genovese, S.N. Quayle, I.F. Dunn, P.K. Agarwalla, M.G. Chheda, B. Campos, A. Wang, C. Brennan, K.L. Ligon, F. Furnari, W.K. Cavenee, R.A. Depinho, L. Chin, W.C. Hahn, Emerging insights into the molecular and cellular basis of glioblastoma. Genes Dev 26, 756–784 (2012)
M. Staberg, S.R. Michaelsen, R.D. Rasmussen, M. Villingshoj, H.S. Poulsen, P. Hamerlik, Inhibition of histone deacetylases sensitizes glioblastoma cells to lomustine. Cell Oncol 40, 21–32 (2017)
D. Matias, J. Balca-Silva, L.G. Dubois, B. Pontes, V.P. Ferrer, L. Rosario, A. do Carmo, J. Echevarria-Lima, A.B. Sarmento-Ribeiro, M.C. Lopes, V. Moura-Neto, Dual treatment with shikonin and temozolomide reduces glioblastoma tumor growth, migration and glial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Oncol 40, 247–261 (2017)
Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 455, 1061–1068 (2008)
T.F. Cloughesy, W.K. Cavenee, P.S. Mischel, Glioblastoma: From molecular pathology to targeted treatment. Annu Rev Pathol 9, 1–25 (2014)
M.E. Halatsch, U. Schmidt, J. Behnke-Mursch, A. Unterberg, C.R. Wirtz, Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme and other malignant brain tumours. Cancer Treat Rev 32, 74–89 (2006)
R. Nishikawa, X.D. Ji, R.C. Harmon, C.S. Lazar, G.N. Gill, W.K. Cavenee, H.J. Huang, A mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human glioma confers enhanced tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91, 7727–7731 (1994)
I.K. Mellinghoff, M.Y. Wang, I. Vivanco, D.A. Haas-Kogan, S. Zhu, E.Q. Dia, K.V. Lu, K. Yoshimoto, J.H. Huang, D.J. Chute, B.L. Riggs, S. Horvath, L.M. Liau, W.K. Cavenee, P.N. Rao, R. Beroukhim, T.C. Peck, J.C. Lee, W.R. Sellers, D. Stokoe, M. Prados, T.F. Cloughesy, C.L. Sawyers, P.S. Mischel, Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353, 2012–2024 (2005)
E. Carrasco-Garcia, M. Saceda, S. Grasso, L. Rocamora-Reverte, M. Conde, A. Gomez-Martinez, P. Garcia-Morales, J.A. Ferragut, I. Martinez-Lacaci, Small tyrosine kinase inhibitors interrupt EGFR signaling by interacting with erbB3 and erbB4 in glioblastoma cell lines. Exp Cell Res 317, 1476–1489 (2011)
G. Ramis, E. Thomas-Moya, S. Fernandez de Mattos, J. Rodriguez, P. Villalonga, EGFR inhibition in glioma cells modulates rho signaling to inhibit cell motility and invasion and cooperates with Temozolomide to reduce cell growth. PLoS One 7, e38770 (2012)
H.W. Lo, EGFR-targeted therapy in malignant glioma: Novel aspects and mechanisms of drug resistance. Curr Mol Pharmacol 3, 37–52 (2010)
G. Karpel-Massler, C. R. Wirtz, M.E. Halatsch, Drug combinations enhancing the antineoplastic effects of erlotinib in high-grade glioma. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 6, 384–394 (2011)
Q.W. Fan, K.M. Specht, C. Zhang, D.D. Goldenberg, K.M. Shokat, W.A. Weiss, Combinatorial efficacy achieved through two-point blockade within a signaling pathway-a chemical genetic approach. Cancer Res 63, 8930–8938 (2003)
M.Y. Wang, K.V. Lu, S. Zhu, E.Q. Dia, I. Vivanco, G.M. Shackleford, W.K. Cavenee, I.K. Mellinghoff, T.F. Cloughesy, C.L. Sawyers, P.S. Mischel, Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition promotes response to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors in PTEN-deficient and PTEN-intact glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66, 7864–7869 (2006)
Q.W. Fan, C.K. Cheng, T.P. Nicolaides, C.S. Hackett, Z.A. Knight, K.M. Shokat, W.A. Weiss, A dual phosphoinositide-3-kinase alpha/mTOR inhibitor cooperates with blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor in PTEN-mutant glioma. Cancer Res 67, 7960–7965 (2007)
B.M. Burgering, A brief introduction to FOXOlogy. Oncogene 27, 2258–2262 (2008)
E.W. Lam, R.E. Francis, M. Petkovic, FOXO transcription factors: Key regulators of cell fate. Biochem Soc Trans 34, 722–726 (2006)
J. Shi, L. Zhang, A. Shen, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhao, L. Zou, Q. Ke, F. He, P. Wang, C. Cheng, G. Shi, Clinical and biological significance of forkhead class box O 3a expression in glioma: Mediation of glioma malignancy by transcriptional regulation of p27kip1. J Neuro-Oncol 98, 57–69 (2010)
J.Y. Yang, M.C. Hung, A new fork for clinical application: Targeting forkhead transcription factors in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15, 752–757 (2009)
T.C. Chou, P. Talalay, Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzym Regul 22, 27–55 (1984)
M.W. Pfaffl, A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29, e45–e445 (2001)
M.M. Bradford, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72, 248–254 (1976)
R.H. Medema, G.J. Kops, J.L. Bos, B.M. Burgering, AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature 404, 782–787 (2000)
F. Zanella, A. Rosado, B. Garcia, A. Carnero, W. Link, Using multiplexed regulation of luciferase activity and GFP translocation to screen for FOXO modulators. BMC Cell Biol 10, 14 (2009)
M. Schmidt, S. Fernandez de Mattos, A. van der Horst, R. Klompmaker, G.J. Kops, E.W. Lam, B.M. Burgering, R.H. Medema, Cell cycle inhibition by FoxO forkhead transcription factors involves downregulation of cyclin D. Mol Cell Biol 22, 7842–7852 (2002)
A. Essaghir, N. Dif, C.Y. Marbehant, P.J. Coffer, J.B. Demoulin, The transcription of FOXO genes is stimulated by FOXO3 and repressed by growth factors. J Biol Chem 284, 10334–10342 (2009)
U.B. McGovern, R.E. Francis, B. Peck, S.K. Guest, J. Wang, S.S. Myatt, J. Krol, J.M. Kwok, A. Polychronis, R.C. Coombes, E.W. Lam, Gefitinib (Iressa) represses FOXM1 expression via FOXO3a in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 8, 582–591 (2009)
L. Jiang, X.C. Cao, J.G. Cao, F. Liu, M.F. Quan, X.F. Sheng, K.Q. Ren, Casticin induces ovarian cancer cell apoptosis by repressing FoxM1 through the activation of FOXO3a. Oncol Lett 5, 1605–1610 (2013)
T.R. Kau, F. Schroeder, S. Ramaswamy, C.L. Wojciechowski, J.J. Zhao, T.M. Roberts, J. Clardy, W.R. Sellers, P.A. Silver, A chemical genetic screen identifies inhibitors of regulated nuclear export of a Forkhead transcription factor in PTEN-deficient tumor cells. Cancer Cell 4, 463–476 (2003)
S. Fernandez de Mattos, P. Villalonga, J. Clardy, E.W. Lam, FOXO3a mediates the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin in colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7, 3237–3246 (2008)
A. Obrador-Hevia, M. Serra-Sitjar, J. Rodriguez, P. Villalonga, S. Fernandez de Mattos, The tumour suppressor FOXO3 is a key regulator of mantle cell lymphoma proliferation and survival. Br J Haematol 156, 334–345 (2012)
E. Berry, J.L. Hardt, J. Clardy, J.R. Lurain, J.J. Kim, Induction of apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells by psammaplysene a involves FOXO1. Gynecol Oncol 112, 331–336 (2009)
A.V. Hoekstra, E.C. Sefton, E. Berry, Z. Lu, J. Hardt, E. Marsh, P. Yin, J. Clardy, D. Chakravarti, S. Bulun, J.J. Kim, Progestins activate the AKT pathway in leiomyoma cells and promote survival. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94, 1768–1774 (2009)
J. Sangodkar, N.S. Dhawan, H. Melville, V.J. Singh, E. Yuan, H. Rana, S. Izadmehr, C. Farrington, S. Mazhar, S. Katz, T. Albano, P. Arnovitz, R. Okrent, M. Ohlmeyer, M. Galsky, D. Burstein, D. Zhang, K. Politi, A. Difeo, G. Narla, Targeting the FOXO1/KLF6 axis regulates EGFR signaling and treatment response. J Clin Invest 122, 2637–2651 (2012)
S. Zona, L. Bella, M.J. Burton, G.N. de Moraes, E.W. Lam, FOXM1: An emerging master regulator of DNA damage response and genotoxic agent resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839, 1316–1322 (2014)
M. Liu, B. Dai, S.H. Kang, K. Ban, F.J. Huang, F.F. Lang, K.D. Aldape, T.X. Xie, C.E. Pelloski, K. Xie, R. Sawaya, S. Huang, FoxM1B is overexpressed in human glioblastomas and critically regulates the tumorigenicity of glioma cells. Cancer Res 66, 3593–3602 (2006)
B. Dai, S.H. Kang, W. Gong, M. Liu, K.D. Aldape, R. Sawaya, S. Huang, Aberrant FoxM1B expression increases matrix metalloproteinase-2 transcription and enhances the invasion of glioma cells. Oncogene 26, 6212–6219 (2007)
Y. Zhang, N. Zhang, B. Dai, M. Liu, R. Sawaya, K. Xie, S. Huang, FoxM1B transcriptionally regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression and promotes the angiogenesis and growth of glioma cells. Cancer Res 68, 8733–8742 (2008)
Y. Lee, K.H. Kim, D.G. Kim, H.J. Cho, Y. Kim, J. Rheey, K. Shin, Y.J. Seo, Y.S. Choi, J.I. Lee, J. Lee, K.M. Joo, D.H. Nam, FoxM1 promotes Stemness and radio-resistance of glioblastoma by regulating the master stem cell regulator Sox2. PLoS One 10, e0137703 (2015)
A.H. Gong, P. Wei, S. Zhang, J. Yao, Y. Yuan, A.D. Zhou, F.F. Lang, A.B. Heimberger, G. Rao, S. Huang, FoxM1 drives a feed-forward STAT3-activation signaling loop that promotes the self-renewal and Tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cancer Res 75, 2337–2348 (2015)
K. Joshi, Y. Banasavadi-Siddegowda, X. Mo, S.H. Kim, P. Mao, C. Kig, D. Nardini, R.W. Sobol, L.M. Chow, H.I. Kornblum, R. Waclaw, M. Beullens, I. Nakano, MELK-dependent FOXM1 phosphorylation is essential for proliferation of glioma stem cells. Stem Cells 31, 1051–1063 (2013)
N. Zhang, X. Wu, L. Yang, F. Xiao, H. Zhang, A. Zhou, Z. Huang, S. Huang, FoxM1 inhibition sensitizes resistant glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by downregulating the expression of DNA-repair gene Rad51. Clin Cancer Res 18, 5961–5971 (2012)
N. Zhang, P. Wei, A. Gong, W.T. Chiu, H.T. Lee, H. Colman, H. Huang, J. Xue, M. Liu, Y. Wang, R. Sawaya, K. Xie, W.K. Yung, R.H. Medema, X. He, S. Huang, FoxM1 promotes beta-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 20, 427–442 (2011)
K. Xu, H.K. Shu, Transcription factor interactions mediate EGF-dependent COX-2 expression. Mol Cancer Res : MCR 11, 875–886 (2013)
J. Krol, R.E. Francis, A. Albergaria, A. Sunters, A. Polychronis, R.C. Coombes, E.W. Lam, The transcription factor FOXO3a is a crucial cellular target of gefitinib (Iressa) in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6, 3169–3179 (2007)
S. Fernandez de Mattos, A. Essafi, I. Soeiro, A.M. Pietersen, K.U. Birkenkamp, C.S. Edwards, A. Martino, B.H. Nelson, J.M. Francis, M.C. Jones, J.J. Brosens, P.J. Coffer, E.W. Lam, FoxO3a and BCR-ABL regulate cyclin D2 transcription through a STAT5/BCL6-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 24, 10058–10071 (2004)
A. Sunters, S. Fernandez de Mattos, M. Stahl, J.J. Brosens, G. Zoumpoulidou, C.A. Saunders, P.J. Coffer, R.H. Medema, R.C. Coombes, E.W. Lam, FoxO3a transcriptional regulation of Bim controls apoptosis in paclitaxel-treated breast cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 278, 49795–49805 (2003)
F. Zhao, E.W. Lam, Role of the forkhead transcription factor FOXO-FOXM1 axis in cancer and drug resistance. Front Med 6, 376–380 (2012)
J.E. Allen, G. Krigsfeld, P.A. Mayes, L. Patel, D.T. Dicker, A.S. Patel, N.G. Dolloff, E. Messaris, K.A. Scata, W. Wang, J.Y. Zhou, G.S. Wu, W.S. El-Deiry, Dual inactivation of Akt and ERK by TIC10 signals Foxo3a nuclear translocation, TRAIL gene induction, and potent antitumor effects. Sci Transl Med 5, 171ra117 (2013)
J. Sunayama, A. Sato, K. Matsuda, K. Tachibana, E. Watanabe, S. Seino, K. Suzuki, Y. Narita, S. Shibui, K. Sakurada, T. Kayama, A. Tomiyama, C. Kitanaka, FoxO3a functions as a key integrator of cellular signals that control glioblastoma stem-like cell differentiation and tumorigenicity. Stem Cells 29, 1327–1337 (2011)
Z. Qian, L. Ren, D. Wu, X. Yang, Z. Zhou, Q. Nie, G. Jiang, S. Xue, W. Weng, Y. Qiu, Y. Lin, Overexpression of FoxO3a is associated with glioblastoma progression and predicts poor patient prognosis. Int J Cancer 140, 2792–2804 (2017)
F.C. Schroeder, T.R. Kau, P.A. Silver, J. Clardy, The psammaplysenes, specific inhibitors of FOXO1a nuclear export. J Nat Prod 68, 574–576 (2005)
S.H. Curry, R.B. Stewart, P.K. Springer, J.E. Pope, Plasma-trifluoperazine concentrations during high dose therapy. Lancet 1, 395–396 (1981)
B.M. Cohen, J.F. Lipinski, C. Waternaux, A fixed dose study of the plasma concentration and clinical effects of thioridazine and its major metabolites. Psychopharmacology 97, 481–488 (1989)
I. Gil-Ad, B. Shtaif, Y. Levkovitz, M. Dayag, E. Zeldich, A. Weizman, Characterization of phenothiazine-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma and glioma cell lines: Clinical relevance and possible application for brain-derived tumors. J Mol Neurosci : MN 22, 189–198 (2004)
H.W. Cheng, Y.H. Liang, Y.L. Kuo, C.P. Chuu, C.Y. Lin, M.H. Lee, A.T. Wu, C.T. Yeh, E.I. Chen, J. Whang-Peng, C.L. Su, C.Y. Huang, Identification of thioridazine, an antipsychotic drug, as an antiglioblastoma and anticancer stem cell agent using public gene expression data. Cell Death Dis 6, e1753 (2015)
S.Y. Shin, K.S. Lee, Y.K. Choi, H.J. Lim, H.G. Lee, Y. Lim, Y.H. Lee, The antipsychotic agent chlorpromazine induces autophagic cell death by inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway in human U-87MG glioma cells. Carcinogenesis 34, 2080–2089 (2013)
J.K. Lee, D.H. Nam, J. Lee, Repurposing antipsychotics as glioblastoma therapeutics: Potentials and challenges. Oncol Lett 11, 1281–1286 (2016)
J. Colomer, A.A. Schmitt, E.J. Toone, A.R. Means, Identification and inhibitory properties of a novel ca(2+)/calmodulin antagonist. Biochemistry 49, 4244–4254 (2010)
F. Zanella, A. Rosado, B. Garcia, A. Carnero, W. Link, Chemical genetic analysis of FOXO nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling by using image-based cell screening. Chembiochem 9, 2229–2237 (2008)
J. Li, S. Zhu, D. Kozono, K. Ng, D. Futalan, Y. Shen, J.C. Akers, T. Steed, D. Kushwaha, M. Schlabach, B.S. Carter, C.H. Kwon, F. Furnari, W. Cavenee, S. Elledge, C.C. Chen, Genome-wide shRNA screen revealed integrated mitogenic signaling between dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 5, 882–893 (2014)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Joan Seoane (Institut de Recerca Hospital Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona), Hans Skovgaard (Rigshospitalet, Oslo) and Isabel Martínez-Lacaci (Hospital Universitario Virgen de la Arrixaca, Murcia) for the gift of human glioma cell lines, to Jon Clardy (Harvard University) for Psammaplysene A and to Eric W-F Lam (Imperial College London) and Wolfgang Link (CNIO, Madrid) for expression plasmids. We are also grateful to Roche for providing erlotinib hydrochloride. The Cancer Cell Biology Laboratory is supported by a Consolider Ingenio grant (CSD2010-00065, Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, Spain, to G.R., R.V-P., S.FdM. and P.V.) and a grant from Junta de Balears-AECC (to G.R., S.FdM. and P.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
For tumor sample collection informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study and the study was approved by the ethical committee (Comitè d’Ètica de la Investigació-Illes Balears, CEI-IB, Ref. N° 3198/16).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramis, G., Villalonga-Planells, R., Serra-Sitjar, M. et al. The tumor suppressor FOXO3a mediates the response to EGFR inhibition in glioblastoma cells. Cell Oncol. 42, 521–536 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00443-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00443-1