Abstract
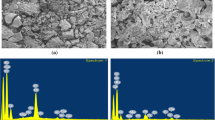
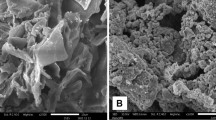
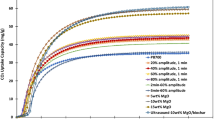
The unrestricted discharge of chlorpyrifos (CPS) pesticides into the aquatic environment entails significant environmental and health risks; therefore, their management is essential. In the current study, a dually modified novel biochar of Trapa bispinosa peel (UFBC) with improved adsorption capacity for CPS was synthesized utilizing ultrasonic vibrations and alkali functionalization, and its removal capacity was compared to unmodified or single modified biochar. Characteristic changes induced by the simultaneous mechanical and chemical modifications of biochar were revealed by energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra. Three hundred and twenty data sets produced from triplicate batch experiments on several parameters (temperature, pH, adsorbent dose, initial pollutant concentration, and contact time) and linear interpolation technique were applied for the development of artificial neuron network (ANN) as well as adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) models, which successfully predicted % CPS removal by UFBC with low statistical errors (MSE < 0.0009, SSE < 0.159, RMSE < 0.031). The equilibrium data were well fitted to the Elovich model of kinetics (R2 > 0.94) and Freundlich isotherm (R2 > 0.98) for all the sorbents, which showed chemisorption on highly heterogeneous surface and multi-layer adsorption with pollutant–pollutant interaction, respectively. Thermodynamic study demonstrated the exothermic nature and feasibility of the process at room temperature (∆H < -71.32 kJmol−1). The synthesized material is a sustainable and effective adsorbent having low equilibrium time and high adsorption capacity for CPS elimination and industrial scalability.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Centner TJ (2018) Cancelling pesticide registrations and revoking tolerances: The case of chlorpyrifos. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 57:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ETAP.2017.11.009
Hassaan MA, el Nemr A (2020) Pesticides pollution: Classifications, human health impact, extraction and treatment techniques. Egypt J Aquat Res 46:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJAR.2020.08.007
Das A, Jaswal V, Yogalakshmi KN (2020) Degradation of chlorpyrifos in soil using laccase immobilized iron oxide nanoparticles and their competent role in deterring the mobility of chlorpyrifos. Chemosphere 246:125676. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2019.125676
Liu Y, Nie Y, Lu X, Zhang X, He H, Pan F, Zhou L, Liu X, Ji X, Zhang S (2019) Cascade utilization of lignocellulosic biomass to high-value products. Green Chem 21:3499–3535. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC00473D
Dalsager L, Fage-Larsen B, Bilenberg N, Jensen TK, Nielsen F, Kyhl HB, Grandjean P, Andersen HR (2019) Maternal urinary concentrations of pyrethroid and chlorpyrifos metabolites and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms in 2–4-year-old children from the Odense Child Cohort. Environ Res 176:108533. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2019.108533
Zahran M, Khalifa Z, Zahran M A-H, Abdel Azzem M (2021) Abiotic sensor for electrochemical determination of chlorpyrifos in natural water based on the inhibition of silver nanoparticles oxidation. Microchem J 165:106173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROC.2021.106173
González T, Dominguez JR, Correia S (2020) Neonicotinoids removal by associated binary, tertiary and quaternary advanced oxidation processes: Synergistic effects, kinetics and mineralization. J Environ Manage 261:110156. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2020.110156
Bisaria K, Sinha S, Singh R, Iqbal HMN (2021) Recent advances in structural modifications of photo-catalysts for organic pollutants degradation – A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 284:131263. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.131263
Singh R, Bisaria K, Chugh P, Batra L, Sinha S (2021) Agricultural Waste: A Potential Solution to Combat Heavy Metal Toxicity. 101–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77795-1_4
Moradeeya PG, Kumar MA, Thorat RB, Rathod M, Khambhaty Y, Basha S (2017) Nanocellulose for biosorption of chlorpyrifos from water: chemometric optimization, kinetics and equilibrium. Cellulose 24(3 24):1319–1332. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-017-1197-X
Sizmur T, Fresno T, Akgül G, Frost H, Moreno-Jiménez E (2017) Biochar modification to enhance sorption of inorganics from water. Biores Technol 246:34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2017.07.082
Akdeniz N (2019) A systematic review of biochar use in animal waste composting. Waste Manage 88:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2019.03.054
Qiu B, Duan F (2019) Synthesis of industrial solid wastes/biochar composites and their use for adsorption of phosphate: From surface properties to sorption mechanism. Colloids Surf, A 571:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2019.03.041
Suo F, Liu X, Li C, Yuan M, Zhang B, Wang J, Ma Y, Lai Z, Ji M (2019) Mesoporous activated carbon from starch for superior rapid pesticides removal. Int J Biol Macromol 121:806–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2018.10.132
Othmani A, John J, Rajendran H, Mansouri A, Sillanpää M, Velayudhaperumal Chellam P (2021) Biochar and activated carbon derivatives of lignocellulosic fibers towards adsorptive removal of pollutants from aqueous systems: Critical study and future insight. Sep Purif Technol 274:119062. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2021.119062
Azad FN, Ghaedi M, Dashtian K, Hajati S, Pezeshkpour V (2016) Ultrasonically assisted hydrothermal synthesis of activated carbon-HKUST-1-MOF hybrid for efficient simultaneous ultrasound-assisted removal of ternary organic dyes and antibacterial investigation: Taguchi optimization. Ultrason Sonochem 31:383–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.01.024
Cazetta AL, Vargas AMM, Nogami EM, Kunita MH, Guilherme MR, Martins AC, Silva TL, Moraes JCG, Almeida VC (2011) NaOH-activated carbon of high surface area produced from coconut shell: Kinetics and equilibrium studies from the methylene blue adsorption. Chem Eng J 174:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2011.08.058
Wang T, Li G, Yang K, Zhang X, Wang K, Cai J, Zheng J (2021) Enhanced ammonium removal on biochar from a new forestry waste by ultrasonic activation: Characteristics, mechanisms and evaluation. Sci Total Environ 778:146295. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.146295
Bisaria K, Sinha S, Iqbal HMN, Singh R (2022) Ultrasonication expedited As(III) adsorption onto chitosan impregnated Ni–Fe layered double hydroxide biosorbent: Optimization studies and artificial intelligence modelling. Environ Res 212:113184. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2022.113184
Othmani A, Kesraoui A, Seffen M (2020) Removal of phenol from aqueous solution by coupling alternating current with biosorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(34 28):46488–46503. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-020-09976-7
Kumar N, Sinha S, Mehrotra T, Singh R, Tandon S, Thakur IS (2019) Biodecolorization of azo dye Acid Black 24 by Bacillus pseudomycoides: Process optimization using Box Behnken design model and toxicity assessment. Bioresour Technol Rep 8:100311. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BITEB.2019.100311
Othmani A, Kesraoui A, Seffen M (2017) The alternating and direct current effect on the elimination of cationic and anionic dye from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation and coagulation flocculation. Eur Mediterr J Environ Integr 2(1 2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/S41207-017-0016-Y
Saad M, Tahir H, Khan J, Hameed U, Saud A (2017) Synthesis of polyaniline nanoparticles and their application for the removal of Crystal Violet dye by ultrasonicated adsorption process based on Response Surface Methodology. Ultrason Sonochem 34:600–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2016.06.022
Onu CE, Nwabanne JT, Ohale PE, Asadu CO (2021) Comparative analysis of RSM, ANN and ANFIS and the mechanistic modeling in eriochrome black-T dye adsorption using modified clay. S Afr J Chem Eng 36:24–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SAJCE.2020.12.003
Peng X, Ye LL, Wang CH, Zhou H, Sun B (2011) Temperature- and duration-dependent rice straw-derived biochar: Characteristics and its effects on soil properties of an Ultisol in southern China. Soil Tillage Res 112:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.STILL.2011.01.002
Liu J, Yang X, Liu H, Cheng W, Bao Y (2020) Modification of calcium-rich biochar by loading Si/Mn binary oxide after NaOH activation and its adsorption mechanisms for removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A 601:124960. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2020.124960
Wang L, Bolan NS, Tsang DCW, Hou D (2020) Green immobilization of toxic metals using alkaline enhanced rice husk biochar: Effects of pyrolysis temperature and KOH concentration. Sci Total Environ 720:137584. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.137584
An Q, Miao Y, Zhao B, Li Z, Zhu S (2020) An alkali modified biochar for enhancing Mn2+ adsorption: Performance and chemical mechanism. Mater Chem Phys 248:122895. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2020.122895
Sajjadi B, Broome JW, Chen WY, Mattern DL, Egiebor NO, Hammer N, Smith CL (2019) Urea functionalization of ultrasound-treated biochar: A feasible strategy for enhancing heavy metal adsorption capacity. Ultrason Sonochem 51:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2018.09.015
YL Verma MP Singh RK Singh 2012 Effect of ultrasonic irradiation on preparation and properties of ionogels J Nanomater 2012 https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/570719
Son EB, Poo KM, Chang JS, Chae KJ (2018) Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions using engineered magnetic biochars derived from waste marine macro-algal biomass. Sci Total Environ 615:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2017.09.171
Uchimiya M, Orlov A, Ramakrishnan G, Sistani K (2013) In situ and ex situ spectroscopic monitoring of biochar’s surface functional groups. J Anal Appl Pyrol 102:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAAP.2013.03.014
Wang J, Wang S (2019) Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J Clean Prod 227:1002–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.04.282
Pezoti O, Cazetta AL, Bedin KC, Souza LS, Martins AC, Silva TL, Santos Júnior OO, Visentainer JV, Almeida VC (2016) NaOH-activated carbon of high surface area produced from guava seeds as a high-efficiency adsorbent for amoxicillin removal: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 288:778–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.12.042
Zhang P, Zheng S, Liu J, Wang B, Liu F, Feng Y (2018) Surface properties of activated sludge-derived biochar determine the facilitating effects on Geobacter co-cultures. Water Res 142:441–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2018.05.058
Lian F, Cui G, Liu Z, Duo L, Zhang G, Xing B (2016) One-step synthesis of a novel N-doped microporous biochar derived from crop straws with high dye adsorption capacity. J Environ Manage 176:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2016.03.043
Chatterjee R, Sajjadi B, Chen WY, Mattern DL, Hammer N, Raman V, Dorris A (2020) Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on PhysicoChemical Properties and Acoustic-Based Amination of Biochar for Efficient CO2 Adsorption. Frontiers Energy Res 8:85. https://doi.org/10.3389/FENRG.2020.00085/BIBTEX
Ezekiel I, Kasim SR, Ismail YMB, Noor AFM (2018) Nanoemulsion synthesis of carbonated hydroxyapatite nanopowders: Effect of variant CO32−/PO43− molar ratios on phase, morphology, and bioactivity. Ceram Int 44:13082–13089. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2018.04.128
Tulun Ş, Akgül G, Alver A, Çelebi H (2021) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system modelling for chlorpyrifos removal with walnut shell biochar. Arab J Chem 14:103443. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARABJC.2021.103443
John EM, Shaike JM (2015) Chlorpyrifos: pollution and remediation. Environ Chem Lett 13(3 13):269–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-015-0513-7
Mahdavi V, Taghadosi F, Dashtestani F, Bahadorikhalili S, Farimani MM, Ma’mani L, MousaviKhaneghah A (2021) Aminoguanidine modified magnetic graphene oxide as a robust nanoadsorbent for efficient removal and extraction of chlorpyrifos residue from water. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106117. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2021.106117
Hamadeen HM, Elkhatib EA, Badawy MEI, Abdelgaleil SAM (2021) Green low cost nanomaterial produced from Moringa oleifera seed waste for enhanced removal of chlorpyrifos from wastewater: Mechanism and sorption studies. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105376. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2021.105376
Boukhelkhal A, Benkortbi O, Hamadache M, Ghalem N, Hanini S, Amrane A (2016) Adsorptive removal of amoxicillin from wastewater using wheat grains: equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic studies and mass transfer. Desalin Water Treat 57:27035–27047. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1166991
Ali I, Alharbi OML, ALOthman ZA, Al-Mohaimeed AM, Alwarthan A (2019) Modeling of fenuron pesticide adsorption on CNTs for mechanistic insight and removal in water. Environ Res 170:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2018.12.066
Bisaria K, Wadhwa S, Mathur A, Roy S, Dixit A, Singh R (2022) New bismuth oxyiodide/chitosan nanocomposite for ultrasonic waves expedited adsorptive removal of amoxicillin from aqueous medium: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic investigations. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-021-17546-8
Gulati A, Mandeep MJ, Kakkar R (2020) Mesoporous rGO@ZnO composite: Facile synthesis and excellent water treatment performance by pesticide adsorption and catalytic oxidative dye degradation. Chem Eng Res Des 160:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHERD.2020.04.040
Milagres JL, Bellato CR, Ferreira SO, de Moura GL (2020) Preparation and evaluation of hydrocalumite-iron oxide magnetic intercalated with dodecyl sulfate for removal of agrichemicals. J Environ Manage 255:109845. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2019.109845
Zambrano-Intriago LA, Gorozabel-Mendoza ML, Córdova Mosquera A, Delgado-Demera MH, Duarte MMMB, Rodríguez-Díaz JM (2020) Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics of the blue 19 dye adsorption process using residual biomass attained from rice cultivation. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 2020:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13399-020-00944-2
Reghioua A, Barkat D, Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Rangabhashiyam S, Khan MR, ALOthman ZA, (2021) Magnetic Chitosan-Glutaraldehyde/Zinc Oxide/Fe3O4 Nanocomposite: Optimization and Adsorptive Mechanism of Remazol Brilliant Blue R Dye Removal. J Polym Environ 2021:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10924-021-02160-Z
Bisht D, Sinha S, Nigam S, Bisaria K, Mehrotra T, Singh R (2021) Adsorptive decontamination of paper mill effluent by nano fly ash: response surface methodology, adsorption isotherm and reusability studies. Water Sci Technol 83:1662–1676. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2021.066
Deniz F (2022) Integration of biosorption operation with biorefinery and biofuel production processes in context of bioeconomy and zero-waste approaches: a pre-feasibility study on Nigella sativa L. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 2022:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13399-021-02022-7
Sharma L, Kakkar R (2017) Hierarchical Porous Magnesium Oxide (Hr-MgO) Microspheres for Adsorption of an Organophosphate Pesticide: Kinetics, Isotherm, Thermodynamics, and DFT Studies. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:38629–38642. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.7B14370/SUPPL_FILE/AM7B14370_SI_001.PDF
ul Haq A, Saeed M, Usman M, Naqvi SAR, Bokhari TH, Maqbool T, Ghaus H, Tahir T, Khalid H (2020) Sorption of chlorpyrifos onto zinc oxide nanoparticles impregnated Pea peels (Pisum sativum L): Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Environ Technol Innov 17:100516. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ETI.2019.100516
Rodriguez-Cruz S, Andrades MS, Sanchez-Camazano M, Sanchez-Martin MJ (2007) Relationship between the adsorption capacity of pesticides by wood residues and the properties of woods and pesticides. Environ Sci Technol 41:3613–3619. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES062616F/SUPPL_FILE/ES062616FSI20070416_113027.PDF
Karri RR, Sahu JN (2018) Modeling and optimization by particle swarm embedded neural network for adsorption of zinc (II) by palm kernel shell based activated carbon from aqueous environment. J Environ Manage 206:178–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2017.10.026
Al-Musawi TJ, Arghavan SMA, Allahyari E, Arghavan FS, Othmani A, Nasseh N (2022) Adsorption of malachite green dye onto almond peel waste: a study focusing on application of the ANN approach for optimization of the effect of environmental parameters. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 2021:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13399-021-02174-6
Kaveh M, Rasooli Sharabiani V, Amiri Chayjan R, Taghinezhad E, Abbaspour-Gilandeh Y, Golpour I (2018) ANFIS and ANNs model for prediction of moisture diffusivity and specific energy consumption potato, garlic and cantaloupe drying under convective hot air dryer. Inf Process Agric 5:372–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INPA.2018.05.003
GamzeTuran N, Başak M, Ozgonenel O (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling Zn(II) adsorption from leachate using a new biosorbent. Chem Eng J 173:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.042
Ghosal PS, Kattil KV, Yadav MK, Gupta AK (2018) Adsorptive removal of arsenic by novel iron/olivine composite: Insights into preparation and adsorption process by response surface methodology and artificial neural network. J Environ Manag 209:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2017.12.040
Mehrabpour M, Esfandyari M, Alidadi H, Davoudi M, Dolatabadi M, Professor A (2018) Accepted Manuscript Modeling of simultaneous adsorption of dye and metal ion by sawdust from aqueous solution using of ANN and ANFIS Modeling of Simultaneous adsorption of dye and metal ion by sawdust from aqueous solution using of ANN and ANFIS. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2018.07.012
Franco DSP, Duarte FA, Salau NPG, Dotto GL (2019) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANIFS) and artificial neural network (ANN) applied for indium (III) adsorption on carbonaceous materials. 206:1463–1473. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2019.1566129
Wong YJ, Arumugasamy SK, Chung CH, Selvarajoo A, Sethu V (2020) Comparative study of artificial neural network (ANN) adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and multiple linear regression (MLR) for modeling of Cu (II) adsorption from aqueous solution using biochar derived from rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum) peel. Environ Monitor Assess 192(7 192):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-020-08268-4
Souza PR, Dotto GL, Salau NPG (2018) Artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system (ANFIS) modelling for nickel adsorption onto agro-wastes and commercial activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 6:7152–7160. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2018.11.013
Yu Y, Qiao N, Wang D, Zhu Q, Fu F, Cao R, Wang R, Liu W, Xu B (2019) Fluffy honeycomb-like activated carbon from popcorn with high surface area and well-developed porosity for ultra-high efficiency adsorption of organic dyes. Biores Technol 285:121340. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2019.121340
Wang P, Yin Y, Guo Y, Wang C (2015) Removal of chlorpyrifos from waste water by wheat straw-derived biochar synthesized through oxygen-limited method. RSC Adv 5:72572–72578. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA10487D
Yan T, Zhang H, Huang D, Feng S, Fujita M, Gao XD (2017) Chitosan-Functionalized Graphene Oxide as a Potential Immunoadjuvant. Nanomaterials 7:59. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO7030059
Yang J, Ma C, Tao J, Li J, Du K, Wei Z, Chen C, Wang Z, Zhao C, Ma MG (2020) Optimization of polyvinylamine-modified nanocellulose for chlorpyrifos adsorption by central composite design. Carbohyd Polym 245:116542. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2020.116542
Celso Gonçalves A, Zimmermann J, Schwantes D, Tarley CRT, Conradi Junior E, Dias H, de Oliveira V, Campagnolo MA, Ziemer GL (2021) Renewable Eco-Friendly Activated Biochar from Tobacco: Kinetic. Equilibrium Thermodyn Stud Chlorpyrifos Removal 57:159–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2021.1890776
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Amity Institute of Biotechnology, Amity University Uttar Pradesh, India, for providing the laboratory facilities. We are also thankful to Dr Saif Khan, Inter-University Accelerator Centre for SEM analysis, Mr Charu Chandra Pant, UPES Central Instrumentation facility for DLS and FTIR.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the support of Ministry of Commerce and Industries, India. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kavya Bisaria did conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft. Merry Gupta was involved in visualization and resources. Ashish Mathur provided resources. Ashwani Dixit done project administration and writing—review and editing. Rachana Singh contributed to supervision, writing—review and editing, project administration, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bisaria, K., Singh, R., Gupta, M. et al. Novel acoustic-activated alkali-functionalized Trapa bispinosa peel biochar for green immobilization of chlorpyrifos from wastewater: artificial intelligence modelling and experimental validation. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 14, 7763–7782 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02898-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02898-z