Abstract
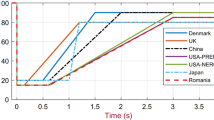
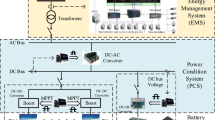
Due to favourable economic and environmental concerns, reduced power losses, and technological advancements in data science, large-scale renewable energy sources (RESs) are being inserted into smart microgrids (MGs). Generally, these resources are inserted at the distribution level and feed consumers locally with better reliability. The planning and stable operation of the power networks are complicated at numerous levels as a result of large-scale renewable integration, as the infeed from renewable sources like wind and solar is highly intermittent and uncertain, significantly affecting the resilient, intelligent, and optimal operation of the power system. The creation of scenarios is an essential step in the planning and stable operation of renewable-rich power systems. Scenarios can be generated based on seasonal events to mitigate growing complexity and intermittency. In this paper, time-series solar data is used for forecasting solar irradiance using long-short-term memory (LSTM). Besides, a cost-based optimisation model has been developed by using stochastic programming to obtain both the optimal sizing and optimal switching sequence of distributed units as well as the optimal number of required units. The stochastic nature of solar and load demand is considered in beta (\(\beta \)) distribution. The objective function formulated covers different costs, like capital, operational, and switching costs associated with required units. The running cost incorporated with the capital cost gives us a broader design for planning the MG, thus making it both planning and operational problem. The entire proposed MG planning problem has been developed in a Python and MATLAB ® environment.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DG:
-
Distributed generation
- DEG:
-
Diesel engine generator
- ESS:
-
Energy storage system
- LSTM:
-
Long short-term memory
- ML:
-
Machine learning
- NOCT:
-
Normal optimum cell temperature
- OM:
-
Operation and maintenance
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- SR:
-
Spinning reserve
- RES:
-
Renewable energy sources
- s :
-
Index of generated scenario
- T :
-
Data samples
- t :
-
Index of time span
- \(C_\textrm{chr}\)(S,t)\(\backslash D_\textrm{chr}\)(s,t):
-
Charging\(\backslash \)discharging capacity of BS unit.
- \({\text {IC}}_\textrm{spv}\) :
-
Installation cost of solar photo voltaic
- \(X_\textrm{spv}\) :
-
Rating of solar photo voltaic
- \({\text {OM}}_\textrm{SPV}\) :
-
Operation and maintenance cost
- \(N_\textrm{spv}\) :
-
Total no. of panels
- \({\text {IC}}_\textrm{bio}\) :
-
Installation cost related to biogas
- \(X_\textrm{bio}\) :
-
Rating of biogas
- \(N_\textrm{DEG}\) :
-
Number of diesel generators
- \(N_\textrm{batt}\) :
-
Number of batteries
- \({\text {CE}}_\textrm{tax}\) :
-
Carbon emission tax
- \(T_\textrm{spv}\) :
-
Cell temperature
- \(X_\textrm{batt}\) :
-
Battery rating
- \(C_{d,\textrm{run}}\) :
-
Daily running cost
- \({\text {SR}}_\textrm{min}\) :
-
Minimum spinning reserve
References
Ahmed, S.D.; Al-Ismail, F.S.M.; Shafiullah, M.; Al-Sulaiman, F.A.; El-Amin, I.M.: Grid integration challenges of renewable energy: a review. IEEE Access 8, 10857–10878 (2020)
Sun, M.; Teng, F.; Konstantelos, I.; Strbac, G.: An objective-based scenario selection method for transmission network expansion planning with multivariate stochasticity in load and renewable energy sources. Energy 145, 871–885 (2018)
Xie, H.; Zheng, S.; Ni, M.: Microgrid development in china: a method for renewable energy and energy storage capacity configuration in a megawatt-level isolated microgrid. IEEE Electr. Mag. 5(2), 28–35 (2017)
Solanki, B.V.; Bhattacharya, K.; Ca nizares, C.A.: A sustainable energy management system for isolated microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 8(4), 1507–1517 (2017)
[Online]. Available: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/global-greenhouse-gas-emissions-data
Rehman, N.; Mufti, M.; Gupta, N.: Steady state analysis of distribution system with wind and solar under various electric vehicle load models. In: 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON). IEEE, pp. 1–6 (2021)
Rehman, N.; Gupta, N., et al.: Optimal location of electric vehicles in a wind integrated distribution system using reptile search algorithm. Distrib. Gener. Altern. Energy J. 141–168 (2023)
Rehman, N.; Mufti, M.-U.D.; Gupta, N.: Metaheuristic method for a wind-integrated distribution network to support voltage stabilisation employing electric vehicle loads. Appl. Sci. 13(4), 2254 (2023)
Hart, E.K.; Jacobson, M.Z.: A Monte Carlo approach to generator portfolio planning and carbon emissions assessments of systems with large penetrations of variable renewables. Renew. Energy 36(8), 2278–2286 (2011)
Kumar, M.; Tyagi, B.: An optimal multivariable constrained nonlinear (mvcnl) stochastic microgrid planning and operation problem with renewable penetration. IEEE Syst. J. 14(3), 4143–4154 (2020)
Ahmed, W.; Ansari, H.; Khan, B.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, S.M.; Mehmood, C.A.A.; Qureshi, M.B.; Hussain, I.; Jawad, M.; Khan, M.U.S.; et al.: Machine learning based energy management model for smart grid and renewable energy districts. IEEE Access 8, 185059–185078 (2020)
Ali, E.; Abd Elazim, S.; Abdelaziz, A.: Optimal allocation and sizing of renewable distributed generation using ant lion optimization algorithm. Electr. Eng. 100, 99–109 (2018)
Hafez, O.; Bhattacharya, K.: Optimal planning and design of a renewable energy based supply system for microgrids. Renew. Energy 45, 7–15 (2012)
Duchesne, L.; Karangelos, E.; Wehenkel, L.: Recent developments in machine learning for energy systems reliability management. Proc. IEEE 108(9), 1656–1676 (2020)
Jiayi, H.; Chuanwen, J.; Rong, X.: A review on distributed energy resources and microgrid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 12(9), 2472–2483 (2008)
Ahmed, W.; Ansari, H.; Khan, B.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, S.M.; Mehmood, C.A.A.; Qureshi, M.B.; Hussain, I.; Jawad, M.; Khan, M.U.S.; et al.: Machine learning based energy management model for smart grid and renewable energy districts. IEEE Access 8, 185 059-185 078 (2020)
Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, B.; Lin, C.: Data-driven dg capacity assessment method for active distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 32(5), 3946–3957 (2016)
Jabbari-Sabet, R.; Moghaddas-Tafreshi, S.-M.; Mirhoseini, S.-S.: Microgrid operation and management using probabilistic reconfiguration and unit commitment. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 75, 328–336 (2016)
Rigo-Mariani, R.; Sareni, B.; Roboam, X.: Integrated optimal design of a smart microgrid with storage. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 8(4), 1762–1770 (2015)
Sharifzadeh, M.; Sikinioti-Lock, A.; Shah, N.: Machine-learning methods for integrated renewable power generation: a comparative study of artificial neural networks, support vector regression, and gaussian process regression. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 108, 513–538 (2019)
Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Lei, H.; Cui, B.; Li, S.: Incorporating energy storage and user experience in isolated microgrid dispatch using a multi-objective model. IET Renew. Power Gener. 13(6), 973–981 (2019)
Shishkov, E.; Pronichev, A.; Soldusova, E.: Microgrid energy management system for reducing required power reserves, pp. 1–4 (2019).
Giraldo, J.S.; Castrillon, J.A.; Lopez, J.C.; Rider, M.J.; Castro, C.A.: Microgrids energy management using robust convex programming. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 10(4), 4520–4530 (2018)
Xie, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Mei, S.: Operationally constrained optimal dispatch of multiple pulsed loads in an isolated microgrid, pp. 1–5 (2018)
Nejabatkhah, F.; Li, Y.W.; Nassif, A.B.; Kang, T.: Optimal design and operation of a remote hybrid microgrid. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 3(1), 3–13 (2018)
Hart, E.K.; Jacobson, M.Z.: A Monte Carlo approach to generator portfolio planning and carbon emissions assessments of systems with large penetrations of variable renewables. Renew. Energy 36(8), 2278–2286 (2011)
Pannala, S.; Patari, N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Padhy, N.P.: Effective control and management scheme for isolated and grid connected dc microgrid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 56(6), 6767–6780 (2020)
Liu, P.; Cai, Z.; Xie, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.: A decomposition-coordination planning method for flexible generation resources in isolated microgrids. IEEE Access 7, 76 720-76 730 (2019)
Bani-Ahmed, A.; Rashidi, M.; Nasiri, A.; Hosseini, H.: Reliability analysis of a decentralized microgrid control architecture. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 10(4), 3910–3918 (2018)
Guo, Y.; Zhao, C.: Islanding-aware robust energy management for microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 9(2), 1301–1309 (2016)
Sengupta, M.; Xie, Y.; Lopez, A.; Habte, A.; Maclaurin, G.; Shelby, J.: The national solar radiation data base (nsrdb). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 89, 51–60 (2018)
Narayan, A.; Ponnambalam, K.: Risk-averse stochastic programming approach for microgrid planning under uncertainty. Renew. Energy 101, 399–408 (2017)
[Online]. Available: https://www.nrel.gov
Wang, K.; Qi, X.; Liu, H.; Song, J.: Deep belief network based k-means cluster approach for short-term renewable power forecasting. Energy 165, 840–852 (2018)
Jung, J.; Broadwater, R.P.: Current status and future advances for wind speed and power forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 31, 762–777 (2014)
Wang, H.; Huang, J.: Joint investment and operation of microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 8(2), 833–845 (2015)
Johansen, T.A.; Fossen, T.I.; Berge, S.P.: Constrained nonlinear control allocation with singularity avoidance using sequential quadratic programming. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 12(1), 211–216 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahangar, P.A., Lone, S.A. & Gupta, N. A Data-Driven-Based Optimal Planning of Renewable Rich Microgrid System. Arab J Sci Eng 49, 6241–6257 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08153-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08153-5