Abstract
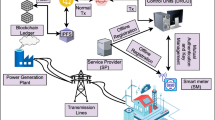
Due to recent technical breakthroughs in wireless communication and the Internet of Things (IoT), the smart grid (SG) has been recognized as a next-generation network for intelligent and efficient electric power transmission. Electric vehicle charging is becoming one of the most popular SG application. However, in SG environment the communication between a vehicle user and smart meter is mostly performed using insecure channel for managing demand response during peak hours. This raises serious security and privacy issues. Motivated from the aforementioned challenges, this paper presents a secure and privacy-preserving framework for IoT-enabled SG environment. The proposed framework first uses a secure mutual authentication scheme to register and exchange session key among SG participants. Second, a deep learning method that uses a stacked sparse denoising autoencoder to convert data into a new encoded format is suggested. The attention-based truncated long short-term memory uses this modified data to identify intrusions. The proposed blockchain architecture uses the proof of authentication consensus mechanism to propagate regular transactions in order to validate data integrity and prevent data poisoning attacks. The suggested framework outperforms several current state-of-the-art solutions in terms of security and numerical discoveries.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jogunola, O.; Adebisi, B.; Anoh, K.; Ikpehai, A.; Hammoudeh, M.; Harris, G.: Multi-commodity optimization of peer-to-peer energy trading resources in smart grid. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 10(1), 29–39 (2022)
Avancini, D.B.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Rabêlo, R.A.; Das, A.K.; Kozlov, S.; Solic, P.: A new IoT-based smart energy meter for smart grids. Int. J. Energy Res. 45(1), 189–202 (2021)
Hammoudeh, M.; Epiphaniou, G.; Belguith, S.; Unal, D.; Adebisi, B.; Baker, T.; Kayes, A.S.M.; Watters, P.: A service-oriented approach for sensing in the internet of things: Intelligent transportation systems and privacy use cases. IEEE Sens. J. 21(14), 15753–15761 (2021)
Srinivas, J.; Das, A.K.; Li, X.; Khan, M.K.; Jo, M.: Designing anonymous signature-based authenticated key exchange scheme for internet of things-enabled smart grid systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 17(7), 4425–4436 (2020)
Siniosoglou, I.; Radoglou-Grammatikis, P.; Efstathopoulos, G.; Fouliras, P.; Sarigiannidis, P.: A unified deep learning anomaly detection and classification approach for smart grid environments. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 18(2), 1137–1151 (2021)
Anoh, K.; Ikpehai, A.; Bajovic, D.; Jogunola, O.; Adebisi, B.; Vukobratovic, D.; Hammoudeh, M.: Virtual microgrids: a management concept for peer-to-peer energy trading. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Future Networks and Distributed Systems, ser. ICFNDS ’18. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2018) (Online). https://doi.org/10.1145/3231053.3231096
Wazid, M.; Das, A.K.; Kumar, N.; Rodrigues, J.J.: Secure three-factor user authentication scheme for renewable-energy-based smart grid environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 13(6), 3144–3153 (2017)
Park, K.; Lee, J.; Das, A. K.; Park, Y.: Bpps:blockchain-enabled privacy-preserving scheme for demand-response management in smart grid environments. In: IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, pp. 1–1 (2022)
Rjaibi, W.; Hammoudeh, M.: Enhancing and simplifying data security and privacy for multitiered applications. J. Parall. Distrib. Comput. 139, 53–64 (2020)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Islam, A.K.M.N.; Shorfuzzaman, M.: Permissioned blockchain and deep-learning for secure and efficient data sharing in industrial healthcare systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 1, 1 (2022)
Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R.; Srivastava, G.: P2tif: a blockchain and deep learning framework for privacy-preserved threat intelligence in industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 1, 1 (2022)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Srivastava, G.: Sp2f: a secured privacy-preserving framework for smart agricultural unmanned aerial vehicles. Comput. Networks 187, 107819 (2021)
Kumar, P.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R.: Tp2sf: A trustworthy privacy-preserving secured framework for sustainable smart cities by leveraging blockchain and machine learning. J. Syst. Archit. 115, 101954 (2021)
Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R.; Jolfaei, A.; Islam, A.N.: A blockchain-orchestrated deep learning approach for secure data transmission in IoT-enabled healthcare system. J. Parall. Distrib. Comput. 172, 69–83 (2023)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Aloqaily, M.; Aljuhani, A.: Deep learning-based blockchain for secure zero touch networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 1, 1–7 (2022)
Kumar, R.; Aljuhani, A.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Franklin, A.; Jolfaei, A.: Blockchain-enabled secure communication for unmanned aerial vehicle (uav) networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th International ACM Mobicom Workshop on Drone Assisted Wireless Communications for 5G and Beyond, ser. DroneCom ’22, pp. 37–42. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2022) (Online). https://doi.org/10.1145/3555661.3560861
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Aljuhani, A.; Islam, A.K.M.N.; Jolfaei, A.; Garg, S.: Deep learning and smart contract-assisted secure data sharing for IoT-based intelligent agriculture. IEEE Intell. Syst. 1, 1–8 (2022)
Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Franklin, A.A.; Jolfaei, A.: Blockchain and deep learning empowered secure data sharing framework for softwarized uavs. In: IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops) 2022, 770–775 (2022)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Franklin, A.A.; Jolfaei, A.: Blockchain and deep learning for cyber threat-hunting in software-defined industrial IoT. In: IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops) 2022, 776–781 (2022)
Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Franklin, A.A.; Garg, S.; Singh, S.: Blockchain and deep learning for secure communication in digital twin empowered industrial IoT network. IEEE Trans. Network Sci. Eng. 1, 1–13 (2022)
Odelu, V.; Das, A.K.; Wazid, M.; Conti, M.: Provably secure authenticated key agreement scheme for smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 9(3), 1900–1910 (2016)
Kumar, N.; Aujla, G.S.; Das, A.K.; Conti, M.: Eccauth: a secure authentication protocol for demand response management in a smart grid system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 15(12), 6572–6582 (2019)
Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Srivastava, G.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Xiong, N.N.: Ppsf: a privacy-preserving and secure framework using blockchain-based machine-learning for IoT-driven smart cities. IEEE Trans. Network Sci. Eng. 8(3), 2326–2341 (2021)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Garg, S.; Hassan, M.M.: Bdtwin: an integrated framework for enhancing security and privacy in cybertwin-driven automotive industrial internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 1, 1 (2021)
Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R.: Bdedge: blockchain and deep-learning for secure edge-envisioned green cavs. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Networking 1, 1 (2022)
Gai, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.: Permissioned blockchain and edge computing empowered privacy-preserving smart grid networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(5), 7992–8004 (2019)
Bera, B.; Saha, S.; Das, A.K.; Vasilakos, A.V.: Designing blockchain-based access control protocol in IoT-enabled smart-grid system. IEEE Internet Things J. 8(7), 5744–5761 (2021)
Khoei, T.T.; Aissou, G.; Hu, W.C.; Kaabouch, N.: Ensemble learning methods for anomaly intrusion detection system in smart grid. In: IEEE International Conference on Electro Information Technology (EIT) 2021, 129–135 (2021)
Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.; Ahmim, A.; Derdour, M.; Janicke, H.: Rdtids: rules and decision tree-based intrusion detection system for Internet-of-Things networks. Fut. Internet 12(3), 44 (2020)
Khan, S.; Kifayat, K.; Kashif Bashir, A.; Gurtov, A.; Hassan, M.: Intelligent intrusion detection system in smart grid using computational intelligence and machine learning. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 32(6), e4062 (2021)
Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Han, G.; Rodrigues, J.J.: Intrusion detection based on hybrid classifiers for smart grid. Comput. Electr. Eng. 93, 107212 (2021)
Alsaedi, A.; Moustafa, N.; Tari, Z.; Mahmood, A.; Anwar, A.: Ton_iot telemetry dataset: a new generation dataset of IoT and IIoT for data-driven intrusion detection systems. IEEE Access 8, 165130–165150 (2020)
Booij, T.M.; Chiscop, I.; Meeuwissen, E.; Moustafa, N.; den Hartog, F.T.H.: Ton_IoT: the role of heterogeneity and the need for standardization of features and attack types in IoT network intrusion datasets. IEEE Internet Things J. 1, 1 (2021)
Gad, A. R.; Nashat, A. A.; Barkat, T. M.: Intrusion detection system using machine learning for vehicular ad hoc networks based on ton-IoT dataset. IEEE Access (2021)
Dolev, D.; Yao, A.: On the security of public key protocols. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 29(2), 198–208 (1983)
Canetti, R.; Krawczyk, H.: Universally composable notions of key exchange and secure channels. In: International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, pp. 337–351. Springer (2002)
Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Gui, W.; Yin, H.; Jahanshahi, H.: Toward robust fault identification of complex industrial processes using stacked sparse-denoising autoencoder with softmax classifier. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2021)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Kumar, N.; Hassan, M.M.: A privacy-preserving-based secure framework using blockchain-enabled deep-learning in cooperative intelligent transport system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 1, 1–12 (2021)
Moustafa, D.N.: Ton_iot datasets for cybersecurity applications based artificial intelligence (2019) (Online). https://www.unsw.adfa.edu.au/unsw-canberra-cyber/cybersecurity/ADFA-ton-iot-Datasets/. Accessed 10 December 2021
Booij, T.M.; Chiscop, I.; Meeuwissen, E.; Moustafa, N.; den Hartog, F.T.: Ton_IoT: The role of heterogeneity and the need for standardization of features and attack types in IoT network intrusion data sets. IEEE Internet Things J. 9(1), 485–496 (2021)
Koroniotis, N., Moustafa, N., Sitnikova, E., Turnbull, B.: The bot-IoT dataset (2018). https://cloudstor.aarnet.edu.au/plus/s/umT99TnxvbpkkoE (Online). Accessed 15 March 2021.
Koroniotis, N.; Moustafa, N.; Sitnikova, E.; Turnbull, B.: Towards the development of realistic botnet dataset in the internet of things for network forensic analytics: Bot-IoT dataset. Fut. Gener. Comput. Syst. 100, 779–796 (2019)
Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R.: A distributed framework for detecting DDoS attacks in smart contract-based blockchain-IoT systems by leveraging fog computing. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 32(6), e4112 (2021)
Kumar, P.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R.: Pefl: deep privacy-encoding-based federated learning framework for smart agriculture. IEEE Micro 42(1), 33–40 (2022)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, R.; Gupta, G.P.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Srivastava, G.: Sp2f: a secured privacy-preserving framework for smart agricultural unmanned aerial vehicles. Comput. Netw. 187, 107819 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, C., Chittora, P. Secure and Privacy-Preserving Framework for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid Environment. Arab J Sci Eng 49, 3063–3078 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07900-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07900-y