Abstract
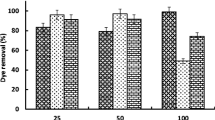
The biosorption of five anionic dyes, namely, Brilliant Blue R, Remazol Brilliant Blue R, Reactive Orange 14, Reactive Red 120, and Reactive Black 5 onto dried Aspergillus tubingensis, a newly isolated filamentous fungus, was examined. The most important parameters for the biosorption process, such as dye type, pH (2–10), time (0–240 min), and initial dye concentrations (40–390 mg/l), were optimized. The highest equilibrium uptake was determined as 143.0 mg/g at 390 mg/l Brilliant Blue R concentration at pH 2. The adsorption equilibrium data fit the Langmuir model best in the Brilliant Blue R dye concentration range studied. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model has high efficiency and performance for the interpretation of real data. The application of A. tubingensis biosorbent for the removal of Brilliant Blue R dye from wastewaters can be suitable for the fabrication and designing of wastewater treatment plants by using these equilibrium and kinetic parameters. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report about the usage of A. tubingensis biomass for low cost synthetic dye removal process.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
da Rosa ALD, Carissimi E, Dotto GL, Sander H, Feris LA (2018) Biosorption of Rhodamine B dye from dyeing stones effluents using the green microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J Clean Prod 198:1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.128
Tahir N, Bhatti HN, Iqbal M, Noreen S (2017) Biopolymers composites with peanut hull waste biomass and application for crystal violet adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 94:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.013
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Ghezelbash GR, Pepe F (2017) Application of experimental design and derivative spectrophotometry methods in optimization and analysis of biosorption of binary mixtures of basic dyes from aqueous solutions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.043
Shah AI, Din Dar MU, Bhat RA, Singh JP, Singh K, Bhat SA (2020) Prospectives and challenges of wastewater treatment technologies to combat contaminants of emerging concerns. Ecol Eng 152:105882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.105882
Dallel R, Kesraoui A, Seffen M (2018) Biosorption of cationic dye onto “Phragmites australis” fibers: characterization and mechanism. J Environ Chem Eng 6:7247–7256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.024
Majhi PK, Kothari R, Pandey A, Tyagi VV (2020) Adsorptive behavior of free and immobilized Chlorella pyrenoidosa for decolorization. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00770-6
Bouras HD, Yeddou AR, Bouras N, Hellel D, Holtz MD, Sabaou N, Chergui A, Nadjemi B (2017) Biosorption of Congo red dye by Aspergillus carbonarius M333 and Penicillium glabrum Pg1: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 80:915–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.08.002
Jarusiripot C (2014) Removal of reactive dye by adsorption over chemical pretreatment coal based bottom ash. Procedia Chem 9:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2014.05.015
Hassan SHA, Koutb M, Nafady NA, Hassan EA (2018) Potentiality of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora ASU1 in biosorption of cadmium and zinc. Chemosphere 202:750–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.114
Adeniyi AG, Ighalo JO (2019) Biosorption of pollutants by plant leaves: an empirical review. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103100
Nguyen TA, Fu CC, Juang RS (2016) Biosorption and biodegradation of a sulfur dye in high-strength dyeing wastewater by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J Environ Manag 182:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.083
Dil EA, Ghaedi M, Ghezelbash GR, Asfaram A (2017) Multi-responses optimization of simultaneous biosorption of cationic dyes by live yeast Yarrowia lipolytica 70562 from binary solution: application of first order derivative spectrophotometry. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.030
Almeida EJR, Corso CR (2014) Comparative study of toxicity of azo dye Procion Red MX-5B following biosorption and biodegradation treatments with the fungi Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus terreus. Chemosphere 112:317–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.060
Louati I, Elloumi-Mseddi J, Cheikhrouhou W, Hadrich B, Nasri M, Aifa S, Woodward S, Mechichi T (2020) Simultaneous cleanup of Reactive Black 5 and cadmium by a desert soil bacterium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110103
Fu Y, Viraraghavan T (2002) Dye biosorption sites in Aspergillus Niger. Bioresour Technol 82:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00172-9
Dhankhar R, Hooda A (2011) Fungal biosorption-an alternative to meet the challenges of heavy metal pollution in aqueous solutions. Environ Technol 32:467–491. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2011.572922
Kumari K, Abraham TE (2007) Biosorption of anionic textile dyes by nonviable biomass of fungi and yeast. Bioresour Technol 98:1704–1710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.07.030
Aksu Z, Dönmez G (2000) The use of molasses in copper(II) containing wastewaters: effects on growth and copper(II) bioaccumulation properties of Kluyveromyces marxianus. Process Biochem 36:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(00)00234-X
Crini G, Badot PM (2008) Application of chitosan, a natural aminopolysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using batch studies: a review of recent literature. Prog Polym Sci 33:399–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.11.001
Kodal SP, Aksu Z (2017) Cationic surfactant-modified biosorption of anionic dyes by dried Rhizopus arrhizus. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 38:2551–2561. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1270357
O’Mahony T, Guibal E, Tobin JM (2002) Reactive dye biosorption by Rhizopus arrhizus biomass. Enzym Microb Technol 31:456–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00110-2
Çabuk A, Aytar P, Gedikli S, Özel YK, Kocabıyık E (2013) Biosorption of acidic textile dyestuffs from aqueous solution by Paecilomyces sp. isolated from acidic mine drainage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:4540–4550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1396-9
Akar T, Divriklioglu M (2010) Biosorption applications of modified fungal biomass for decolorization of Reactive Red 2 contaminated solutions: batch and dynamic flow mode studies. Bioresour Technol 101:7271–7277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.044
Huang J, Liu D, Lu J, Wang H, Wei X, Liu J (2016) Biosorption of Reactive Black 5 by modified Aspergillus versicolor biomass: kinetics, capacity and mechanism studies. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 492:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.11.071
Cardoso NF, Lima EC, Royer B, Bach MV, Dotto GL, Pinto LAA, Calvete T (2012) Comparison of Spirulina platensis microalgae and commercial activated carbon as adsorbents for the removal of Reactive Red 120 dye from aqueous effluents. J Hazard Mater 241–242:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.09.026
Saroyan H, Ntagiou D, Rekos K, Deliyanni E (2019) Reactive Black 5 degradation on manganese oxides supported on sodium hydroxide modified Graphene oxide. Appl Sci 9:2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102167
Vakili M, Zwain HM, Mojiri A et al (2020) Effective adsorption of Reactive Black 5 onto hybrid hexadecylamine impregnated chitosan-powdered activated carbon beads. Water 12:1–14
Sharma G, Naushad M, Kumar A, Rana S, Sharma S, Bhatnagar A, J. Stadler F, Ghfar AA, Khan MR (2017) Efficient removal of coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 dye using starch/poly(alginic acid-cl-acrylamide) nanohydrogel. Process Saf Environ Prot 109:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.04.011
Tikhomirova TI, Ramazanova GR, Apyari VV (2018) Effect of nature and structure of synthetic anionic food dyes on their sorption onto different sorbents: peculiarities and prospects. Microchem J 143:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.08.022
Crini G, Peindy HN, Gimbert F, Robert C (2007) Removal of C.I. Basic Green 4 (malachite green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep Purif Technol 53:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.018
Farooq U, Kozinski JA, Khan MA, Athar M (2010) Biosorption of heavy metal ions using wheat based biosorbents - a review of the recent literature. Bioresour Technol 101:5043–5053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.030
Negm NA, Abd El Wahed MG, Hassan ARA, Abou Kana MTH (2018) Feasibility of metal adsorption using brown algae and fungi: effect of biosorbents structure on adsorption isotherm and kinetics. J Mol Liq 264:292–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.027
Patel R, Suresh S (2008) Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the biosorption of Reactive Black 5 dye by Aspergillus foetidus. Bioresour Technol 99:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.12.003
Ranjusha VR, Pundir R, Kumar K et al (2010) Biosorption of Remazol Black B dye (Azo dye) by the growing Aspergillus flavus. J Environ Sci Heal - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst Environ Eng 45:1256–1263. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2010.493812
Mathur M, Gola D, Panja R, Malik A, Ahammad SZ (2018) Performance evaluation of two Aspergillus spp. for the decolourization of reactive dyes by bioaccumulation and biosorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0417-0
Souza FHM, Leme VFC, Costa GOB et al (2020) Biosorption of Rhodamine B using a low-cost biosorbent prepared from inactivated Aspergillus oryzae cells: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Water Air Soil Pollut 231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04633-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karatay, S.E., Aksu, Z., Özeren, İ. et al. Potentiality of newly isolated Aspergillus tubingensis in biosorption of textile dyes: equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 13, 4777–4784 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01523-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01523-9