Abstract
Purpose
Chemoradiotherapy is the standard treatment modality for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, drug and radiation resistance remain major factors influencing its clinical outcome. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether MDMX can affect the chemosensitivity and clinical outcome of NSCLC.
Methods
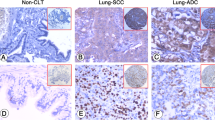
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to assess MDMX mRNA expression levels in 105 primary NSCLC tissues, its corresponding non-cancerous tissues and two NSCLC-derived cell lines (A549 and SK-MES-1). In addition, immunohistochemistry was carried out to detect MDMX protein expression in the primary NSCLC tissues. The MDMX expression levels were correlated with clinicopathological and survival features. The effects of MDMX expression knockdown on NSCLC cell proliferation and chemosensitivity were evaluated using MTT, flow cytometry and soft agar colony assays.
Results
We found that the mRNA expression level of MDMX in NSCLC tissues was significantly higher than that in its corresponding non-tumorous tissues. High MDMX expression was found to be related to poor tumor cell differentiation, advanced TNM stages and the occurrence of lymph node metastases. Patients with a high MDMX expression level exhibited a lower overall survival rate than those with a low expression level. Multivariate analysis showed that a high MDMX protein expression level may serve as an independent prognostic factor for NSCLC patients. In addition, we found that MDMX expression knockdown combined with cisplatin treatment in vitro significantly increased apoptosis and decreased soft agar colony formation in NSCLC-derived cells.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that MDMX expression may serve as an independent unfavorable prognostic factor for NSCLC patient outcome, which in turn may at least partly be due to the ability of the MDMX protein to regulate the proliferative capacity and chemosensitivity of NSCLC cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.E. DeSantis, C.C. Lin, A.B. Mariotto, R.L. Siegel, K.D. Stein, J.L. Kramer, R. Alteri, A.S. Robbins, A. Jemal, Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 64, 252–271 (2014)
M. Reck, D.F. Heigener, T. Mok, J.C. Soria, K.F. Rabe, Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent developments. Lancet 382, 709–719 (2013)
L.E. Coate, T. John, M.S. Tsao, F.A. Shepherd, Molecular predictive and prognostic markers in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol 10, 1001–1010 (2009)
Y.X. Bao, X.D. Zhao, H.B. Deng, C.L. Lu, Y. Guo, X. Lu, L.L. Deng, Schedule-dependent cytotoxicity of sunitinib and TRAIL in human non-small cell lung cancer cells with or without EGFR and KRAS mutations. Cell Oncol 39, 343–352 (2016)
C.C. Koning, S.J. Wouterse, J.G. Daams, L.L. Uitterhoeve, M.M. van den Heuvel, J.S. Belderbos, Toxicity of concurrent radiochemotherapy for locally advanced non--small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review of the literature. Clin Lung Cancer 14, 481–487 (2013)
P. Chen, J. Li, Y.C. Chen, H. Qian, Y.J. Chen, J.Y. Su, M. Wu, T. Lan, The functional status of DNA repair pathways determines the sensitization effect to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Oncol 39, 511–522 (2016)
Y.L. Chen, T.Y. Yang, K.C. Chen, C.L. Wu, S.L. Hsu, C.M. Hsueh, Hypoxia can impair doxorubicin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting MRP1 and P-gp expression and boosting the chemosensitizing effects of MRP1 and P-gp blockers. Cell Oncol 39, 411–433 (2016)
R. Shavit, M. Ilouze, T. Feinberg, Y.R. Lawrence, Y. Tzur, N. Peled, Mitochondrial induction as a potential radio-sensitizer in lung cancer cells - a short report. Cell Oncol 39, 247–252 (2015)
A. Shvarts, W.T. Steegenga, N. Riteco, T. van Laar, P. Dekker, M. Bazuine, R.C. van Ham, W. van der Houven van Oordt, G. Hateboer, A.J. van der Eb, A.G. Jochemsen, MDMX: A novel p53-binding protein with some functional properties of MDM2. EMBO J 15, 5349–5357 (1996)
R. Stad, Y.F. Ramos, N. Little, S. Grivell, J. Attema, A.J. van Der Eb, A.G. Jochemsen, Hdmx stabilizes Mdm2 and p53. J Biol Chem 275, 28039–28044 (2000)
J.C. Marine, A.G. Jochemsen, Mdmx and Mdm2: Brothers in arms. Cell Cycle 3, 900–904 (2004)
D. Danovi, E. Meulmeester, D. Pasini, D. Migliorini, M. Capra, R. Frenk, P. de Graaf, S. Francoz, P. Gasparini, A. Gobbi, K. Helin, P.G. Pelicci, A.G. Jochemsen, J.C. Marine, Amplification of Mdmx (or Mdm4) directly contributes to tumor formation by inhibiting p53 tumor suppressor activity. Mol Cell Biol 24, 5835–5843 (2004)
H. Wang, C. Yan, A small-molecule p53 activator induces apoptosis through inhibiting MDMX expression in breast cancer cells. Neoplasia 13, 611–619 (2011)
M.J. Riemenschneider, C.B. Knobbe, G. Reifenberger, Refined mapping of 1q32 amplicons in malignant gliomas confirms MDM4 as the main amplification target. Int J Cancer 104, 752–757 (2003)
X. Han, G. Garcia-Manero, T.J. McDonnell, G. Lozano, L.J. Medeiros, L. Xiao, G. Rosner, M. Nguyen, M. Fernandez, Y.A. Valentin-Vega, J. Barboza, D.M. Jones, G.Z. Rassidakis, H.M. Kantarjian, C.E. Bueso-Ramos, HDM4 (HDMX) is widely expressed in adult pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia and is a potential therapeutic target. Mod Pathol 20, 54–62 (2007)
Y.A. Valentin-Vega, J.A. Barboza, G.P. Chau, A.K. El-Naggar, G. Lozano, High levels of the p53 inhibitor MDM4 in head and neck squamous carcinomas. Hum Pathol 38, 1553–1562 (2007)
T. Sun, G.S. Lee, W.K. Oh, M. Pomerantz, M. Yang, W. Xie, M.L. Freedman, P.W. Kantoff, Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in p53 pathway and aggressiveness of prostate cancer in a Caucasian population. Clin Cancer Res 16, 5244–5251 (2010)
R. Tirabosco, G. De Maglio, M. Skrap, G. Falconieri, S. Pizzolitto, Expression of the Polycomb-group protein BMI1 and correlation with p16 in astrocytomas an immunohistochemical study on 80 cases. Pathol Res Pract 204, 625–631 (2008)
D. Li, D.Q. Li, D. Liu, X.J. Tang, MiR-613 induces cell cycle arrest by targeting CDK4 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Oncol 39, 139–147 (2016)
F. Toledo, G.M. Wahl, MDM2 and MDM4: p53 regulators as targets in anticancer therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39, 1476–1482 (2007)
Q. Li, G. Lozano, Molecular pathways: Targeting Mdm2 and Mdm4 in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 19, 34–41 (2013)
J. Parant, A. Chavez-Reyes, N.A. Little, W. Yan, V. Reinke, A.G. Jochemsen, G. Lozano, Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm4-null mice by loss of Trp53 suggests a nonoverlapping pathway withMDM2 to regulate p53. Nat Genet 29, 92–95 (2001)
G. Jin, S. Cook, B. Cui, W.C. Chen, S.T. Keir, P. Killela, C. Di, C.A. Payne, S.G. Gregory, R. McLendon, D.D. Bigner, H. Yan, HDMX regulates p53 activity and confers chemoresistance to 3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea. Neuro-Oncology 12, 956–966 (2010)
S. Haupt, D. Buckley, J.M. Pang, J. Panimaya, P.J. Paul, C. Gamell, E.A. Takano, Y.Y. Lee, S. Hiddingh, T.M. Rogers, A.F. Teunisse, M.J. Herold, J.C. Marine, S.B. Fox, A. Jochemsen, Y. Haupt, Targeting Mdmx to treat breast cancers with wild-type p53. Cell Death Dis 6, e1821 (2015)
K. Heminger, M. Markey, M. Mpagi, S.J. Berberich, Alterations in gene expression and sensitivity to genotoxic stress following HdmX or Hdm2 knockdown in human tumor cells harboring wild-type p53. Aging 1, 89–108 (2009)
Q. Yu, Y. Li, K. Mu, Z. Li, Q. Meng, X. Wu, Y. Wang, L. Li, Amplification of Mdmx and overexpression of MDM2 contribute to mammary carcinogenesis by substituting for p53 mutations. Diagn Pathol 9, 71 (2014)
L. Marcar, B. Ihrig, J. Hourihan, S.E. Bray, P.R. Quinlan, L.B. Jordan, A.M. Thompson, T.R. Hupp, D.W. Meek, MAGE-A cancer/testis antigens inhibit MDM2 ubiquitylation function and promote increased levels of MDM4. PLoS One 10, e0127713 (2015)
A.M. Carrillo, A. Bouska, M.P. Arrate, C.M. Eischen, Mdmx promotes genomic instability independent of p53 and Mdm2. Oncogene 34, 846–856 (2015)
M.P. Markey, Regulation of MDM4. Front Biosci 16, 1144–1156 (2011)
M. Shadfan, V. Lopez-Pajares, Z.M. Yuan, MDM2 and MDMX: Alone and together in regulation of p53. Transl Cancer Res 1, 88–89 (2012)
V. Sulzyc-Bielicka, P. Domagala, D. Bielicki, K. Safranow, W. Domagala, Thymidylate synthase expression and p21(WAF1)/p53 phenotype of colon cancers identify patients who may benefit from 5-fluorouracil based therapy. Cell Oncol 37, 17–28 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 81201803).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Xie, YZ., Xing, R. et al. MDMX is a prognostic factor for non-small cell lung cancer and regulates its sensitivity to cisplatin. Cell Oncol. 40, 357–365 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0325-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0325-9