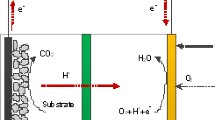
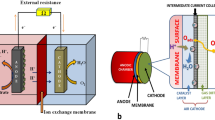
Abstract
The increasing demands of efficient and sustainable energy generation methods from waste products have taken a giant leap in the last century, and especially in the previous two decades. Wastewater treatment has also been a much-researched topic in recent years owing to the exponential increase in effluent-laden wastewater from industries, the agricultural sector and food sector, and its effects on the environment. There have been plenty of wastewater treatment techniques over the years, but most of them lack in terms of cost-effectiveness, durability, and energy recovery rates. Microbial fuel cells can prove to be of great use to tackle both of these issues in one go, as they perform bioelectrochemical processes on organic biodegradable compounds to oxidize them to generate power which can be harnessed by various means. This article explains the aim, construction, mechanism, and application of microbial fuel cells; the economic and scientific challenges that they face in the future; and microbial fuel cell (MFC) hybrid systems which make use of MFCs combined with other useful technologies for greater aims and better efficiencies. It overall discusses the various ways in which MFCs outperform other wastewater treatment technologies by significantly decreasing sludge production and being environment-friendly, and also some limitations and drawbacks that MFCs face owing to the fact that they are relatively newer technologies and still require decades of modifications until they reach excellent output rates. MFCs are known not only for wastewater treatment but also for contaminant removal, heavy metal removal, biohydrogen production, applications in biosensors, etc., as also discussed in this article.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEM:
-
anion exchange membrane
- AFT:
-
anodic Fenton treatment
- ANAMMOX:
-
anaerobic ammonium oxidation
- AQDS:
-
anthraquinone-2,6-disulphonicsalt
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- BOD:
-
biological oxygen demand
- CEM:
-
cation exchange membrane
- CF:
-
carbon felt
- COD:
-
chemical oxygen demand
- HEPES:
-
2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanesulfonic acid
- MD:
-
membrane distillation
- MDC:
-
microbial desalination cell
- MEC:
-
microbial electrolysis cell
- MED:
-
multi-effect distillation
- MEDC:
-
microbial electrolysis desalination cell
- MES:
-
2-Morpholinoethanesulfonic acid
- MFC:
-
microbial fuel cell
- MLMFC:
-
membrane-less microbial fuel cell
- MPEC:
-
microbial photoelectrochemical cell
- MSF:
-
multi-stage flash distillation
- OLR:
-
organic loading rate
- PEC:
-
photoelectrochemical cell
- PEM:
-
proton exchange membrane
- PFC:
-
photocatalytic fuel cells
- pH:
-
power of hydrogen
- PIPES:
-
piperazinediethanesulfonic acid
- PPy:
-
polypyrrole
- RO:
-
reverse osmosis
- SLR:
-
sludge loading rate
- UV:
-
ultraviolet
- VSS:
-
volatile suspended solid
References
James C, Hema Meenal S, Elakkiya S, Logarshani S (2020) Sustainable environment through treatment of domestic sewage using MFC. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.110
Sugawara E, Nikaido H (2014) Properties of AdeABC and AdeIJK efflux systems of Acinetobacter baumannii compared with those of the AcrAB-TolC system of Escherichia coli 58:7250–7257
Santoro C, Arbizzani C, Erable B, Ieropoulos I (2017) Microbial fuel cells: From fundamentals to applications. A review. J Power Sources 356:225–244
Pandey P, Shinde VN, Deopurkar RL et al (2016) Recent advances in the use of different substrates in microbial fuel cells toward wastewater treatment and simultaneous energy recovery. Appl Energy 168:706–723
Agarwal A, Upadhyay U, Sreedhar I et al (2020) A review on valorization of biomass in heavy metal removal from wastewater. J Water Process Eng
Logan BE, Elimelech M (2012) Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature 488:313–319
Mansor M, Timmiati SN, Lim KL et al (2019) Recent progress of anode catalysts and their support materials for methanol electrooxidation reaction. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:14744–14769
Logan BE, Rabaey K (2012) Conversion of wastes into bioelectricity and chemicals by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Science 337(80):686–690
Palanisamy G, Jung HY, Sadhasivam T et al (2019) A comprehensive review on microbial fuel cell technologies: processes, utilization, and advanced developments in electrodes and membranes. J Clean Prod 221:598–621
Slate AJ, Whitehead KA, Brownson DAC, Banks CE (2019) Microbial fuel cells: an overview of current technology. Renew Sust Energ Rev 101:60–81
Do MH, Ngo HH, Guo WS et al (2018) Challenges in the application of microbial fuel cells to wastewater treatment and energy production: a mini review. Sci Total Environ 639:910–920
Aghababaie M, Farhadian M, Jeihanipour A, Biria D (2015) Effective factors on the performance of microbial fuel cells in wastewater treatment–a review. Environ Technol Rev 4:71–89
Sreedhar I, Upadhyay U, Roy P et al (2020) Carbon capture and utilization by graphenes-path covered and ahead. J Clean Prod
Flimban SGA, Ismail IMI, Kim T, Oh SE (2019) Overview of recent advancements in the microbial fuel cell from fundamentals to applications: design, major elements, and scalability. Energies 12:12173390
Virdis B, Freguia S, Rozendal RA, et al (2011) Microbial fuel cells. In: Treatise on water science. 641–665
Rahimnejad M, Adhami A, Darvari S et al (2015) Microbial fuel cell as new technology for bioelectricity generation: a review. Alexandria Eng J 54:745–756
Nitisoravut R, Regmi R (2017) Plant microbial fuel cells: a promising biosystems engineering. Renew Sust Energ Rev 76:81–89
Nemeth T, Schröer P, Kuipers M, Sauer DU (2020) Lithium titanate oxide battery cells for high-power automotive applications – electro-thermal properties, aging behavior and cost considerations. J Energy Storage 31:101656
Tatinclaux M, Gregoire K, Leininger A et al (2018) Electricity generation from wastewater using a floating air cathode microbial fuel cell. Water-Energy Nexus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wen.2018.09.001
Salar-Garcia MJ, Obata O, Kurt H et al (2020) Impact of inoculum type on the microbial community and power performance of urine-fed microbial fuel cells. Microorganisms 8:1–16
Yaqoob AA, Ibrahim MNM, Rafatullah M et al (2020) Recent advances in anodes for microbial fuel cells: an overview. Materials (Basel) 13:2078
Schneider K, Thorne RJ, Cameron PJ (2016) An investigation of anode and cathode materials in photomicrobial fuel cells. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 374:20150080
Paquin F, Rivnay J, Salleo A et al (2015) Multi-phase semicrystalline microstructures drive exciton dissociation in neat plastic semiconductors. J Mater Chem C 3:10715–10722
Kim JR, Jung SH, Regan JM, Logan BE (2007) Electricity generation and microbial community analysis of alcohol powered microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 98:2568–2577
Liu H, Cheng S, Logan BE (2005) Production of electricity from acetate or butyrate using a single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 39:658–662
Rahimnejad M, Ghoreyshi AA, Najafpour G, Jafary T (2011) Power generation from organic substrate in batch and continuous flow microbial fuel cell operations. Appl Energy 88:3999–4004
Ahn Y, Logan BE (2010) Effectiveness of domestic wastewater treatment using microbial fuel cells at ambient and mesophilic temperatures. Bioresour Technol 101:469–475
Ishii S, Watanabe K, Yabuki S et al (2008) Comparison of electrode reduction activities of Geobacter sulfurreducens and an enriched consortium in an air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7348–7355
Zou Y, Xiang C, Yang L et al (2008) A mediatorless microbial fuel cell using polypyrrole coated carbon nanotubes composite as anode material. Int J Hydrog Energy 33:4856–4862
Jung RK, Dec J, Bruns MA, Logan BE (2008) Removal of odors from swine wastewater by using microbial fuel cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2540–2543
Logan BE, Murano C, Scott K et al (2005) Electricity generation from cysteine in a microbial fuel cell. Water Res 39:942–952
Chakraborty I, Das S, Dubey BK, Ghangrekar MM (2020) Novel low cost proton exchange membrane made from sulphonated biochar for application in microbial fuel cells. Mater Chem Phys 239:122025
Lin CW, Wu CH, Chiu YH, Tsai SL (2014) Effects of different mediators on electricity generation and microbial structure of a toluene powered microbial fuel cell. Fuel 125:30–35
Yu F, Wang C, Ma J (2016) Applications of graphene-modified electrodes in microbial fuel cells. Materials (Basel):9
Firdous S, Jin W, Shahid N et al (2018) The performance of microbial fuel cells treating vegetable oil industrial wastewater. Environ Technol Innov 10:143–151
Ghadge AN, Jadhav DA, Pradhan H, Ghangrekar MM (2015) Enhancing waste activated sludge digestion and power production using hypochlorite as catholyte in clayware microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 182:225–231
Chouler J, Padgett GA, Cameron PJ et al (2016) Towards effective small scale microbial fuel cells for energy generation from urine. Electrochim Acta 192:89–98
Fu Y, Xu Q, Zai X et al (2014) Low electrical potential anode modified with Fe/ferric oxide and its application in marine benthic microbial fuel cell with higher voltage and power output. Appl Surf Sci 289:472–477
Liu YF, Zhang XL, Li CJ (2020) Advances in carbon-based anode materials for microbial fuel cells. Gongcheng Kexue Xuebao/Chinese J Eng 42:270–277
Sonawane JM, Pant D, Ghosh PC, Adeloju SB (2019) Fabrication of a carbon paper/polyaniline-copper hybrid and its utilization as an air cathode for microbial fuel cells. ACS Appl Energy Mater 2:1891–1902
Abourached C, English MJ, Liu H (2016) Wastewater treatment by microbial fuel cell (MFC) prior irrigation water reuse. J Clean Prod 137:144–149
Liu YF, Zhang XL, Li CJ (2020) Advances in carbon-based anode materials for microbial fuel cells. Gongcheng Kexue Xuebao/Chinese. J Eng Des
Pattanayak P, Pramanik N, Papiya F et al (2020) Metal-free keratin modified poly(pyrrole-co-aniline)-reduced graphene oxide based nanocomposite materials: a promising cathode catalyst in microbial fuel cell application. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103813
Ucar D, Zhang Y, Angelidaki I (2017) An overview of electron acceptors in microbial fuel cells. Front Microbiol 8:00643
Huang L, Regan JM, Quan X (2011) Electron transfer mechanisms, new applications, and performance of biocathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102:316–323
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:375–381
Deng Q, Li X, Zuo J et al (2010) Power generation using an activated carbon fiber felt cathode in an upflow microbial fuel cell. J Power Sources 195:1130–1135
Ter Heijne A, Hamelers HVM, De Wilde V et al (2006) A bipolar membrane combined with ferric iron reduction as an efficient cathode system in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40:5200–5205
You S, Zhao Q, Zhang J et al (2008) Increased sustainable electricity generation in up-flow air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 23:1157–1160
Chen GW, Choi SJ, Lee TH et al (2008) Application of biocathode in microbial fuel cells: cell performance and microbial community. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:379–388
Papiya F, Pattanayak P, Kumar V et al (2020) Sulfonated graphene oxide and titanium dioxide coated with nanostructured polyaniline nanocomposites as an efficient cathode catalyst in microbial fuel cells. Mater Sci Eng C 108:110498
Tajdid Khajeh R, Aber S, Nofouzi K (2020) Efficient improvement of microbial fuel cell performance by the modification of graphite cathode via electrophoretic deposition of CuO/ZnO. Mater Chem Phys 240:122208
Merino-Jimenez I, Celorrio V, Fermin DJ et al (2017) Enhanced MFC power production and struvite recovery by the addition of sea salts to urine. Water Res 109:46–53
Harnisch F, Schröder U (2009) Selectivity versus mobility: separation of anode and cathode in microbial bioelectrochemical systems. ChemSusChem 2:921–926
Chen Y, Zhao Z, Weng Z, et al (2019) Performance study of polypyrrole-nanowires based microbial fuel cells. In: 2019 3rd International Conference on Circuits, System and Simulation, ICCSS 2019. 235–238
Ghasemi M, Wan Daud WR, Alam J et al (2016) Sulfonated poly ether ether ketone with different degree of sulphonation in microbial fuel cell: application study and economical analysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:4862–4871
Asensio Y, Fernandez-Marchante CM, Lobato J et al (2018) Influence of the ion-exchange membrane on the performance of double-compartment microbial fuel cells. J Electroanal Chem 808:427–432
Zhang Y, Liu M, Zhou M et al (2019) Microbial fuel cell hybrid systems for wastewater treatment and bioenergy production: synergistic effects, mechanisms and challenges. Renew Sust Energ Rev 103:13–29
Choudhury P, Prasad Uday US, Bandyopadhyay TK et al (2017) Performance improvement of microbial fuel cell (MFC) using suitable electrode and Bioengineered organisms: a review. Bioengineered 8:471–487
Goswami R, Mishra VK (2018) A review of design, operational conditions and applications of microbial fuel cells. Biofuels 9:203–220
Li M, Zhou M, Tian X et al (2018) Microbial fuel cell (MFC) power performance improvement through enhanced microbial electrogenicity. Biotechnol Adv 36:1316–1327
Ramachandran R, Chen SM, peter G k G (2015) Enhancement of different fabricated electrode materials for microbial fuel cell applications: an overview. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:7111–7137
Naina Mohamed S, Thota Karunakaran R, Manickam M (2018) Enhancement of bioelectricity generation from treatment of distillery wastewater using microbial fuel cell. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12734
Nam JY, Kim HW, Lim KH et al (2010) Variation of power generation at different buffer types and conductivities in single chamber microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1155–1159
Srivastava P, Yadav AK, Mishra BK (2015) The effects of microbial fuel cell integration into constructed wetland on the performance of constructed wetland. Bioresour Technol 195:223–230
Kim C, Lee CR, Song YE et al (2017) Hexavalent chromium as a cathodic electron acceptor in a bipolar membrane microbial fuel cell with the simultaneous treatment of electroplating wastewater. Chem Eng J 328:703–707
Wu S, Liang P, Zhang C et al (2015) Enhanced performance of microbial fuel cell at low substrate concentrations by adsorptive anode. Electrochim Acta 161:245–251
Saba B, Christy AD, Yu Z, Co AC (2017) Sustainable power generation from bacterio-algal microbial fuel cells (MFCs): an overview. Renew Sust Energ Rev 73:75–84
Torres CI, Lee HS, Rittmann BE (2008) Carbonate species as OH- carriers for decreasing the pH gradient between cathode and anode in biological fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 42:8773–8777
Ren H, Jiang C, Chae J (2017) Effect of temperature on a miniaturized microbial fuel cell (MFC). Micro Nano Syst Lett 5:13
Wang XL, Wu C, Zhang JQ, et al (2011) Acclimation stage on the performance of microbial fuel cells subjected to variation in COD, temperature, and electron acceptor. In: Advanced Materials Research 2346–2350
Gadkari S, Fontmorin JM, Yu E, Sadhukhan J (2020) Influence of temperature and other system parameters on microbial fuel cell performance: numerical and experimental investigation. Chem Eng J 388:124176
Uria N, Ferrera I, Mas J (2017) Electrochemical performance and microbial community profiles in microbial fuel cells in relation to electron transfer mechanisms. BMC Microbiol 17:208
Gonzalez del Campo A, Lobato J, Cañizares P et al (2013) Short-term effects of temperature and COD in a microbial fuel cell. Appl Energy 101:213–217
Commault AS, Barrière F, Lapinsonnière L et al (2015) Influence of inoculum and anode surface properties on the selection of Geobacter-dominated biofilms. Bioresour Technol 195:265–272
Patil SA, Harnisch F, Kapadnis B, Schröder U (2010) Electroactive mixed culture biofilms in microbial bioelectrochemical systems: the role of temperature for biofilm formation and performance. Biosens Bioelectron 26:803–808
Michie IS, Kim JR, Dinsdale RM et al (2011) The influence of psychrophilic and mesophilic start-up temperature on microbial fuel cell system performance. Energy Environ Sci 4:1011–1019
Cheng S, Xing D, Logan BE (2011) Electricity generation of single-chamber microbial fuel cells at low temperatures. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1913–1917
Oliveira VB, Simões M, Melo LF, Pinto AMFR (2013) Overview on the developments of microbial fuel cells. Biochem Eng J 73:53–64
Behera M, Ghangrekar MM (2009) Performance of microbial fuel cell in response to change in sludge loading rate at different anodic feed pH. Bioresour Technol 100:5114–5121
Martin E, Savadogo O, Guiot SR, Tartakovsky B (2010) The influence of operational conditions on the performance of a microbial fuel cell seeded with mesophilic anaerobic sludge. Biochem Eng J 51:132–139
Di Lorenzo M, Scott K, Curtis TP, Head IM (2010) Effect of increasing anode surface area on the performance of a single chamber microbial fuel cell. Chem Eng J 156:40–48
Velvizhi G, Venkata Mohan S (2012) Electrogenic activity and electron losses under increasing organic load of recalcitrant pharmaceutical wastewater. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:5969–5978
Moon H, In SC, Jae KJ, Kim BH (2005) Residence time distribution in microbial fuel cell and its influence on COD removal with electricity generation. Biochem Eng J 27:59–65
Aelterman P, Versichele M, Marzorati M et al (2008) Loading rate and external resistance control the electricity generation of microbial fuel cells with different three-dimensional anodes. Bioresour Technol 99:8895–8902
Ieropoulos I, Winfield J, Greenman J (2010) Effects of flow-rate, inoculum and time on the internal resistance of microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 101:3520–3525
Juang DF, Yang PC, Chou HY, Chiu LJ (2011) Effects of microbial species, organic loading and substrate degradation rate on the power generation capability of microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Lett 33:2147–2160
Herbert-Guillou D, Tribollet B, Festy D (2001) Influence of the hydrodynamics on the biofilm formation by mass transport analysis. Bioelectrochemistry 53:119–125
Pham HT, Boon N, Aelterman P et al (2008) High shear enrichment improves the performance of the anodophilic microbial consortium in a microbial fuel cell. Microb Biotechnol 1:487–496
Rickard AH, McBain AJ, Stead AT, Gilbert P (2004) Shear rate moderates community diversity in freshwater biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7426–7435
Rochex A, Godon JJ, Bernet N, Escudié R (2008) Role of shear stress on composition, diversity and dynamics of biofilm bacterial communities. Water Res 42:4915–4922
Gajda I, Greenman J, Melhuish C, Ieropoulos I (2015) Self-sustainable electricity production from algae grown in a microbial fuel cell system. Biomass Bioenergy 82:87–93
Li J, Yang W, Zhang B, et al (2018) Electricity from microbial fuel cells. Green Energy and Technology 54:745–756
Tharali AD, Sain N, Osborne WJ (2016) Microbial fuel cells in bioelectricity production. Front Life Sci 9:252–266
Logan BE (2004) Extracting hydrogen and electricity from renewable resources. Environ Sci Technol 38:160–167
Min B, Kim JR, Oh SE et al (2005) Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells. Water Res 39:4961–4968
Heilmann J, Logan BE (2006) Production of electricity from proteins using a microbial fuel cell. Water Environ Res 78:531–537
Jafary T, Wan Daud WR, Ghasemi M et al (2019) Clean hydrogen production in a full biological microbial electrolysis cell. Int J Hydrog Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.01.010
Hu J, Zhang Q, Lee DJ, Ngo HH (2018) Feasible use of microbial fuel cells for pollution treatment. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.02.001
Habermann W, Pommer EH (1991) Biological fuel cells with sulphide storage capacity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:128–133
Naina Mohamed S, Ajit Hiraman P, Muthukumar K, Jayabalan T (2020) Bioelectricity production from kitchen wastewater using microbial fuel cell with photosynthetic algal cathode. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122226
Li WW, Yu HQ, He Z (2014) Towards sustainable wastewater treatment by using microbial fuel cells-centered technologies. Energy Environ Sci 7:911–924
Yu D, Wang G, Xu F et al (2013) Electricity generation from artificial wastewater using an upflow microbial fuel cell electricity generation from artificial wastewater using an upflow microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 39:5262–5267
Kumar SS, Kumar V, Malyan SK et al (2019) Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for bioelectrochemical treatment of different wastewater streams. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.05.109
Xu P, Xu H, Shi Z (2018) A novel bio-electro-Fenton process with FeVO4/CF cathode on advanced treatment of coal gasification wastewater. Sep Purif Technol 194:457–461
Miran W, Nawaz M, Jang J, Lee DS (2016) Conversion of orange peel waste biomass to bioelectricity using a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Sci Total Environ 547:197–205
Kumar SS, Kumar V, Kumar R et al (2019) Microbial fuel cells as a sustainable platform technology for bioenergy, biosensing, environmental monitoring, and other low power device applications. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115682
Lee H, Yang W, Wei X, et al (2015) A microsized microbial fuel cell based biosensor for fast and sensitive detection of toxic substances in water. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS). 573–576
Felix FS, Angnes L (2018) Electrochemical immunosensors – a powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens Bioelectron 102:470–478
Rocchitta G, Spanu A, Babudieri S et al (2016) Enzyme biosensors for biomedical applications: strategies for safeguarding analytical performances in biological fluids. Sensors (Switzerland) 16:780
Mehrotra P (2016) Biosensors and their applications - a review. J Oral Biol Craniofacial Res 6:153–159
Justino CIL, Gomes AR, Freitas AC et al (2017) Graphene based sensors and biosensors. Trends Anal Chem 91:53–66
Gerritsen M, Jansen JA, Lutterman JA (1999) Performance of subcutaneously implanted glucose sensors for continuous monitoring. Neth J Med 54:167–179
Yang W, Wei X, Fraiwan A et al (2016) Fast and sensitive water quality assessment: a μl-scale microbial fuel cell-based biosensor integrated with an air-bubble trap and electrochemical sensing functionality. Sensors Actuators B Chem 226:191–195
Zhuang L, Zhou S, Li Y et al (2010) In situ Fenton-enhanced cathodic reaction for sustainable increased electricity generation in microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 195:1379–1382
Lu A, Li Y, Jin S et al (2012) Growth of non-phototrophic microorganisms using solar energy through mineral photocatalysis. Nat Commun 3:105497
Morel A, Zuo K, Xia X et al (2012) Microbialdesalination cells packed with ion-exchange resin to enhance water desalination rate. Bioresour Technol 118:243–248
Sun M, Sheng GP, Mu ZX et al (2009) Manipulating the hydrogen production from acetate in a microbial electrolysis cell-microbial fuel cell-coupled system. J Power Sources 191:338–343
Ardakani MN, Badalians Gholikandi G (2020) Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) in integration with anaerobic treatment processes (AnTPs) and membrane bioreactors (MBRs) for simultaneous efficient wastewater/sludge treatment and energy recovery -a state-of-the-art review. Biomass Bioenergy 141:105726
Nordin N, Ho LN, Ong SA et al (2017) Hybrid system of photocatalytic fuel cell and Fenton process for electricity generation and degradation of Reactive Black 5. Sep Purif Technol 177:135–141
Feng CH, Li FB, Mai HJ, Li XZ (2010) Bio-electro-Fenton process driven by microbial fuel cell for wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 44:1875–1880
Rozendal RA, Leone E, Keller J, Rabaey K (2009) Efficient hydrogen peroxide generation from organic matter in a bioelectrochemical system. Electrochem Commun 11:1752–1755
Zhu X, Ni J (2009) Simultaneous processes of electricity generation and p-nitrophenol degradation in a microbial fuel cell. Electrochem Commun 11:274–277
Singh HM, Pathak AK, Chopra K et al (2019) Microbial fuel cells: a sustainable solution for bioelectricity generation and wastewater treatment. Biofuels. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2017.1413860
Chen JY, Zhao L, Li N, Liu H (2015) A microbial fuel cell with the three-dimensional electrode applied an external voltage for synthesis of hydrogen peroxide from organic matter. J Power Sources 287:291–296
Ramirez JH, Costa CA, Madeira LM et al (2007) Fenton-like oxidation of Orange II solutions using heterogeneous catalysts based on saponite clay. Appl Catal B Environ 71:44–56
Zhao K, Zeng Q, Bai J et al (2017) Enhanced organic pollutants degradation and electricity production simultaneously via strengthening the radicals reaction in a novel Fenton-photocatalytic fuel cell system. Water Res 108:293–300
Zhu X, Logan BE (2013) Using single-chamber microbial fuel cells as renewable power sources of electro-Fenton reactors for organic pollutant treatment. J Hazard Mater 252–253:198–203
de DMAF, Iglesias O, Bocos E et al (2014) Application of benthonic microbial fuel cells and electro-Fenton process to dye decolourisation. J Ind Eng Chem 20:3754–3760
Xu H, Quan X, Xiao Z, Chen L (2018) Effect of anodes decoration with metal and metal oxides nanoparticles on pharmaceutically active compounds removal and power generation in microbial fuel cells. Chem Eng J 335:539–547
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Angelidaki I (2015) Alternate switching between microbial fuel cell and microbial electrolysis cell operation as a new method to control H2O2 level in Bioelectro-Fenton system. J Power Sources 291:108–116
Zhang L, Yin X, Li SFY (2015) Bio-electrochemical degradation of paracetamol in a microbial fuel cell-Fenton system. Chem Eng J 276:185–192
Luo Y, Zhang R, Liu G et al (2011) Simultaneous degradation of refractory contaminants in both the anode and cathode chambers of the microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 102:3827–3832
Feng C, Ma L, Li F et al (2010) A polypyrrole/anthraquinone-2,6-disulphonic disodium salt (PPy/AQDS)-modified anode to improve performance of microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1516–1520
Feng C, Li F, Liu H et al (2010) A dual-chamber microbial fuel cell with conductive film-modified anode and cathode and its application for the neutral electro-Fenton process. Electrochim Acta 55:2048–2054
Yong XY, Gu DY, Wu YD et al (2017) Bio-Electron-Fenton (BEF) process driven by microbial fuel cells for triphenyltin chloride (TPTC) degradation. J Hazard Mater 324:178–183
Yuan GE, Li Y, Lv J et al (2017) Integration of microbial fuel cell and catalytic oxidation reactor with iron phthalocyanine catalyst for Congo red degradation. Biochem Eng J 120:118–124
Kment SK, Naldoni A et al (2020) FeO-based nanostructures and nanohybrids for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Prog Mater Sci
Lianos P (2017) Review of recent trends in photoelectrocatalytic conversion of solar energy to electricity and hydrogen. Appl Catal B Environ 210:235–254
Antolini E (2019) Photoelectrocatalytic fuel cells and photoelectrode microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment and power generation. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103241
Bak T, Nowotny J, Rekas M, Sorrell CC (2002) Photo-electrochemical hydrogen generation from water using solar energy. Materials-related aspects. Int J Hydrog Energy 27:991–1022
Wang Y, Zu M, Zhou X et al (2020) Designing efficient TiO2-based photoelectrocatalysis systems for chemical engineering and sensing. Chem Eng J
Fischer F (2018) Photoelectrode, photovoltaic and photosynthetic microbial fuel cells. Renew Sust Energ Rev 90:16–27
Fu S, Deng B, Ma D et al (2018) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic fuel cell with an Ag-TiO2 carbon foam anode for simultaneous 4-chlorophenol degradation and energy recovery. ChemEngineering 2:1–10
Yu T, Liu L, Li L, Yang F (2016) A self-biased fuel cell with TiO2/g-C3N4 anode catalyzed alkaline pollutant degradation with light and without light - what is the degradation mechanism? Electrochim Acta 210:122–129
Zeng Q, Bai J, Li J et al (2018) Highly-stable and efficient photocatalytic fuel cell based on an epitaxial TiO2/WO3/W nanothorn photoanode and enhanced radical reactions for simultaneous electricity production and wastewater treatment. Appl Energy 220:127–137
Khan ME, Khan MM, Min BK, Cho MH (2018) Microbial fuel cell assisted band gap narrowed TiO2 for visible light induced photocatalytic activities and power generation. Sci Rep 8
Wang H, Qian F, Wang G et al (2013) Self-biased solar-microbial device for sustainable hydrogen generation. ACS Nano 7:8728–8735
Li M, He X, Zeng Y et al (2015) Solar-microbial hybrid device based on oxygen-deficient niobium pentoxide anodes for sustainable hydrogen production. Chem Sci 6:6799–6805
Logan BE, Call D, Cheng S et al (2008) Microbial electrolysis cells for high yield hydrogen gas production from organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 42:8630–8640
Chorbadzhiyska E, Apostolova D, Bardarov I et al (2020) Hybrid MFC-MEC systems: principles and applications. Bulg Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.34049/bcc.52.A.178
Jung RK, Cheng S, Oh SE, Logan BE (2007) Power generation using different cation, anion, and ultrafiltration membranes in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 41:1004–1009
Wang A, Sun D, Cao G et al (2011) Integrated hydrogen production process from cellulose by combining dark fermentation, microbial fuel cells, and a microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour Technol 102:4137–4143
Cheng S, Logan BE (2007) Sustainable and efficient biohydrogen production via electrohydrogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18871–18873
Rezaei F, Richard TL, Brennan RA, Logan BE (2007) Substrate-enhanced microbial fuel cells for improved remote power generation from sediment-based systems. Environ Sci Technol 41:4053–4058
Ren Z, Ward TE, Logan BE, Regan JM (2007) Characterization of the cellulolytic and hydrogen-producing activities of six mesophilic Clostridium species. J Appl Microbiol 103:2258–2266
Azwar MY, Hussain MA, Abdul-Wahab AK (2014) Development of biohydrogen production by photobiological, fermentation and electrochemical processes: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 31:158–173
Sun M, Sheng GP, Zhang L et al (2008) An MEC-MFC-coupled system for biohydrogen production from acetate. Environ Sci Technol 42:8095–8100
Rago L, Monpart N, Cortés P et al (2016) Performance of microbial electrolysis cells with bioanodes grown at different external resistances. Water Sci Technol 73:1129–1135
Huang L, Yao B, Wu D, Quan X (2014) Complete cobalt recovery from lithium cobalt oxide in self-driven microbial fuel cell - microbial electrolysis cell systems. J Power Sources 259:54–64
Li Y, Wu Y, Liu B et al (2015) Self-sustained reduction of multiple metals in a microbial fuel cell-microbial electrolysis cell hybrid system. Bioresour Technol 192:238–246
Li Z, Wang Q, Liu D et al (2013) Ionic liquid-mediated electrochemical CO2 reduction in a microbial electrolysis cell. Electrochem Commun 35:91
Liu H, Leng F, Guan Y et al (2017) Simultaneous pollutant removal and electricity generation in a combined ABR-MFC-MEC system treating fecal wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:179
Zhao H, Zhang Y, Zhao B et al (2012) Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in an MFC-MEC system with a layer-by-layer self-assembly carbon nanotube/cobalt phthalocyanine modified electrode. Environ Sci Technol 46:5198–5204
Wang X, Tian Y, Liu H et al (2019) Optimizing the performance of organics and nutrient removal in constructed wetland–microbial fuel cell systems. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.005
Cusick RD, Logan BE (2012) Phosphate recovery as struvite within a single chamber microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour Technol 107:110–115
Gude VG (2016) Wastewater treatment in microbial fuel cells - an overview. J Clean Prod 122:287–307
Elabed A, El Abed S, Ibnsouda S, Erable B (2019) Sustainable approach for tannery wastewater treatment: bioelectricity generation in bioelectrochemical systems. Arab J Sci Eng 44:10057–10066
Sevda S, Yuan H, He Z, Abu-Reesh IM (2015) Microbial desalination cells as a versatile technology: functions, optimization and prospective. Desalination 371:9–17
Yuan L, Yang X, Liang P et al (2012) Capacitive deionization coupled with microbial fuel cells to desalinate low-concentration salt water. Bioresour Technol 110:735–738
Chen X, Xia X, Liang P et al (2011) Stacked microbial desalination cells to enhance water desalination efficiency. Environ Sci Technol 45:2465–2470
Watson VJ, Logan BE (2011) Analysis of polarization methods for elimination of power overshoot in microbial fuel cells. Electrochem Commun 13:54–56
Pandit S, Sarode S, Das D (2017) Fundamentals of microbial desalination cell. In: Microbial fuel cell: a bioelectrochemical system that converts waste to watts. 18:353–371
Luo H, Xu P, Jenkins PE, Ren Z (2012) Ionic composition and transport mechanisms in microbial desalination cells. J Membr Sci 409–410:16–23
Harnisch F, Schröder U (2010) From MFC to MXC: chemical and biological cathodes and their potential for microbial bioelectrochemical systems. Chem Soc Rev 39:4433–4448
Borjas Z, Esteve-Núñez A, Ortiz JM (2017) Strategies for merging microbial fuel cell technologies in water desalination processes: start-up protocol and desalination efficiency assessment. J Power Sources. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.02.052
Luo H, Jenkins PE, Ren Z (2011) Concurrent desalination and hydrogen generation using microbial electrolysis and desalination cells. Environ Sci Technol 45:340–344
Zhang L, Zhu X, Kashima H et al (2015) Anolyte recirculation effects in buffered and unbuffered single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 179:26–34
Kim Y, Logan BE (2013) Microbial desalination cells for energy production and desalination. Desalination 308:122–130
Oguz Koroglu E, Civelek Yoruklu H, Demir A, Ozkaya B (2019) Scale-up and commercialization issues of the MFCs. In: Microbial electrochemical technology
Prestigiacomo C, Fernandez-Marchante CM, Fernández-Morales FJ et al (2016) New prototypes for the isolation of the anodic chambers in microbial fuel cells. Fuel 181:704–710
Kuntke P, Sleutels THJA, Saakes M, Buisman CJN (2014) Hydrogen production and ammonium recovery from urine by a microbial electrolysis cell. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:4771–4778
Papillon J, Ondel O, Maire É (2021) Scale up of single-chamber microbial fuel cells with stainless steel 3D anode: Effect of electrode surface areas and electrode spacing. Bioresour Technol Reports 13:100632
Pasternak G, Greenman J, Ieropoulos I (2017) Self-powered, autonomous biological oxygen demand biosensor for online water quality monitoring. Sensors Actuators B Chem 244:815–822
Koroglu EO, Yoruklu HC, Demir A, Ozkaya B (2018) Scale-up and commercialization issues of the MFCs: challenges and implications. In: Biomass, biofuels, biochemicals: microbial electrochemical technology: sustainable platform for fuels, chemicals and remediation. Elsevier, 565–583
Kim B, Chang IS, Dinsdale RM, Guwy AJ (2021) Accurate measurement of internal resistance in microbial fuel cells by improved scanning electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 366:137388
Ghasemi B, Yaghmaei S, Ghaderi S et al (2020) Effects of chemical, electrochemical, and electrospun deposition of polyaniline coatings on surface of anode electrodes for evaluation of MFCs’ performance. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104039
Wei J, Liang P, Huang X (2011) Recent progress in electrodes for microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102:9335–9344
Nwaokocha CN, Giwa SO, Layeni AT et al (2020) Microbial fuel cell: bio-energy production from Nigerian corn starch wastewater using iron electrodes. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.345
Peera SG, Maiyalagan T, Liu C et al (2020) A review on carbon and non-precious metal based cathode catalysts in microbial fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.07.252
Stoll ZA, Ma Z, Trivedi CB et al (2016) Sacrificing power for more cost-effective treatment: a techno-economic approach for engineering microbial fuel cells. Chemosphere 161:10–18
Serra PMD, ES A (2021) Sourcing power with microbial fuel cells: a timeline. J Power Sources 482:228921
Yaqoob AA, Ibrahim MNM, Rodríguez-Couto S (2020) Development and modification of materials to build cost-effective anodes for microbial fuel cells (MFCs): an overview. Biochem Eng J 164:107779
Babauta JT, Kerber M, Hsu L et al (2018) Scaling up benthic microbial fuel cells using flyback converters. J Power Sources 395:98–105
López-Hincapié JD, Picos-Benítez AR, Cercado B et al (2020) Improving the configuration and architecture of a small-scale air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell (MFC) for biosensing organic matter in wastewater samples. J Water Process Eng 38:101671
Neethu B, Ghangrekar MM (2017) Electricity generation through a photo sediment microbial fuel cell using algae at the cathode. Water Sci Technol 76:3269–3277
Narayanasamy S, Jayaprakash J (2018) Improved performance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa catalyzed MFCs with graphite/polyester composite electrodes doped with metal ions for azo dye degradation. Chem Eng J 343:258–269
Nguyen DT, Taguchi K (2019) Enhancing the performance of E. coli-powered MFCs by using porous 3D anodes based on coconut activated carbon. Biochem Eng J 151:107357
Tajdid Khajeh R, Aber S, Zarei M (2020) Comparison of NiCo2O4, CoNiAl-LDH, and CoNiAl-LDH@NiCo2O4 performances as ORR catalysts in MFC cathode. Renew Energy 154:1263–1271
Theodosiou P, Greenman J, Ieropoulos I (2019) Towards monolithically printed Mfcs: development of a 3d-printable membrane electrode assembly (mea). Int J Hydrog Energy 44:4450–4462
He W, Wei J, Huang T, Zhang E (2020) Enhanced electricity production in single-chamber MFCs with air cathodes decorated by Fe–N–C catalysts derived from 5H-dibenz [b,f] azepine-5-carboxamide (Carbamazepine). Int J Hydrog Energy 45:17525–17532
Juang DF, Lee CH, Hsueh SC (2012) Comparison of electrogenic capabilities of microbial fuel cell with different light power on algae grown cathode. Bioresour Technol 123:23–29
Bakonyi P, Koók L, Rózsenberszki T et al (2020) Development and application of supported ionic liquid membranes in microbial fuel cell technology: a concise overview. Membranes (Basel) 10:10011016
Khalili HB, Mohebbi-Kalhori D, Afarani MS (2017) Microbial fuel cell (MFC) using commercially available unglazed ceramic wares: low-cost ceramic separators suitable for scale-up. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:8233–8241
Das I, Das S, Dixit R, Ghangrekar MM (2020) Goethite supplemented natural clay ceramic as an alternative proton exchange membrane and its application in microbial fuel cell. Ionics (Kiel). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03472-1
You J, Fan H, Winfield J, Ieropoulo IA (2020) Complete microbial fuel cell fabrication using additive layer manufacturing. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133051
Nagar H, Aniya V (2020) Microporous material induced composite membrane with reduced oxygen leakage for MFC application. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104117
Koroglu EO, Yoruklu HC, Demir A, Ozkaya B (2018) Scale-up and commercialization issues of the MFCs: challenges and implications. In: Biomass, biofuels, biochemicals: microbial electrochemical technology: sustainable platform for fuels, chemicals and remediation. Elsevier, 565–583
Taşkan E, Bulak S, Taşkan B et al (2019) Nitinol as a suitable anode material for electricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 128:118–125
Ardakani MN, Badalians Gholikandi G (2020) Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) in integration with anaerobic treatment processes (AnTPs) and membrane bioreactors (MBRs) for simultaneous efficient wastewater/sludge treatment and energy recovery - a state-of-the-art review. Biomass Bioenergy 141
Li C, Song Y, Wang X, Zhang Q (2020) Synthesis, characterization and application of S-TiO2/PVDF-g-PSSA composite membrane for improved performance in MFCs. Fuel 264:116847
Yang W, Li J, Fu Q et al (2021) Minimizing mass transfer losses in microbial fuel cells: theories, progresses and prospectives. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 136:110460
Kardi SN, Ibrahim N, Rashid NAA, Darzi GN (2019) Investigating effect of proton-exchange membrane on new air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cell configuration for bioenergy recovery from Azorubine dye degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:21201–21215
Fischer F, Sugnaux M, Savy C, Hugenin G (2018) Microbial fuel cell stack power to lithium battery stack: pilot concept for scale up. Appl Energy 230:1633–1644
Tremouli A, Greenman J, Ieropoulos I (2018) Investigation of ceramic MFC stacks for urine energy extraction. Bioelectrochemistry 123:19–25
Huang S, Zhang J, Pi J et al (2021) Long-term electricity generation and denitrification performance of MFCs with different exchange membranes and electrode materials. Bioelectrochemistry 140:107748
Chakraborty I, Sathe SM, Dubey BK, Ghangrekar MM (2020) Waste-derived biochar: applications and future perspective in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123587
He L, Du P, Chen Y et al (2017) Advances in microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment. Renew Sust Energ Rev 71:388–403
Acknowledgements
The authors of this article would like to express their gratitude to the Association of Chemical Engineers, BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus, for facilitating and giving them the opportunity to conduct the studies and research involved in the making of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, S., Bhatnagar, P., Dhingra, S. et al. Wastewater treatment and energy production by microbial fuel cells. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 13, 3569–3592 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01411-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01411-2