Abstract
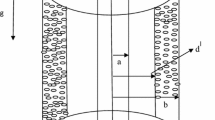
This work analyzes the behaviors of fully developed mixed convection flow of an incompressible and viscous fluid in a vertical micro-porous-annulus (MPA) taking into account the velocity slip and temperature jump at the outer surface of inner porous cylinder and inner surface of outer porous cylinder. The present study explores the effects of the suction/injection, mixed convection, the Knudsen number, Prandtl number and the radius ratio on the MPA hydrodynamic and thermal behaviours. It is interesting to remark that as suction/injection on the MPA increases, the fluid velocity and temperature is enhanced. In addition, the rate of heat transfer at outer surface of inner porous cylinder decrease with increase in Knudsen number for suction at the inner porous cylinder and simultaneous injection at the outer porous cylinder while the result is just contrast at inner surface of outer porous cylinder.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(C_p =\) :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
- \(D_h =\) :
-
Hdraulic diameter \([{2( {r_2 -r_1 })}]\)
- \(F_v =\) :
-
Tangential momentum accommodation coefficient
- \(F_t =\) :
-
Thermal accommodation coefficient
- \(g=\) :
-
Gravitational acceleratioin
- \(Gr=\) :
-
Grashof number
- \(GR=\) :
-
Mixed convection parameter \(( {Gr/Re})\)
- \(h=\) :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient
- \(k=\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \(Kn=\) :
-
Knudsen number
- \(Nu_0 =\) :
-
Rate of heat transfer at the outer surface of the inner porous cylinder
- \(Nu_1 =\) :
-
Rate of heat transfer at the inner surface of the outer porous cylinder
- \(P=\) :
-
Pressure difference
- \(Pr=\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(Re=\) :
-
Reynolds number
- \(r^*=\) :
-
Ratio of radius \((r_1 /r_2 )\)
- \(r_1 =\) :
-
Radius of the inner porous cylinder
- \(r_2 =\) :
-
Radius of the outer porous cylinder
- \(S =\) :
-
Suction/injection parameter
- \(T=\) :
-
Fluid temperature
- \(T_0 =\) :
-
Reference fluid temperature
- \(u=\) :
-
Axial velocity
- \(U=\) :
-
Dimensionless axial velocity
- \(V_0 =\) :
-
Constant suction/injection velocity
- \(z,r=\) :
-
Axial and radial coordinate, respectively
- \(Z,R=\) :
-
Dimensionless axial and radial coordinate, respectively
- \(\alpha =\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(\beta =\) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient
- \(\beta _t ,\beta _\nu =\) :
-
Dimensionless variables
- \(\gamma =\) :
-
Ratio of specific heats (\(C_p /C_v )\)
- \(\lambda =\) :
-
Molecular mean free path
- \(\mu =\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- \(\theta =\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\rho _0 =\) :
-
Density
- \(\nu =\) :
-
Fluid kinematic viscosity
- \(1=\) :
-
Value on inner cylinder
- \(2=\) :
-
Value on outer cylinder
- \(b=\) :
-
Bulk value
- \(s_1 =\) :
-
Fluid properties on inner cylinder
- \(s_2 =\) :
-
Fluid properties on outer cylinder
- \(m=\) :
-
Mean value
References
Womac, D.J., Incropera, F.P., Ramadhyani, S.: Correlating equations for impingement cooling of small heat sources with multiple circular liquidjets. ASME J. Heat Transfer 116, 482–486 (1994)
Darabi, J., Ekula, K.: Development of a chip-integrated micro cooling device. Microelectron. J. 34, 1067–1074 (2003)
Amon, C.H., Murthyj, Y., and Yao S.C.: MEMS enabled thermal management of high heat flux devices EDIFICE: embedded droplet impingement for integrated cooling of electronics, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. pp. 231–242. (2001)
Schaaf, S.A., Chambre, P.L.: Flow of Rarefied Gases. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1961)
Chen, C.K., Weng, H.C.: Natural convection in a vertical microchannel. J. Heat Transfer 127, 1053–1056 (2005)
Jha, B.K., Aina, B., Joseph, S.B.: Natural convection flow in a vertical micro-channel with suction/injection. J. Process Mech. Eng. (2013). doi:10.1177/0954408913492719
Chen, C.K., Weng, H.C.: Natural convection in a vertical microchannel with thermal creep in a vertical microchannel. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 3107–3118 (2005)
Weng, H.C., Chen, C.K.: Drag reduction and heat transfer enhancement over a heated wall of a vertical annular microchannel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 52, 1075–1079 (2009)
Jha, B.K., Aina, B., Shehu, A.M.: Combined effects of suction/Injection and wall surface curvature on natural convection flow in a vertical micro-porous-annulus. J. Thermophys. Aerodyn. [in press].
Avci, M., Aydin, O.: Mixed convection in a vertical parallel plate microchannel. ASME J. Heat Transfer 129, 162–166 (2007)
Avci, M., Aydin, O.: Mixed convection in a vertical parallel plate microchannel with asymmetric wall heat fluxes. ASME J. Heat Transfer 129, 1091–1095 (2007)
Avci, M., Aydin, O.: Mixed convection in a vertical microannulus between two concemtric microtubes. ASME J. Heat Transfer 131, 014502–014504 (2009)
Hajmohammadi, M.R., Nourazer, S.S.: on the insertion of a thin gas layer in micro cylindrical Couette flows involving power-law liquids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 75, 97–108 (2014)
Hajmohammadi, M.R., Nourazer, S.S., Campo, A.: Analytical solution for two-phase flow between two rotating cylinders filled with power law liquid and a micro layer of gas. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 28(5), 1–7 (2014). doi:10.1007/s12206-013-0913-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The constants used in the work are as follows:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, B.K., Aina, B. Mathematical modelling and exact solution of steady fully developed mixed convection flow in a vertical micro-porous-annulus. Afr. Mat. 26, 1199–1213 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13370-014-0277-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13370-014-0277-4