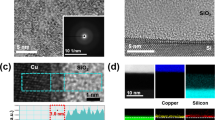
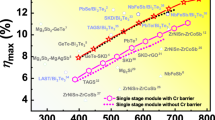
Abstract
We studied the improvement of interfacial stability and contact resistance by applying Cu with high electrical conductivity but high diffusivity to thin film type thermoelectric devices. Since the thin film device has a large surface to volume ratio, it is necessary to minimize the contact resistance occurring at the interface in order to minimize heat generation due to resistance. For the reliability of such a device, long duration phase stability is required, especially when using Cu electrodes with high diffusivity. The interconnect system, including Cu and the barrier materials, was selected based on a phase diagram with a thermodynamic-based calculation. The interlayer was required to improve the unstable interface to prevent the reaction of Cu and Bi2Te3. Ta and Mo, which are low diffusivity materials, were selected as candidates. Thermodynamic calculation results showed that Ta has a stable interface with Bi2Te3, while Mo reacts with Te. The calculation was confirmed by experiments, and it was determined that the longer the annealing process, the higher the contact resistance is when the Mo interlayer is applied, which is in accordance with the thermodynamic calculation. The thermodynamic calculations are a useful methodology when selecting materials with a stable interface with highly reactive chalcogenide materials.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bulman, G., Barletta, P., Lewis, J., Baldasaro, N., Manno, M., Bar-Cohen, A., Yang, B.: Superlattice-based thin-film thermoelectric modules with high cooling fluxes. Nat. Commun. 7, 10302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10302
Takashiri, M., Miyazaki, K., Tanaka, S., Kurosaki, J., Nagai, D., Tsukamoto, H.: Effect of grain size on thermoelectric properties of n-type nanocrystalline bismuth-telluride based thin films. J. Appl. Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2990774
Bailini, A., Donati, F., Zamboni, M., Russo, V., Passoni, M., Casari, C.S., Li Bassi, A., Bottani, C.E.: Pulsed laser deposition of Bi2Te3 thermoelectric films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254(4), 1249–1254 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.039
Agarwal, K., Sharma, R., Mehta, B.R.: Synthesis and characterization of Bi2Te3 nanostructured thin films. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15(4), 2882–2886 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2015.7441
Chowdhury, I., Prasher, R., Lofgreen, K., Chrysler, G., Narasimhan, S., Mahajan, R., Koester, D., Alley, R., Venkatasubramanian, R.: On-chip cooling by superlattice-based thin-film thermoelectrics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(4), 235–238 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.417
Snyder, G.J., Toberer, E.S.: Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat. Mater. 7(2), 105–114 (2008)
da Silva, L.W., Kaviany, M.: Micro-thermoelectric cooler: interfacial effects on thermal and electrical transport. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47(10–11), 2417–2435 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2003.11.024
Mizoshiri, M., Mikami, M., Ozaki, K., Shikida, M., Hata, S.: Lift-off patterning of thermoelectric thick films deposited by a thermally assisted sputtering method. Appl. Phys. Express (2014). https://doi.org/10.7567/apex.7.057101
Goncalves, L.M., Rocha, J.G., Couto, C., Alpuim, P., Min, G., Rowe, D.M., Correia, J.H.: Fabrication of flexible thermoelectric microcoolers using planar thin-film technologies. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17(7), S168–S173 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/17/7/s14
Yang, F., Zheng, S., Wang, H., Chu, W., Dong, Y.: A thin film thermoelectric device fabricated by a self-aligned shadow mask method. J. Micromech. Microeng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6439/aa64a3
Sullivan, O., Gupta, M.P., Mukhopadhyay, S., Kumar, S.: On-chip power generation using ultrathin thermoelectric generators. J. Electron. Packag. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4027995
Kwon, S.-D., Ju, B.-K., Yoon, S.-J., Kim, J.-S.: Fabrication of bismuth telluride-based alloy thin film thermoelectric devices grown by metal organic chemical vapor deposition. J. Electron. Mater. 38(7), 920–924 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0704-8
Takashiri, M., Shirakawa, T., Miyazaki, K., Tsukamoto, H.: Fabrication and characterization of bismuth–telluride-based alloy thin film thermoelectric generators by flash evaporation method. Sens. Actuators A 138(2), 329–334 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2007.05.030
Liu, W., Jie, Q., Kim, H.S., Ren, Z.: Current progress and future challenges in thermoelectric power generation: from materials to devices. Acta Mater. 87, 357–376 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.12.042
Jing, H., Li, Y., Xu, L., Han, Y., Lu, G., Zhang, H.: interfacial reaction and shear strength of SnAgCu/Ni/Bi2Te3-based TE materials during aging. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24(12), 4844–4852 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1809-2
Lo, L.-C., Wu, A.T.: Interfacial reactions between diffusion barriers and thermoelectric materials under current stressing. J. Electron. Mater. 41(12), 3325–3330 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-2275-3
Li, Z., Xiao, C., Zhu, H., Xie, Y.: Defect chemistry for thermoelectric materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(45), 14810–14819 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b08748
Lin, C.-F., Hau, N.Y., Huang, Y.-T., Chang, Y.-H., Feng, S.-P., Chen, C.-M.: Synergetic effect of Bi 2 Te 3 alloys and electrodeposition of Ni for interfacial reactions at solder/Ni/Bi 2 Te 3 joints. J. Alloy. Compd. 708, 220–230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.300
Gupta, R.P., Xiong, K., White, J.B., Cho, K., Alshareef, H.N., Gnade, B.E.: Low resistance ohmic contacts to Bi[sub 2]Te[sub 3] using Ni and Co Metallization. J. Electrochem. Soc. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3385154
Zhu, X., Cao, L., Zhu, W., Deng, Y.: Enhanced interfacial adhesion and thermal stability in bismuth telluride/nickel/copper multilayer films with low electrical contact resistance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201801279
Jeong, M.-W., Na, S., Shin, H., Park, H.-B., Lee, H.-J., Joo, Y.-C.: Thermomechanical in situ monitoring of Bi2Te3 thin film and its relationship with microstructure and thermoelectric performances. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14(4), 426–431 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0054-x
Fujimoto, S., Sano, S., Kajitani, T.: Analysis of diffusion mechanism of Cu in polycrystalline Bi2Te3-based alloy with the aging of electrical conductivity. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46(8A), 5033–5039 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1143/jjap.46.5033
Pennec, F., Peyrou, D., Leray, D., Pons, P., Plana, R., Courtade, F.: Impact of the surface roughness description on the electrical contact resistance of ohmic switches under low actuation forces. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2(1), 85–94 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcpmt.2011.2108655
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Creative Materials Discovery Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (2017M3D1A1040688). This work also was supported by the IT R&D program of MOTIE/KEIT [10049130]. Development of planar-type cooling technology for mobile applications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, MW., Lee, SY., Park, HB. et al. Stable Interconnect System for Horizontal Thermoelectric Coolers by Thermodynamic-Based Prediction. Electron. Mater. Lett. 15, 654–662 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00159-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00159-2