Abstract
Background
The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) is a potent cellular inhibitor of apoptosis, based on its unique capability to bind and to inhibit caspases. However, XIAP is also involved in a number of additional cellular activities independent of its caspase inhibitory function. The aim of this study was to investigate whether modulation of XIAP expression affects apoptosis-independent functions of XIAP in melanoma cells, restores their sensitivity to apoptosis and/or affects their invasive and metastatic capacities.
Methods
XIAP protein levels were analyzed by immunohistochemical staining of human tissues and by Western blotting of melanoma cell lysates. The effects of pharmacological inhibition or of XIAP down-regulation were investigated using ex-vivo and transwell invasion assays. The biological effects of XIAP down-regulation on melanoma cells were analyzed in vitro using BrdU/PI, nucleosome quantification, adhesion and migration assays. In addition, new XIAP binding partners were identified by co-immunoprecipitation followed by mass spectrometry.
Results
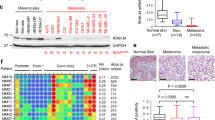
Here we found that the expression of XIAP is increased in metastatic melanomas and in invasive melanoma-derived cell lines. We also found that the bivalent IAP antagonist birinapant significantly reduced the invasive capability of melanoma cells. This reduction could be reproduced by downregulating XIAP in melanoma cells. Furthermore, we found that the migration of melanoma cells and the formation of focal adhesions at cellular borders on fibronectin-coated surfaces were significantly reduced upon XIAP knockdown. This reduction may depend on an altered vimentin-XIAP association, since we identified vimentin as a new binding partner of XIAP. As a corollary of these molecular alterations, we found that XIAP down-regulation in melanoma cells led to a significant decrease in invasion of dermal skin equivalents.
Conclusion
From our data we conclude that XIAP acts as a multifunctional pro-metastatic protein in skin melanomas and, as a consequence, that XIAP may serve as a therapeutic target for these melanomas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Shtivelman, M.Q. Davies, P. Hwu, J. Yang, M. Lotem, M. Oren, K.T. Flaherty, D.E. Fisher, Pathways and therapeutic targets in melanoma. Oncotarget 5, 1701–1752 (2014)
S. Goldar, M.S. Khaniani, S.M. Derakhshan, B. Baradaran, Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer development and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16, 2129–2144 (2015)
P. Liston, S.S. Young, A.E. Mackenzie, R.G. Korneluk, Life and death decisions: The role of the IAPs in modulating programmed cell death. Apoptosis 2, 423–441 (1997)
J. Silke, D. Vucic, IAP family of cell death and signaling regulators. Methods Enzymol 545, 35–65 (2014)
S. Fulda, Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins as targets for anticancer therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 7, 1255–1264 (2007)
Y.L. Yang, X.M. Li, The IAP family: Endogenous caspase inhibitors with multiple biological activities. Cell Res 10, 169–177 (2000)
B.P. Eckelman, G.S. Salvesen, F.L. Scott, Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: Why XIAP is the black sheep of the family. EMBO Rep 7, 988–994 (2006)
H. Kashkar, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis: A chemoresistance factor or a hollow promise. Clin Cancer Res 16, 4496–4502 (2010)
Y. Liu, B. Zhang, T. Shi, H. Qin, Inhibition of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein suppresses tumorigenesis and enhances chemosensitivity in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget 8, 95764–95772 (2017)
S. Fulda, Regulation of cell migration, invasion and metastasis by IAP proteins and their antagonists. Oncogene 33, 671–676 (2014)
H. Wu, J. Tschopp, S.C. Lin, Smac mimetics and TNFalpha: A dangerous liaison? Cell 131, 655–658 (2007)
G.A. Ward, E.J. Lewis, J.S. Ahn, C.N. Johnson, J.F. Lyons, V. Martins, J.M. Munck, S.J. Rich, T. Smyth, N.T. Thompson, P.A. Williams, N.E. Wilsher, N.G. Wallis, G. Chessari, ASTX660, a novel non-peptidomimetic antagonist of cIAP1/2 and XIAP, potently induces TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis in Cancer cell lines and inhibits tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther 17, 1381–1391 (2018)
K.S. Prabhu, I.W. Achkar, S. Kuttikrishnan, S. Akhtar, A.Q. Khan, K.S. Siveen, S. Uddin, Embelin: A benzoquinone possesses therapeutic potential for the treatment of human cancer. Future Med Chem 10, 961–976 (2018)
A. Witt, J.M. Seeger, O. Coutelle, P. Zigrino, P. Broxtermann, M. Andree, K. Brinkmann, C. Jungst, A.C. Schauss, S. Schull, D. Wohlleber, P.A. Knolle, M. Kronke, C. Mauch, H. Kashkar, IAP antagonization promotes inflammatory destruction of vascular endothelium. EMBO Rep 16, 719–727 (2015)
K.D. Bromberg, H.M. Kluger, A. Delaunay, S. Abbas, K.A. DiVito, S. Krajewski, Z. Ronai, Increased expression of the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF5 is associated with decreased survival in breast cancer. Cancer Res 67, 8172–8179 (2007)
M. Lu, S.C. Lin, Y. Huang, Y.J. Kang, R. Rich, Y.C. Lo, D. Myszka, J. Han, H. Wu, XIAP induces NF-kappaB activation via the BIR1/TAB1 interaction and BIR1 dimerization. Mol Cell 26, 689–702 (2007)
A. Krieg, R.G. Correa, J.B. Garrison, G. Le Negrate, K. Welsh, Z. Huang, W.T. Knoefel, J.C. Reed, XIAP mediates NOD signaling via interaction with RIP2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106, 14524–14529 (2009)
M. Andree, J.M. Seeger, S. Schull, O. Coutelle, D. Wagner-Stippich, K. Wiegmann, C.M. Wunderlich, K. Brinkmann, P. Broxtermann, A. Witt, M. Fritsch, P. Martinelli, H. Bielig, T. Lamkemeyer, E.I. Rugarli, T. Kaufmann, A. Sterner-Kock, F.T. Wunderlich, A. Villunger, L.M. Martins, M. Kronke, T.A. Kufer, O. Utermohlen, H. Kashkar, BID-dependent release of mitochondrial SMAC dampens XIAP-mediated immunity against Shigella. EMBO J 33, 2171–2187 (2014)
H. Kashkar, J.M. Seeger, A. Hombach, A. Deggerich, B. Yazdanpanah, O. Utermohlen, G. Heimlich, H. Abken, M. Kronke, XIAP targeting sensitizes Hodgkin lymphoma cells for cytolytic T-cell attack. Blood 108, 3434–3440 (2006)
H. Kashkar, C. Haefs, H. Shin, S.J. Hamilton-Dutoit, G.S. Salvesen, M. Kronke, J.M. Jurgensmeier, XIAP-mediated caspase inhibition in Hodgkin's lymphoma-derived B cells. J Exp Med 198, 341–347 (2003)
R. Dennhofer, P. Kurschat, P. Zigrino, A. Klose, A. Bosserhoff, G. van Muijen, T. Krieg, C. Mauch, N. Hunzelmann, Invasion of melanoma cells into dermal connective tissue in vitro: Evidence for an important role of cysteine proteases. Int J Cancer 106, 316–323 (2003)
P. Zigrino, A.S. Kamiguti, J. Eble, C. Drescher, R. Nischt, J.W. Fox, C. Mauch, The reprolysin jararhagin, a snake venom metalloproteinase, functions as a fibrillar collagen agonist involved in fibroblast cell adhesion and signaling. J Biol Chem 277, 40528–40535 (2002)
C. Mauch, J. Zamek, A.N. Abety, G. Grimberg, J.W. Fox, P. Zigrino, Accelerated wound repair in ADAM-9 knockout animals. J Invest Dermatol 130, 2120–2130 (2010)
U.B. Hofmann, J.R. Westphal, E.T. Waas, A.J. Zendman, I.M. Cornelissen, D.J. Ruiter, G.N. van Muijen, Matrix metalloproteinases in human melanoma cell lines and xenografts: Increased expression of activated matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) correlates with melanoma progression. Br J Cancer 81, 774–782 (1999)
J.M. Kozlowski, I.R. Hart, I.J. Fidler, N. Hanna, A human melanoma line heterogeneous with respect to metastatic capacity in athymic nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 72, 913–917 (1984)
R.S. Kerbel, M.S. Man, D. Dexter, A model of human cancer metastasis: Extensive spontaneous and artificial metastasis of a human pigmented melanoma and derived variant sublines in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 72, 93–108 (1984)
J.M. Seeger, K. Brinkmann, B. Yazdanpanah, D. Haubert, C. Pongratz, O. Coutelle, M. Kronke, H. Kashkar, Elevated XIAP expression alone does not confer chemoresistance. Br J Cancer 102, 1717–1723 (2010)
Y. Hegerfeldt, M. Tusch, E.B. Brocker, P. Friedl, Collective cell movement in primary melanoma explants: Plasticity of cell-cell interaction, beta1-integrin function, and migration strategies. Cancer Res 62, 2125–2130 (2002)
S. Fulda, D. Vucic, Targeting IAP proteins for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11, 109–124 (2012)
E.L. Hiscutt, D.S. Hill, S. Martin, R. Kerr, A. Harbottle, M. Birch-Machin, C.P. Redfern, S. Fulda, J.L. Armstrong, P.E. Lovat, Targeting X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein to increase the efficacy of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis for melanoma therapy. J Invest Dermatol 130, 2250–2258 (2010)
S. Mehrotra, L.R. Languino, C.M. Raskett, A.M. Mercurio, T. Dohi, D.C. Altieri, IAP regulation of metastasis. Cancer Cell 17, 53–64 (2010)
J. Kim, S. Ahn, Y.G. Ko, Y.C. Boo, S.G. Chi, C.W. Ni, Y.M. Go, H. Jo, H. Park, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein controls alpha5-integrin-mediated cell adhesion and migration. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299, H300–H309 (2010)
J. Liu, D. Zhang, W. Luo, Y. Yu, J. Yu, J. Li, X. Zhang, B. Zhang, J. Chen, X.R. Wu, G. Rosas-Acosta, C. Huang, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) mediates cancer cell motility via rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (RhoGDI)-dependent regulation of the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 286, 15630–15640 (2011)
A. Murali, J. Shin, H. Yurugi, A. Krishnan, M. Akutsu, A. Carpy, B. Macek, K. Rajalingam, Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of Cdc42 by XIAP. Cell Death Dis 8, e2900 (2017)
J. Liu, D. Zhang, W. Luo, J. Yu, J. Li, Y. Yu, X. Zhang, J. Chen, X.R. Wu, C. Huang, E3 ligase activity of XIAP RING domain is required for XIAP-mediated cancer cell migration, but not for its RhoGDI binding activity. PLoS One 7, e35682 (2012)
T.K. Oberoi, T. Dogan, J.C. Hocking, R.P. Scholz, J. Mooz, C.L. Anderson, C. Karreman, D. Meyer zu Heringdorf, G. Schmidt, M. Ruonala, K. Namikawa, G.S. Harms, A. Carpy, B. Macek, R.W. Koster, K. Rajalingam, IAPs regulate the plasticity of cell migration by directly targeting Rac1 for degradation. EMBO J 31, 14–28 (2012)
X.D. Ren, W.B. Kiosses, D.J. Sieg, C.A. Otey, D.D. Schlaepfer, M.A. Schwartz, Focal adhesion kinase suppresses rho activity to promote focal adhesion turnover. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 20), 3673–3678 (2000)
B. Xu, J. Lefringhouse, Z. Liu, D. West, L.A. Baldwin, C. Ou, L. Chen, D. Napier, L. Chaiswing, L.D. Brewer, D. St Clair, O. Thibault, J.R. van Nagell, B.P. Zhou, R. Drapkin, J.A. Huang, M.L. Lu, F.R. Ueland, X.H. Yang, Inhibition of the integrin/FAK signaling axis and c-Myc synergistically disrupts ovarian cancer malignancy. Oncogenesis 6, e295 (2017)
D.H. Kim, D. Wirtz, Focal adhesion size uniquely predicts cell migration. FASEB J 27, 1351–1361 (2013)
B.M. Chung, J.D. Rotty, P.A. Coulombe, Networking galore: Intermediate filaments and cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 25, 600–612 (2013)
R. Bhattacharya, A.M. Gonzalez, P.J. Debiase, H.E. Trejo, R.D. Goldman, F.W. Flitney, J.C. Jones, Recruitment of vimentin to the cell surface by beta3 integrin and plectin mediates adhesion strength. J Cell Sci 122, 1390–1400 (2009)
J. Ivaska, H.M. Pallari, J. Nevo, J.E. Eriksson, Novel functions of vimentin in cell adhesion, migration, and signaling. Exp Cell Res 313, 2050–2062 (2007)
C.Y. Liu, H.H. Lin, M.J. Tang, Y.K. Wang, Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal adhesion maturation. Oncotarget 6, 15966–15983 (2015)
Acknowledgments
We thank Claudia Coerper-Ochsman for excellent technical assistance. This work was founded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) (grant MA 1181/7-1 to H.K. and C.M.; and Project number 73111208 - SFB 829 (to P.Z. and C.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
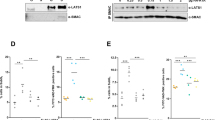
Targeting XIAP. (A) the real-time PCR analysis of XIAP transcript expression in BLM cells. S26 was used as loading control. (B, C) Western blot analysis of the cell lysates. 50 μg of protein extracted from control and sh-XIAP clones was analyzed for XIAP, c-IAP1, c-IAP 2, survivin and MITF expression. β-actin was used as loading control and Ponceau staining of the membrane shows transfer efficiency. (D) Proteins extracted from control and XIAP down-regulated melanoma cell lines clones were analyzed for expression of MITF as a measure of the differentiation status of the cells. Ponceau staining of the membrane was used as loading control and transfer efficiency (∆, crisp/cas9 knockout clones; si, transient down-regulation of XIAP using siRNA). (E) Cells were serum starved for 24 h, afterward medium ± 100 ng/ml TRAIL was added. After 24 h incubation Annexin-V (AV)-allophycocyanin (APC) and PI, stained cells were analyzed using flow cytometry. Quantification of % number of positive cells is shown in the graphs. (p = *0,01, ***0,0001) (PPTX 819 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
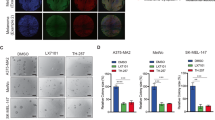
Migration of shXIAP- and scr-BLM cells Monolayers formed on uncoated and fibronectin (10 μg/ml) coated plates, after mitotic inactivation, were scratched and migration of cells into the generated open space was monitored over time (A). Alternatively, after mitotic inactivation, cells were seeded sparsely and migration of single cells monitored for 24 h (B). The graphs represent average measurements. * p < 0.05. (PPTX 298 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayachi, O., Barlin, M., Broxtermann, P.N. et al. The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) is involved in melanoma invasion by regulating cell migration and survival. Cell Oncol. 42, 319–329 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00427-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00427-1