Abstract
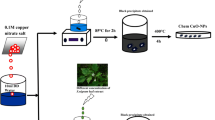
This contribution presents a novel method for simple and rapid colorimetric detection of Hg(II) and Fe(II) ions in real samples using silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The AgNPs were green-synthesized in aqueous solution using γ-irradiated chitosan as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The γ-chitosan stabilized AgNPs were found to be spherical with a diameter of 11.39 ± 2.23 nm. The AgNPs are highly selective for Hg(II) and Fe(II) ions, and when Hg(II) is present in solution, the yellowish AgNPs solution is turned to light yellow, while in the presence of Fe(II) the color of the AgNPs solution is changed to dark brown. The change of solution color is proposed via (i) The reoxidation of Ag(0) in AgNPs to Ag(I) for the Hg(II) detection and (ii) The aggregation of AgNPs in solution for the Fe(II) detection. Under optimal conditions, the method exhibits good linearity from 0.5 to 5.0 ppm (r2 = 0.9965) for Hg(II) and from 0.05 to 10.0 ppm (r2 = 0.9994) for Fe(II). The limit of detections (LODs) for Hg(II) and Fe(II) analyses are 0.22 and 0.18 ppm, respectively. Tap waters spiked with both ions show excellent percentage recoveries (93.48–99.53%) with good precision (%RSD < 5%). The developed method was for the first time successfully applied to the assessment of Fe(II) contents in pharmaceutical products, and has potential to be developed as an effective detection kit for assessing Hg(II) and Fe(II) ions in real samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- AAS/AES:
-
Atomic absorption/emission spectrometry
- ICP-MS:
-
Inductively coupled plasma spectrometry
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
- UV-Vis:
-
Ultraviolet-visible
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron micrographs
- EDX:
-
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer
- FAAS:
-
Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy
- AOAC:
-
Association of Official Analytical Chemists
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
- ppm:
-
Parts per million
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- ND:
-
Not detected
- ΔA:
-
Absorbance ratio
- API:
-
Active pharmaceutical ingredients
- γ:
-
Gamma
- AgNPs:
-
Silver nanoparticles
References
Park, J.D.; Zheng, W.: Human exposure and health effects of inorganic and elemental mercury. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 45(6), 344–352 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.2012.45.6.344
Abbaspour, N.; Hurrell, R.; Kelishadi, R.: Review on iron and its importance for human health. J. Res. Med. Sci. 19(2), 164–174 (2014)
Shrivastava, P.; Jain, V.K.; Nagpal, S.: Nanoparticle intervention for heavy metal detection: a review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 17, 100667 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100667
Fakayode, S.O.; King, A.G.; Yakubu, M.; Mohammed, A.K.; Pollard, D.A.: Determination of Fe content of some food items by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS): a guided-inquiry learning experience in instrumental analysis laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 89(1), 109–113 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ed1011585
Shamspur, T.; Sheikhshoaie, I.; Mashhadizadeh, M.H.: Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) determination of iron(iii) after preconcentration on to modified analcime zeolite with 5-((4-nitrophenylazo)-N-(2′,4′-dimethoxyphenyl))salicylaldimine by column method. J. Anal. At. Spect. 20(5), 476–478 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1039/B416097E
Singh, N.; Chauhan, S.; Singh, K.; Saud, T.; Saxena, M.; Soni, D.; Mandal, T.K.; Bassin, J.K.; Gupta, P.K.: Determination of arsenic and mercury metals in suspended particulate matter by flame/flameless atomic absorption spectrometer. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 1(2), 112–117 (2010). https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2010.014
Ozbek, N.; Akman, S.: Method development for the determination of calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, iron, potassium, phosphorus and zinc in different types of breads by microwave induced plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Food Chem. 200, 245–248 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.043
Astolfi, M.L.; Protano, C.; Marconi, E.; Piamonti, D.; Massimi, L.; Brunori, M.; Vitali, M.; Canepari, S.: Simple and rapid method for the determination of mercury in human hair by cold vapour generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Microchem. J. 150, 104186 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104186
Rodrigues, S.S.M.; Lima, A.S.; Teixeira, L.S.G.; Korn, M.D.G.A.; Santos, J.L.M.: Determination of iron in biodiesel based on fluorescence quenching of CdTe quantum dots. Fuel 117, 520–527 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.045
dos Santos, J.S.; de la Guárdia, M.; Pastor, A.; dos Santos, M.L.P.: Determination of organic and inorganic mercury species in water and sediment samples by HPLC on-line coupled with ICP-MS. Talanta 80(1), 207–211 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.06.053
Terán-Baamonde, J.; Bouchet, S.; Tessier, E.; Amouroux, D.: Development of a large volume injection method using a programmed temperature vaporization injector–gas chromatography hyphenated to ICP-MS for the simultaneous determination of mercury, tin and lead species at ultra-trace levels in natural waters. J. Chromatogr. A 1547, 77–85 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.02.056
Shariff, R.; Aachary, A.A.; Pacquette, L.H.; Mittal, A.K.; Girdhar, R.: Analytical method validation and determination of iron and phosphorus in vegetable oil by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry with microwave assisted digestion. Anal. Lett. 51(11), 1774–1788 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2017.1387554
Karthika, A.; Ramasamy Raja, V.; Karuppasamy, P.; Suganthi, A.; Rajarajan, M.: Electrochemical behaviour and voltammetric determination of mercury (II) ion in cupric oxide/poly vinyl alcohol nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchem. J. 145, 737–744 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.11.030
Locatelli, C.; Melucci, D.: Voltammetric determination of ultra-trace total mercury and toxic metals in meals. Food Chem. 130(2), 460–466 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.070
Qu, J.-W.; Song, P.; Gong, X.; Ruan, M.-B.; Xu, W.-L.: Electroanalysis of iron in groundwater by defective carbon black modified electrode. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 49(6), e21112–e21117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(21)60106-8
Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Chen, L.: Nanomaterial-based optical sensors for mercury ions. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 82, 175–190 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.05.015
Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, J.; You, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, L.: Colorimetric detection of heavy metal ions with various chromogenic materials: Strategies and applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 441, 129889 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129889
Buledi, J.A.; Amin, S.; Haider, S.I.; Bhanger, M.I.; Solangi, A.R.: A review on detection of heavy metals from aqueous media using nanomaterial-based sensors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 28(42), 58994–59002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07865-7
Xie, Y.: Colorimetric determination of Hg(II) via the gold amalgam induced deaggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 185(7), 351 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2900-9
Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.: Fluorescent and colorimetric assay for determination of Cu(II) and Hg(II) using AuNPs reduced and wrapped by carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 189(1), 10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05111-6
Lou, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.: Blue-to-Red colorimetric sensing strategy for Hg2+ and Ag+ via redox-regulated surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 3(5), 1568–1573 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/am200130e
Chen, L.; Fu, X.; Lu, W.; Chen, L.: Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Sensing of Hg2+ Based on the Morphology Transition of Silver Nanoprisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 5(2), 284–290 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am3020857
Chen, L.; Li, J.; Chen, L.: Colorimetric detection of mercury species based on functionalized gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6(18), 15897–15904 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am503531c
Nguyen, T.H.A.; Nguyen, V.-C.; Phan, T.N.H.; Le, V.T.; Vasseghian, Y.; Trubitsyn, M.A.; Nguyen, A.-T.; Chau, T.P.; Doan, V.-D.: Novel biogenic silver and gold nanoparticles for multifunctional applications: Green synthesis, catalytic and antibacterial activity, and colorimetric detection of Fe(III) ions. Chemosphere 287, 132271–135564 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132271
Prema, P.; Veeramanikandan, V.; Rameshkumar, K.; Gatasheh, M.K.; Hatamleh, A.A.; Balasubramani, R.; Balaji, P.: Statistical optimization of silver nanoparticle synthesis by green tea extract and its efficacy on colorimetric detection of mercury from industrial waste water. Environ. Res. 204, 111915 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111915
Sabela, M.; Balme, S.; Bechelany, M.; Janot, J.-M.; Bisetty, K.: A review of gold and silver nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensing assays. Adv. Eng. Mater. 19(12), 1700270 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201700270
Govindan, S.; Nivethaa, E.A.K.; Saravanan, R.; Narayanan, V.; Stephen, A.: Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–silver nanocomposite. Appl. Nanosci. 2(3), 299–303 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-012-0109-5
Venkatesham, M.; Ayodhya, D.; Madhusudhan, A.; Veera Babu, N.; Veerabhadram, G.: A novel green one-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles using chitosan: catalytic activity and antimicrobial studies. Appl. Nanosci. 4(1), 113–119 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-012-0180-y
Mori, Y.; Ono, T.; Miyahira, Y.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Matsui, T.; Ishihara, M.: Antiviral activity of silver nanoparticle/chitosan composites against H1N1 influenza A virus. Nanoscale Res Lett 8(1), 93 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276x-8-93
Torabfam, M.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H.: Microwave-enhanced silver nanoparticle synthesis using chitosan biopolymer: optimization of the process conditions and evaluation of their characteristics. Green Process. Synthesis 7(6), 530–537 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2017-0139
Zaheer, Z.: Chitosan-capped silver nanoparticles: fabrication, oxidative dissolution, sensing properties, and antimicrobial activity. J. Polym. Res. 28(9), 348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02673-0
Mirajkar, S.; Rathod, P.; Pawar, B.; Penna, S.; Dalvi, S.: γ-Irradiated chitosan mediates enhanced synthesis and antimicrobial properties of chitosan-silver (Ag) Nanocomposites. ACS Omega 6(50), 34812–34822 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c05358
Lim, L.-Y.; Khor, E.; Koo, O.: γ Irradiation of chitosan. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 43(3), 282–290 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(199823)43:3%3c282::AID-JBM9%3e3.0.CO;2-J
Susilowati, E.: Maryani; Ashadi: Green synthesis of silver-chitosan nanocomposite and their application as antibacterial material. J. Phys: Conf Ser 1153, 012135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1153/1/012135
Rezazadeh, N.H.; Buazar, F.; Matroodi, S.: Synergistic effects of combinatorial chitosan and polyphenol biomolecules on enhanced antibacterial activity of biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 19615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76726-7
Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W.: NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9(7), 671–675 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Koronkiewicz, S.: Photometric determination of iron in pharmaceutical formulations using double-beam direct injection flow detector. Molecules 26(15), 4498 (2021)
Murugan, K.; Jaganathan, A.; Suresh, U.; Rajaganesh, R.; Jayasanthini, S.; Higuchi, A.; Kumar, S.; Benelli, G.: Towards bio-encapsulation of chitosan-silver nanocomplex? impact on malaria mosquito vectors, human breast adenocarcinoma cells (MCF-7) and behavioral traits of non-target fishes. J. Cluster Sci. 28(1), 529–550 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-1129-1
Khwannimit, D.; Maungchang, R.; Rattanakit, P.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Clitoria ternatea flower: an efficient catalyst for removal of methyl orange. Int J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 102, 5247–5263 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1793974
Roberts, G.A.F.: Chitin chemistry. Macmillan, London (1992)
El-Rafie, H.M.; El-Rafie, M.H.; Zahran, M.K.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using polysaccharides extracted from marine macro algae. Carbohyd. Polym. 96(2), 403–410 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.071
Sen, I.K.; Mandal, A.K.; Chakraborti, S.; Dey, B.; Chakraborty, R.; Islam, S.S.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using glucan from mushroom and study of antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 62, 439–449 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.09.019
Firdaus, M.L.; Fitriani, I.; Wyantuti, S.; Hartati, Y.W.; Khaydarov, R.; McAlister, J.A.; Obata, H.; Gamo, T.: Colorimetric detection of Mercury(II) ion in aqueous solution using silver nanoparticles. Anal. Sci. 33(7), 831–837 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.33.831
Kumar, V.; Singh, D.K.; Mohan, S.; Bano, D.; Gundampati, R.K.; Hasan, S.H.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle for the selective and sensitive colorimetric detection of mercury (II) ion. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 168, 67–77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.01.022
Singh, R.; Mehra, R.; Walia, A.; Gupta, S.; Chawla, P.; Kumar, H.; Thakur, A.; Kaushik, R.; Kumar, N.: Colorimetric sensing approaches based on silver nanoparticles aggregation for determination of toxic metal ions in water sample: a review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 103, 13161–21376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1873315
Zarlaida, F.; Adlim, M.; Syukri Surbakti, M.; Omar, A.F.: Chitosan-stabilized silver nanoparticles for colorimetric assay of mercury (II) Ions in aqueous system. IOP Conf. Ser: Mater. Sci. Eng. 352(1), 012049–065535 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/352/1/012049
May, B.M.M.; Oluwafemi, O.S.: Sugar-reduced gelatin-capped silver nanoparticles with high selectivity for colorimetric sensing of Hg2+ and Fe2+ ions in the midst of other metal ions in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 11, 8096–8108 (2016). https://doi.org/10.20964/2016.09.29
Burns, D.T.; Danzer, K.; Townshend, A.: Use of the term “recovery” and “apparent recovery” in analytical procedures (IUPAC Recommendations 2002). Pure Appl. Chem. 74(11), 2201–2205 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200274112201
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Nanomaterials Chemistry Research Unit, Nakhon Si Thammarat Rajabhat University, Thailand for offering the equipment support required for this project. This work is partially supported by the National Research Council of Thailand (N11A650144) chaired by Assoc. Prof. Dr. Duangjai Nacapricha. We are grateful for the financial support from Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology (Public Organization). Y.T. gratefully acknowledges Asst. Prof. Dr. Parawee Rattanakit for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YT Conceptualization, visualization, methodology, formal analysis, project administration, writing—original draft, and writing—review & editing. NJ Investigation, formal analysis, and visualization. TW Formal analysis, visualization, and writing—review & editing. PN Writing—review & editing. BN Writing—review & editing. NS Writing—review & editing. PS Funding acquisition. NL Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thepchuay, Y., Jommala, N., Wonglakhon, T. et al. γ-Irradiated Chitosan Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles as Novel Colorimetric Sensors for Mercury(II) and Iron(II) Detections in Real Samples. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 7825–7839 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07894-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07894-7