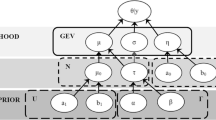
Abstract
In the present paper, the rainfall forecast information is analyzed using model and density based clustering algorithms and good model is fitted by using structural equation modelling and artificial neural networks. Shapiro-Wilk normality test for Water Level, In Flow, Period, Rainfall are 0.7694, 0.2388, 0.7651, 0.4382 respectively with same p-value \(< 2.2 \times 10^{-16}\). It shows that all are highly significantly non-normal. For the percentage on the Water Level, the variances were similar for Yes and No (Rainfall), significantly different, but for inflow the variances were not significantly different in the two groups, whereas for the period, the variances were similar for Yes and No (Rainfall), significantly different. The number of observations in the clusters 0 to cluster 9 are 18, 64, 39, 20, 19, 88, 41, 41, and 36. Here, cluster 0 represents the outlier in which we have 19 observations out of 366 observations in model based clustering. Furthermore, DBSCAN performs better for these data sets and can identify the correct set of clusters compared to k-means algorithms. The Fit indices for our structural equation model in which most of them show that our model is good to fit except the absolute type with Chi-square \(\left( \chi ^2\right) \). Finally, we use 10 fold cross validated MSE for the linear model. The cv.glm is 0.1252 and it is shown in the box plot.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhishek, K., Kumar, A., Ranjan, R., Kumar, S.: A rainfall prediction model using artificial neural network. In: 2012 IEEE Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium, pp. 82–87 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSGRC.2012.6287140
Ananias, D.R.S., Liska, G.R., Beijo, L.A., Liska, G.J.R., de Menezes, F.S.: The assessment of annual rainfall field by applying different interpolation methods in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. SN Appl. Sci. 3(7), 687 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04679-1
Avrithis, Y., Kalantidis, Y., Anagnostopoulos, E., Emiris, I.Z.: Web-Scale Image Clustering Revisited. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), ICCV ’15, pp. 1502–1510. IEEE Computer Society, USA (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.176
Basheer, I.A., Hajmeer, M.: Artificial neural networks: fundamentals, computing, design, and application. J. Microbiol. Methods 43(1), 3–31 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00201-3
Baumgartner, H., Homburg, C.: Applications of structural equation modeling in marketing and consumer research: A review. Int. J. Res. Mark. 13(2), 139–161 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8116(95)00038-0
Bentler, P.M.: Comparative fit indexes in structural models. (1990). https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.107.2.238
Bentler, P.M., Bonett, D.G.: Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychol. Bull. 88(3), 588–606 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.88.3.588
Byrne, B.M.: Structural equation modeling with AMOS: Basic concepts, applications, and programming, 2nd edn. Taylor & Francis/Routledge, New York (2010)
Chaplot, B.: Prediction of rainfall time series using soft computing techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 193(11), 721 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09388-1
Charaniya, N.A., Dudul, S.V.: Article: design of neural network models for daily rainfall prediction. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 61(14), 23–27 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5120/9997-4858
Devijver, P.A., Kittler, J.: Pattern recognition: A statistical approach. Prentice hall, Englewood Cliffs (1982)
Dikbas, F., Firat, M., Koc, A.C., Gungor, M.: Classification of precipitation series using fuzzy cluster method. Int. J. Climatol. 32(10), 1596–1603 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2350
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E.: Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis. John Willey & Sons, New York (1973)
Ester, M., Kriegel, H.P., Sander, J., Xu, X.: A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD’96, pp. 226–231. AAAI Press (1996)
Fayyad, U., Reina, C., Bradley, P.S.: Initialization of Iterative Refinement Clustering Algorithms. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD’98, pp. 194–198. AAAI Press (1998)
Felix, A.Y., Vinay, G., Akhik, G.: K -Means Cluster Using Rainfall and Storm Prediction in Machine Learning Technique. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 16, 3265–3269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1166/jctn.2019.8174
Fraley, C., Raftery, A.E.: Model-Based Clustering, Discriminant Analysis, and Density Estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 97(458), 611–631 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1198/016214502760047131
Ghasemi, A., Zahediasl, S.: Normality tests for statistical analysis: a guide for non-statisticians. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 10(2), 486–489 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.3505
Gorai, S., Ratha, D., Dhir, A.: Adapting Rainfall Variability to Flood Risk: A Case Study of the Ghaggar River Basin. J. Geol. Soc. India 97(11), 1347–1354 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1873-1
Han, J., Kamber, M., Tung, A.K.H.: Spatial clustering methods in data mining: A survey. In: Miller, H.J., Han, J. (eds.) Geographic data mining and knowledge discovery, pp. 33–50. Taylor and Francis, London and New York (2001)
Haq, D.Z., Rini Novitasari, D.C., Hamid, A., Ulinnuha, N., Arnita, Farida, Y., Nugraheni, R.R.D., Nariswari, R., Ilham, Rohayani, H., Pramulya, R., Widjayanto, A.: Long Short-Term Memory Algorithm for Rainfall Prediction Based on El-Nino and IOD Data. Procedia Computer Science 179, 829–837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.01.071
Haviluddin, H., Alfred, R.: Daily Network Traffic Prediction Based on Backpropagation Neural Network. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 8(24), 164–169 (2014)
Hoyle, R.: Structural Equation Modeling for Social and Personality Psychology. Sage Publications Ltd, London (2011). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781446287965. https://methods.sagepub.com/book/structural-equation-modeling-for-social-and-personality-psychology
Hu, L., Bentler, P.M.: Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 6(1), 1–55 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118
Jain, A., Srinivasulu, S.: Integrated approach to model decomposed flow hydrograph using artificial neural network and conceptual techniques. J. Hydrol. 317(3), 291–306 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.05.022
Jain, A.K., Dubes, R.C.: Algorithms for clustering data. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA (1988). http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=46712
Kaufman, L., Rousseeuw, P.J.: Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York (1990). https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470316801
Kavili, H., Imek, G.G.: An application of fuzzy clustering on prevalence of youth tobacco survey. Proc. Econ. Finan. 38, 70–76 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2212-5671(16)30178-2
Kline, R.B.: Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. Guilford Press, New York (2016). http://site.ebrary.com/id/11096679
Levene, H.: Robust Tests for Equality of Variance. In: I. Olkin, S.G. Ghurye, W. Hoeffding, W.G. Madow, H.B. Mann (eds.) Contrib to Probab Stat, vol. 2:, pp. 278–292. Stanford University Press., Stanford, CA (1960)
Li, Y., Wu, H.: A clustering method based on K-means algorithm. Phys. Proc. 25, 1104–1109 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.03.206
Lima, C.H.R., Kwon, H.H., Kim, Y.T.: A Bernoulli-Gamma hierarchical Bayesian model for daily rainfall forecasts. J. Hydrol. 599, 126317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126317
Liyew, C.M., Melese, H.A.: Machine learning techniques to predict daily rainfall amount. J. Big Data 8(1), 153 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00545-4
Lloyd, S.: Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 28(2), 129–137 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1982.1056489
MacCallum, R.C., Browne, M.W., Sugawara, H.M.: Power analysis and determination of sample size for covariance structure modeling. Psychol. Methods 1(2), 130–149 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.1.2.130
Ng, R.T., Han, J.: Efficient and Effective Clustering Methods for Spatial Data Mining. BT - VLDB’94, Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, September 12-15, 1994, Santiago de Chile, Chile (1994). http://www.vldb.org/conf/1994/P144.PDF
Park, H.S., Jun, C.H.: A simple and fast algorithm for K-medoids clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(2, Part 2), 3336–3341 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.01.039
Patil, B.M., Joshi, R.C., Toshniwal, D.: Impact of K-Means on the performance of classifiers for labeled data. In: International Conference on Contemporary Computing, pp. 423–434. Springer (2010)
Pearson, A.V., Hartley, H.O.: Biometrica Tables for Statisticians. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1972)
Pinidluek, P., Konyai, S., Sriboonlue, V.: Regionalization of rainfall in northeastern Thailand. Int. J. Geomate 18(68), 135–141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.21660/2020.68.9220
Ramos, M.C.: Divisive and hierarchical clustering techniques to analyse variability of rainfall distribution patterns in a Mediterranean region. Atmos. Res. 57(2), 123–138 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-8095(01)00065-5.
Ren, Y., Bai, G.: Determination of optimal SVM parameters by using GA/PSO. J. Comput. 5, 1160–1168 (2010)
Ridwan, W.M., Sapitang, M., Aziz, A., Kushiar, K.F., Ahmed, A.N., El-Shafie, A.: Rainfall forecasting model using machine learning methods: Case study Terengganu, Malaysia. Ain Shams Eng. J. 12(2), 1651–1663 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.09.011.
Salehnia, N., Salehnia, N., Ansari, H., Kolsoumi, S., Bannayan, M.: Climate data clustering effects on arid and semi-arid rainfed wheat yield: a comparison of artificial intelligence and K-means approaches. Int. J. Biometeorol. 63(7), 861–872 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01699-w
Saraçolu, R., Tütüncü, K., Allahverdi, N.: A fuzzy clustering approach for finding similar documents using a novel similarity measure. Expert Syst. Appl. 33(3), 600–605 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2006.06.002.
Satyanarayana, P., Srinivas, V.V.: Regionalization of precipitation in data sparse areas using large scale atmospheric variables - A fuzzy clustering approach. J. Hydrol. 405(3), 462–473 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.044.
Schermelleh-Engel, K., Moosbrugger, H., Müller, H.: Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Methods Psychol. Res. 8(2), 23–74 (2003)
Shapiro, S.S., Wilk, M.B.: An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 52(3/4), 591–611 (1965). https://doi.org/10.2307/2333709
Sharma, S., Mukherjee, S., Kumar, A., Dillon, W.R.: A simulation study to investigate the use of cutoff values for assessing model fit in covariance structure models. J. Bus. Res. 58(7), 935–943 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2003.10.007.
Shi, J., Malik, J.: Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(8), 888–905 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.868688
Snedecor, G., Cochran, W.: Statistical Methods, 8th, editio Iowa State University Press, Ames (1989)
Tucker, L.R., Lewis, C.: A reliability coefficient for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika 38(1), 1–10 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291170
Venkatesh, B., Nayak, P.C., Thomas, T., Jain, S.K., Tyagi, J.V.: Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall pattern in the Western Ghats region of India. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 133(4), 1089–1109 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-021-00796-z
Werbos, P.J.: Beyond Regression: New Tools for Prediction and Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. Ph.D. thesis, Harvard University (1974)
Wright, S.: On the nature of size factors. Genetics 3(4), 367 – 374 (1918). http://www.genetics.org/content/3/4/367.abstract
Wu, J., Long, J., Liu, M.: Evolving RBF neural networks for rainfall prediction using hybrid particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. Neurocomputing 148, 136–142 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2012.10.043.
Wu, X., Kumar, V., Ross Quinlan, J., Ghosh, J., Yang, Q., Motoda, H., McLachlan, G.J., Ng, A., Liu, B., Yu, P.S., Zhou, Z.H., Steinbach, M., Hand, D.J., Steinberg, D.: Top 10 algorithms in data mining. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 14(1), 1–37 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-007-0114-2
Xu, H., Ma, C., Lian, J., Xu, K., Chaima, E.: Urban flooding risk assessment based on an integrated k-means cluster algorithm and improved entropy weight method in the region of Haikou, China. J. Hydrol. 563, 975–986 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.06.060.
Yang, M.S., Hu, Y.J., Lin, K.C.R., Lin, C.C.L.: Segmentation techniques for tissue differentiation in MRI of Ophthalmology using fuzzy clustering algorithms. Magn. Reson. Imaging 20(2), 173–179 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0730-725X(02)00477-0.
Yilmaz, N., Inan, O., Uzer, M.S.: A new data preparation method based on clustering algorithms for diagnosis systems of heart and diabetes diseases. J. Med. Syst. 38(5), 48 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0048-7
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X.
Zhang, Q., Couloigner, I.: A New and Efficient K-Medoid Algorithm for Spatial Clustering BT - Computational Science and Its Applications - ICCSA 2005. pp. 181–189. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg (2005)
Zhao, Y., Karypis, G.: Empirical and theoretical comparisons of selected criterion functions for document clustering. Mach. Learn. 55(3), 311–331 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MACH.0000027785.44527.d6
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Fund for Improvement of S &T infrastructure in universities & higher educational institutions (FIST), Government of India(Reference number: SR/FST/MSI-107/ 2015(C)). The authors also thank DST(FIST) for providing financial support and Prof. S. Surianarayanan, School of Civil Engineering, Srinivasa Ramanujan Centre, SASTRA Deemed to be University, Kumbakonam, for providing the data set to enhance the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kannan, K., Menaga, A. An efficient approach in rainfall prediction around Sathanur Dam, India, by model based clustering, structural equation modelling (SEM) and artificial neural networks (ANN). Afr. Mat. 33, 89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13370-022-01023-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13370-022-01023-7