Abstract
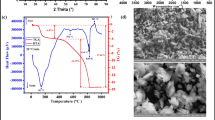
Water contamination by dyeing chemicals has become a worldwide problem. Adsorption by using low-cost adsorbents has been considered as an appropriate and economical method for water remediation. So, the process of the dye adsorption by cured alkali-activated heated clay-cellulose (up to 10 mass%) composites was investigated within the 288–318 K range using methylene blue (MB) as a dye-adsorbate model. For this purpose, X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscope were used. Moreover, the effects of adsorbent dosage, solution pH, contact time and temperature were assessed. Additionally, the dye release in different experimental conditions was studied by using the response surface methodology. It was shown that the composites were the object of formation of zeolites and geopolymers. The use of low adsorbent dosage (0.5 mg/L) and pH > 7 improved MB adsorption. The adsorption occurred spontaneously (ΔG° < – 35 kJ/mol) and endothermically (0 < ΔH° < 12 kJ/mol). The desorption efficiency of the cellulose-rich adsorbent increased with the increase of pH or T, and with the decrease of the ionic strength. It did not exceed 50% in the optimal experimental conditions. The MB retention took place mainly by pores filling, and its rate was controlled by diffusion. MB was adsorbed as monomer, dimer and H-aggregates. Siloxane groups together with hydroxyls were the main active adsorption sites. The adsorption capacity (about 31 mg/g) was higher than those reported for some low-cost adsorbents. The adsorption cost was in the range of 0.19–0.20 US$/g of MB removed.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A.; Shah, T.; Khan, I.: Review on methylene blue: its properties, uses, toxicity and photodegradation. Water 14(2), 242 (2022)
Hang, P.T.; Brindley, G.W.: Methylene blue absorption by clay minerals. Determination of surface areas and cation exchange capacities (clay-organic studies XVIII). Clays Clay Miner. 18, 203–212 (1970)
Santoso, E.; Ediati, R.; Kusumawati, Y.; Bahruji, H.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Prasetyoko, D.: Review on recent advances of carbon based adsorbent for methylene blue removal from wastewater. Mater. Today Chem. 16, 100233 (2020)
Ighalo, J.O.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Adeniyi, A.G.: Verification of pore size effect on aqueous-phase adsorption kinetics: a case study of methylene blue. Colloids and Surfaces : Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 626, 127119 (2021)
Alsukaibi, A.K.: Various approaches for the detoxification of toxic dyes in wastewater. Processes 10(10), 1968 (2022)
Hamad, H.N.; Idrus, S.: Recent developments in the application of bio-waste-derived adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue from wastewater: a review. Polymers 14, 783 (2022)
Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A.: Magsorbents: potential candidates in wastewater treatment technology–A review on the removal of methylene blue dye. J. Magnet. Magnetic. Mater. 500, 166408 (2020)
Iwuozor, K.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Ogunfowora, L.A.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Igwegbe, C.A.: An empirical literature analysis of adsorbent performance for methylene blue uptake from aqueous media. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105658 (2021)
Vishnu, D.; Dhandapani, B.; Authilingam, S.; Sivakumar, S.V.: A comprehensive review of effective adsorbents used for the removal of dyes from wastewater. Curr. Anal. Chem. 18(3), 255–268 (2022)
Cemin, A.; Ferrarini, F.; Poletto, M.; Bonetto, L.R.; Bortoluz, J.; Lemée, L.; Guégan, R.; Esteves, V.I.; Giovanela, M.: Characterization and use of a lignin sample extracted from Eucalyptus grandis sawdust for the removal of methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 170, 375–389 (2021)
Beims, R.F.; Arredondo, R.; Carrero, D.J.S.; Yuan, Z.; Li, H.; Shui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Leitch, M.; Xu, C.C.: Functionalized wood as bio-based advanced materials: properties, applications, and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 157, 112074 (2022)
Al-Aoh, H.A.; Mihaina, I.A.M.; Alsharif, M.A.; Darwish, A.A.A.; Rashad, M.; Mustafa, S.K.; Meshari, M.H.A.; Mohammed, A.A.; Al-Shehri, H.S.: Removal of methylene blue from synthetic wastewater by the selected metallic oxides nanoparticles adsorbent: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. Commun. 207(12), 1719–1735 (2020)
García-Carvajal, C.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; de Souza, V.C.; Sapag, K.: Development of ceramic honeycomb monolith from natural zeolite tested as adsorbent to remove methylene blue in aqueous media. Environ. Sci. Pollution Res. 29(53), 79890–79902 (2022)
Malatji, N.; Makhado, E.; Modibane, K.D.; Ramohlola, K.E.; Maponya, T.C.; Monama, G.R.; Hato, M.J.: Removal of methylene blue from wastewater using hydrogel nanocomposites: a review. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 11, 1–27 (2021)
Dinh, V.P.; Le, H.M.; Nguyen, V.D.; Dao, V.A.; Hung, N.Q.; Tuyen, L.A.; Lee, S.; Yi, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Tan, L.V.: Insight into the adsorption mechanisms of methylene blue and chromium (III) from aqueous solution onto pomelo fruit peel. RSC Adv. 9(44), 25847–25860 (2019)
Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A.: Magnetized Tectonagrandis sawdust as a novel adsorbent: preparation, characterization, and utilization for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Cellulose 27(5), 2613–2635 (2020)
You, X.; Wang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Sui, W.; Cheng, D.: Comparison of adsorption properties of a cellulose-rich modified rice husk for the removal of methylene blue and aluminum (III) from their aqueous solution. Industr. Crops Products 170, 113687 (2021)
Cong, P.; Cheng, Y.: Advances in geopolymer materials: a comprehensive review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (English Edition) 8(3), 283–314 (2021)
Ahmed, H.U.; Mohammed, A.A.; Mohammed, A.S.: The role of nanomaterials in geopolymer concrete composites: a state-of-the-art review. J. Build Eng. 49, 104062 (2022)
Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, D.; Li, H.; Colombo, P.: Porous geopolymer composites: a review. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 150, 106629 (2021)
Ren, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zha, J.; Tian, G.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.: Synthesis of zeolites by in-situ conversion of geopolymers and their performance of heavy metal ion removal in wastewater: a review. J. Cleaner Prod. 349, 131441 (2022)
Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A.: Synthesis of porous biomass fly ash-based geopolymer spheres for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewaters. J. Cleaner Prod. 207, 350–362 (2019)
Maleki, A.; Mohammad, M.; Emdadi, Z.; Asim, N.; Azizi, M.; Safaei, J.: Adsorbent materials based on a geopolymer paste for dye removal from aqueous solutions. Arabian J. Chem. 13(1), 3017–3025 (2020)
Asim, N.; Badiei, M.; Shakeri, M.; Emdadi, Z.; Samsudin, N.A.; Soltani, S.; Mohammed, M.; Amin, N.: Development of green photocatalytic geopolymers for dye removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 283, 126020 (2022)
Medri, V.; Papa, E.; Mor, M.; Vaccari, A.; Muri, A.N.; Piotte, L.; Melandri, C.; Landi, E.: Mechanical strength and cationic dye adsorption ability of metakaolin-based geopolymer spheres. Appl. Clay Sci. 193, 105678 (2020)
Jin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chang, Q.; Li, C.: Rapid removal of methylene blue and nickel ions and adsorption/desorption mechanism based on geopolymer adsorbent. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 45, 100551 (2021)
Kaya-Özkiper, K.; Uzun, A.; Soyer-Uzun, S.: A novel alkali activated magnesium silicate as an effective and mechanically strong adsorbent for methylene blue removal. J. Hazardous Mater. 424, 127256 (2022)
Li, C.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, H.; He, P.Y.; Meng, Q.: Development of porous and reusable geopolymer adsorbents for dye wastewater treatment. J. Cleaner Prod. 348, 131278 (2022)
Chen, Y.; Hanshe, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Mei, C.; Duan, G.; Zheng, J.; Shiju, E.; Jiang, S.: Lightweight and anisotropic cellulose nanofibril/rectorite composite sponges for efficient dye adsorption and selective separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 207, 130–139 (2022)
Akter, M.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Dhar, A.K.; Rahman, F.B.A.; Haque, S.; Rashid, T.U.; Kabir, S.F.: Cellulose-based hydrogels for wastewater treatment: a concise review. Gels 7(1), 30 (2021)
Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C.; Pan, H.: Efficient and selective adsorption of cationic dyes with regenerated cellulose. Chem. Phys. Lett. 784, 139104 (2021)
Malatji, N.; Makhado, E.; Modibane, K.D.; Ramohlola, K.E.; Maponya, T.C.; Monama, G.R.; Hato, M.J.: Removal of methylene blue from wastewater using hydrogel nanocomposites: a review. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 11, 18479804211039424 (2021)
Zougagh, M.; Rudner, P.C.; García de Torres, A.; Pavón, J.M.C.: Application of Doehlert matrix and factorial designs in the optimization of experimental variables associated with the on-line preconcentration and determination of zinc by flow injection inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. J. Anal. Atomic Spectrom. 15, 1589–1594 (2000)
Sokolar, R.; Nguyen, M.: Sintering of anorthite ceramic body based on interstratified illite-smectite clay. Ceram. Int. 48(21), 31783–31789 (2022)
Rocky, B.P.; Thompson, A.J.: Characterization of the crystallographic properties of bamboo plants, natural and viscose fibers by X-ray diffraction method. J. Textile Instit. 112(8), 1295–1303 (2021)
Ouajai, S.; Shanks, R.A.: Composition, structure and thermal degradation of hemp cellulose after chemical treatments. Polym. Degradation Stability 89(2), 327–335 (2005)
Thygesen, A.; Oddershede, J.; Lilholt, H.; Thomsen, A.B.; Ståhl, K.: On the determination of crystallinity and cellulose content in plant fibres. Cellulose 12(6), 563–576 (2005)
Budtova, T.; Navard, P.: Cellulose in NaOH–water based solvents: a review. Cellulose 23(1), 5–55 (2016)
Viegas, R.; Campinas, M.; Costa, H.; Rosa, M.J.: How do the HSDM and Boyd’s model compare for estimating intraparticle diffusion coefficients in adsorption processes. Adsorption 20(5), 737–746 (2014)
Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.: The unit problem in the thermodynamic calculation of adsorption using the Langmuir equation. Chem. Eng. Commun. 201(11), 1459–1467 (2014)
Cerqueira, U.M.F.M.; Bezerra, M.A.; Ferreira, S.L.C.; de Jesus Araújo, R.; da Silva, B.N.; Novaes, C.G.: Doehlert design in the optimization of procedures aiming food analysis–a review. Food Chem. 364, 130429 (2021)
Mathieu, D.; Phan Tan Luu.: Software NEMROD. Université d’Aix, Marseille III, France. (1980)
Verdooren, L.R.: Use of Doehlert designs for second-order polynomial models. Math. Stat. 5(2), 62–67 (2017)
Seltman, H.J.: Experimental design and analysis. Carnegie Mellon University (2012)
Khaleque, A.; Alam, M.M.; Hoque, M.; Mondal, S.; Haider, J.B.; Xu, B.; Johir, M.A.H.; Karmakar, A.K.; Zhou, J.L.; Ahmed, M.B.; Moni, M.A.: Zeolite synthesis from low-cost materials and environmental applications: a review. Environ. Adv. 2, 100019 (2020)
Haouache, S.; Jimenez-Saelices, C.; Cousin, F.; Falourd, X.; Pontoire, B.; Cahier, K.; Jérome, F.; Capron, I.: Cellulose nanocrystals from native and mercerized cotton. Cellulose 29(3), 1567–1581 (2022)
Peter, Z.: Order in cellulosics: Historical review of crystal structure research on cellulose. Carbohydrate Polym. 254, 117417 (2021)
Hajjaji, M.; Beraa, A.; Coppel, Y.; Laurent, R.; Caminade, A.-M.: Adsorption capacity of sodic- and dendrimers-modified stevensite. Clay Minerals 53, 525–544 (2018)
Rytwo, G.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E.: Enthalpies of adsorption of methylene blue and crystal violet to montmorillonite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 71, 751–759 (2003)
Mills, A.; Hazafy, D.; Parkinson, J.; Tuttle, T.; Hutchings, M.G.: Effect of alkali on methylene blue (CI Basic Blue 9) and other thiazine dyes. Dyes Pigments 88(2), 149–155 (2011)
El Alouani, M.; Alehyen, S.; El Achouri, M.; Taibi, M.: Preparation, characterization, and application of metakaolin-based geopolymer for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Chem. 2019, 1–14 (2019)
Vedder, W.: Correlations between infrared spectrum and chemical composition of mica. Am. Mineral.: J. Earth Planetary Mater. 49(5–6), 736–768 (1964)
Szostak, R.: Handbook of molecular sieves. Published by Van Nostrand Reinhold (1992)
El Hafid, K.; Hajjaji, M.: Effects of the experimental factors on the microstructure and the properties of cured alkali-activated heated clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 116, 202–210 (2015)
Ovchinnikov, O.V.; Evtukhova, A.V.; Kondratenko, T.S.; Smirnov, M.S.; Khokhlov, V.Y.; Erina, O.V.: Manifestation of intermolecular interactions in FTIR spectra of methylene blue molecules. Vibr. Spectroscopy 86, 181–189 (2016)
Rożek, P.; Król, M.; Mozgawa, W.: Spectroscopic studies of fly ash-based geopolymers. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectroscopy 198, 283–289 (2018)
Somsesta, N.; Sricharoenchaikul, V.; Aht-Ong, D.: Adsorption removal of methylene blue onto activated carbon/cellulose biocomposite films: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 240, 122221 (2020)
Mohammed, N.; Lian, H.; Islam, M.S.; Strong, M.; Shi, Z.; Berry, R.M.; Yu, H.Y.; Tam, K.C.: Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes using functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chem. Eng. J. 417, 129237 (2021)
Bingül, Z.: Determination of affecting parameters on removal of methylene blue dyestuff from aqueous solutions using natural clay: isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Struct. 1250, 131729 (2021)
Asuha, S.; Fei, F.; Wurendaodi, W.; Zhao, S.; Wu, H.; Zhuang, X.: Activation of kaolinite by a low-temperature chemical method and its effect on methylene blue adsorption. Powder Technol. 361, 624–632 (2020)
Belachew, N.; Hinsene, H.: Preparation of zeolite 4A for adsorptive removal of methylene blue: optimization, kinetics, isotherm, and mechanism study. Silicon 14(4), 1629–1641 (2022)
Padmapriya, M.; Ramesh, S.T.; Biju, V.M.: Synthesis of seawater based geopolymer: characterization and adsorption capacity of methylene blue from wastewater. Mater. Today: Proc. 51, 1770–1776 (2022)
Ighalo, J.O.; Omoarukhe, F.O.; Ojukwu, V.E.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Igwegbe, C.A.: Cost of adsorbent preparation and usage in wastewater treatment: a review. Cleaner Chem. Eng. 3, 100042 (2022)
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mourak, A., Hajjaji, M. & Alagui, A. Cured NaOH-Etched Heated Clay-Cellulose Composites: Characterization, Dye Adsorption, and Desorption Study Using Response Surface Methodology. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 15927–15948 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07838-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07838-1