Abstract
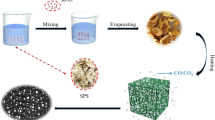
With the rise of wireless communication technology, while bringing convenience to people’s lives, the problem of electromagnetic pollution has become increasingly serious; therefore, there is an urgent need to find a new type of absorbing material with strong absorption performance, wide absorption band, thin thickness, and light weight to improve people’s living environment. Biomass-derived porous carbon has attracted much attention as a dielectric loss absorbing material; through the simple technological process, the composite magnetic metal can achieve excellent impedance matching and high efficient broadband wave absorption performance. In this experiment, Eupatorium adenophora was used as the raw material, and the metal composite porous carbon material was obtained by compounding Fe metals through the impregnation process and pyrolysis. When the impregnation ratio is 9%, the simulated thickness is 3.5 mm, and the frequency is 3.55 GHz; the best reflection loss that can be achieved is − 41.272 dB. The optimal absorption frequency band is 2.64 GHz, and the strongest absorption frequency band can cover 66% of the S band. Meanwhile, the syngas with hydrogen content of 41.77% can also be obtained through Fe metal doping in the pyrolysis process, which has high utilization value and effectively enhances the high-value utilization of waste biomass.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang W, Jiang B, Che S et al (2021) Research progress on carbon-based materials for electromagnetic wave absorption and the related mechanisms. New Carbon Mater 36(6):1016–1030
Jiang B, Qi C, Yang H et al (2023) Recent advances of carbon-based electromagnetic wave absorption materials facing the actual situations. Carbon 208:390–409
Dai B, Ma Y, Dong F et al (2022) Overview of MXene and conducting polymer matrix composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Compos Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(2):704–754
Lou Z, Wang Q, Kara UI et al (2022) Biomass-derived carbon heterostructures enable environmentally adaptive wideband electromagnetic wave absorbers. Nano-Micro Lett 14:1–16
Liu P, Gao S, Wang Y et al (2020) Metal-organic polymer coordination materials derived Co/N-doped porous carbon composites for frequency-selective microwave absorption. Compos B Eng 202:108406
Wang G, Peng X, Yu L et al (2015) Enhanced microwave absorption of ZnO coated with Ni nanoparticles produced by atomic layer deposition. J Mater Chem A 3(6):2734–2740
Lou Z, Han H, Zhou M et al (2018) Synthesis of magnetic wood with excellent and tunable electromagnetic wave-absorbing properties by a facile vacuum/pressure impregnation method. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 6(1):1000–1008
Meng F, Wang H, Huang F et al (2018) Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: a review and prospective. Compos B Eng 137:260–277
Peymanfar R, Javanshir S, Naimi-Jamal MR et al (2021) Morphology and medium influence on microwave characteristics of nanostructures: a review. J Mater Sci 56(31):17457–17477
El-Shafie M, Kambara S, Hayakawa Y (2019) Hydrogen production technologies overview. J Power Energy Eng 7:107–154
Wang H, Shi P, Rui M et al (2020) The green synthesis rGO/Fe3O4/PANI nanocomposites for enhanced electromagnetic waves absorption. Prog Org Coat 139:105476
Wu G, He Y, Zhan H et al (2020) A novel Fe3O4/carbon nanotube composite film with a cratered surface structure for effective microwave absorption. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31:11508–11519
Wang G, Dai Y, Yang H et al (2020) A review of recent advances in biomass pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 34(12):15557–15578
Du Y, Liu W, Qiang R et al (2014) Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core–shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(15):12997–13006
Fan G, Song X, Zhang X, Wang Q, Tang Y, Liu Y (2023) Biomass-derived ferrous magnetic carbon-based nanocomposites from loofah collaterals for excellent electromagnetic wave-absorbing materials. J Alloy Compd 969:172384
Wang S, Li Q, Hu K et al (2021) A facile synthesis of bare biomass derived holey carbon absorbent for microwave absorption. Appl Surf Sci 544:148891
Fang X, Li W, Chen X et al (2022) Controlling the microstructure of biomass-derived porous carbon to assemble structural absorber for broadening bandwidth. Carbon 198:70–79
Wang Y, Gao X, Zhou H et al (2019) Fabrication of biomass-derived carbon decorated with NiFe2O4 particles for broadband and strong microwave absorption. Powder Technol 345:370–378
Zhao H, Cheng Y, Ma J et al (2018) A sustainable route from biomass cotton to construct lightweight and high-performance microwave absorber. Chem Eng J 339:432–441
Qiu X, Wang L, Zhu H et al (2017) Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nano-porous carbon. Nanoscale 9(22):7408–7418
Zhao H, Cheng Y, Lv H, Ji G, Youwei Du (2019) A novel hierarchically porous magnetic carbon derived from biomass for strong lightweight microwave absorption. Carbon 142:245–253
Wu Z, Tian K, Huang T et al (2018) Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(13):11108–11115
Singh SK, Prakash H, Akhtar MJ et al (2018) Lightweight and high-performance microwave absorbing heteroatom-doped carbon derived from chicken feather fibers. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 6(4):5381–5393
Luo C, Jiao T, Tang Y et al (2018) Excellent electromagnetic wave absorption of iron-containing SiBCN ceramics at 1158 K high-temperature. Adv Eng Mater 20(6):1701168
Fang J, Li P, Liu Y et al (2021) Cobalt magnetic particles and carbon composite microtubes as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Mater Chem C 9(7):2474–2482
Wang S, Zhang X, Tang Y et al (2024) Facile fabrication of biomass chitosan-derived magnetic carbon aerogels as multifunctional and high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Carbon 216:118528
Rong Q, Shuaibo F, Wanying Li, Linzhi Y, Qian Ma, Bowen C, Yi C (2022) Preparation of biomass-derived magnetic carbon-based composite materials and their wave absorption properties. Acta Textile Sinica 43(01):21–27
Wang S, Zhang X, Hao S et al (2024) Nitrogen-doped magnetic-dielectric-carbon aerogel for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 16:16
Yunlong X, Xinzhou S, Zongyu W, Ming W (1988) A preliminary report on the chemical constituents of Eupatorium adenophorum. Stud Plants Yunnan 10(2):238–240
Wang L, Guan H, Shunlin Su, Jianqiao Hu, Wang Y (2022) Magnetic FeOX/biomass carbon composites with broadband microwave absorption properties. J Alloy Compd 903:163894
Wang B, Wu Q, Fu Y et al (2021) A review on carbon/magnetic metal composites for microwave absorption. Mater Sci Technol 86:91–109
Lin J, Qiao J, Tian H et al (2023) Ultralight, hierarchical metal–organic framework derivative/graphene hybrid aerogel for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6:177
Pan F, Shi Y, Yang Y, Guo H, Li L, Jiang H, Wang X, Zeng Z, Lu W (2024) Porifera-inspired lightweight, thin, wrinkle-resistance, and multifunctional MXene foam. Adv Mater 2:2311135
Lian Y, Han B, Liu D et al (2020) Solvent-free synthesis of ultrafine tungsten carbide nanoparticles-decorated carbon nanosheets for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 12:153
Kim SS, Kim ST, Yoon YC et al (2005) Magnetic, dielectric, and microwave absorbing properties of iron particles dispersed in rubber matrix in gigahertz frequencies. J Appl Phys 97(10):10F905
Qin M, Zhang L, Wu H (2022) Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv Sci 9(10):2105553
Huang Q, Wang G, Zhou M, Zheng J, Tang S, Ji G (2022) Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers and devices: design and 3D microarchitecture. J Mater Sci Technol 108:90–101
Zheng W, Ye W, Yang P et al (2022) Recent progress in iron-based microwave absorbing composites: a review and prospective. Molecules 27(13):4117
Lan D, Gao Z, Zhao Z et al (2021) Application progress of conductive conjugated polymers in electromagnetic wave absorbing composites. Compos Commun 26:100767
Mohamed MA, Salleh WNW, Jaafar J et al (2017) Physicochemical characterization of cellulose nanocrystal and nanoporous self-assembled CNC membrane derived from Ceiba pentandra. Carbohydr Polym 157:1892–1902
Yang J, Ye M, Han A et al (2019) Preparation and electromagnetic attenuation properties of MoS 2–PANI composites: a promising broadband absorbing material. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:292–301
Bauer I, Knölker HJ (2015) Iron catalysis in organic synthesis. Chem Rev 115(9):3170–3387
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21966019), Yunnan Xingdian Talent Support Project—Industrial Innovation Talents (2019-1096), and Yunnan Xingdian Talent Support Project—Young Talents (2018-73) the Analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weichen Shuai: writing—original draft, investigation, data curation, and writing—review and editing. Chen Liang: conceptualization and validation. Chunyu Li: validation. Hongying Xia: supervision, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing. Libo Zhang: supervision and resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Human and animal rights
This article does not include any studies of human participants performed by the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shuai, W., Xia, H., Liang, C. et al. A magnetic metal composite biomass carbon material with high efficiency and broadband wave absorbing property. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-024-05535-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-024-05535-z