Abstract
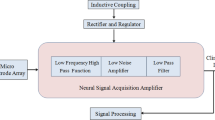
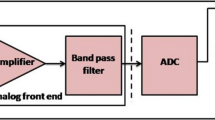
Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals have weak amplitude and have susceptibility to noise from supplies, electrodes and added sources. The preamplifier in analog front end of a neural acquisition system will magnify the signal at low power and low noise, and a low pass filter will restrict the bandwidth. The low power methods are necessary to reduce heat dissipation; otherwise, they will damage the surrounding tissues. These techniques can reduce the use of bulk sized batteries, which will increase the battery lifetime and can avoid the distress of frequent battery replacements. In this article, the focus is given on the design of an OTA-C filter, with challenges in reducing power of the circuit without compromising the noise and bandwidth parameters. These challenges are addressed in the proposed work with comprehensive analysis. The low frequency circuits necessitate huge capacitors and resistors, which occupy large chip-area, but the requirement is for reduced area. The OTA-C filters are widespread because they are fundamentally tunable, resistor-less and can be engineered on small chip areas. The novelty of this work is to reduce power and to create a higher order Gm-C topology filter that can record FRs or high focal oscillations in order to record epileptic signals. The proposed design implements current division and source degeneration techniques to bring down the transconductances in nano scale. The design achieves a mid-band gain of 54.2 dB and a − 3 dB bandwidth in the range 40–650 Hz, with simulations performed in 180 nm SCL Cadence environment.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salanova, V.; Worth, R.: Neurostimulators in epilepsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 7(4), 315–319 (2007)
Nordi, T.M.; Gounella, R.H.; Luppe, M.; Junior, J.N.S.; Fonoff, E.T.; Colombari, E., et al.: Low-noise amplifier for deep-brain stimulation (DBS). Electronics 11(6), 939 (2022)
Dümpelmann, M.: Early seizure detection or closed loop direct neurostimulation devices in epilepsy. J. Neural Eng. 16(4), 041001 (2019)
Yang, J.; Sawan, M.: From seizure detection to smart and fully embedded seizure prediction engine: a review. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 14(5), 1008–1023 (2020)
Amudhan, S.; Gururaj, G.; Satishchandra, P.: Epilepsy in India I: epidemiology and public health. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 18(3), 263–277 (2015)
Kassiri, H.; Tonekaboni, S.; Salam, M.T.; Soltani, N.; Abdelhalim, K.; Velazquez, J.L.P.; Genov, R.: Closed loop neurostimulators: a survey and a seizure predicting design example for intractable epilepsy treatment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 11(5), 1026–1040 (2017)
Harrison, R.R.; Charles, C.: A low-power low-noise CMOS amplifier for neural recording applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 38(6), 958–965 (2003)
Wattanapanitch, W.; Fee, M.; Sarpeshkar, R.: An energy-efficient micropower neural recording amplifier. IEEE Trans. Biomed Circuits Syst. 1(2), 136–147 (2007)
Barsakcioglu, D.Y.; Yan, L.; Bhunjun, P.; Navajas, J.; Eftekhar, A.; Jackson, A.; Quiroga, R.Q.; Constandinou, T.G.: An analogue front-end model for developing neural spike sorting systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed Circuits Syst. 8(2), 216–227 (2014)
Della Sala, R.; Monsurrò, P.; Scotti, G.; Trifiletti, A.: Area-efficient low-power bandpass Gm-C filter for epileptic seizure detection in 130 nm CMOS. In: 2019 26th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), pp 298–301 (2019)
Lee, S.Y.; Cheng, C.J.: Systematic design and modeling of a OTA-C filter for portable ECG detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed Circuits Syst. 3(1), 53–64 (2009)
Bihr, U.; Ortmanns, M.: A front-end circuit with active spike and LFP separation via a switched capacitor filter structure for neural recording applications. In: 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 2231–2234 (2012)
Peng, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Huang, H.C.; Lai, M.R.; Lee, C.H.; Liu, L.H.: A power-efficient reconfigurable OTA-C filter for low-frequency biomedical applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 65(2), 543–555 (2017)
Devi, S.; Guha, K.; Laskar, N.M.; Nath, S.; Baishnab, K.L.; Iannacci, J.; Krishnaswamy, N.: Modelling and analysis of a modified preamplifier for seizuredetection. Microsyst. Technol. 27, 3545–3558 (2021)
Yen, C.J.; Chung, W.Y.; Chi, M.C.: Micro-power low-offset instrumentation amplifier IC design for biomedical system applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 51(4), 691–699 (2004)
Gallegos, S.A.; Huq, H.F.: A 128.7 nW neural amplifier and Gm-C filter for EEG, using gm/ID methodology and a current reference without resistance. In: 2014 IEEE 57th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), pp. 876–880 (2014)
Kaushik, P.; Jain, M.: Design of low power CMOS low pass filter for biomedical application. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. (IJEET) 9(5) (2018)
Practical filter design challenges and considerations for precision ADCs. Available at 9 July 2022 https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/industry-articles/practical-filter-design-challenges-and-considerations-for-precision-adcs/ (Visited on)
Namdari, A.; Mehdi, D.: Design of a low-voltage and low-power, reconfigurable universal OTA-C filter. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 111(2), 169–188 (2022)
Ozenli, D.; Yesil, A.; Kuntman, H.: A current-mode MOSFET-C analog filter for the high-frequency band applications. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 49(3), 890–908 (2021)
Akbari, M.; Nazari, M.; Sharifi, L.; Hashempiour, O.: Improving power efficiency of a two-stage operational amplifier for biomedical application. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 84, 173–183 (2015)
Gray, P.R.; Meyer, R.G.: MOS operational amplifier design—a tutorial overview. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 17(6), 969–982 (1982)
Saidulu, B.; Manoharan, A.; Sundaram, K.: Low noise low power CMOS telescopic-OTA for bio-medical applications. Computers 5(4), 507–512 (2016)
Sawigun, C.; Thanapitak, S.: A 0.9-nW, 101-Hz, and 46.3-μV rms IRN low-pass filter for ECG acquisition using FVF biquads. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 26(11), 2290–2298 (2018)
Mirzaei, M.; Salam, M.T.; Nguyen, D.K.; Sawan, M.: A fully-asynchronous low-power implantable seizure detector for self-triggering treatment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 7(5), 563–572 (2013)
Mahendra, M.; Kumari, S.; Gupta, M.: Low voltage fully differential OTA using DTMOS based self cascode transistor with slew-rate enhancement and its filter application. Integration 84, 47–61 (2022)
Metin, B.; et al.: MOSFET-C transimpedance filters with center frequency tunability feature. Int. J. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207217.2022.2025459
Tran, L.; Cha, H.: An ultra-low-power neural signal acquisition analog front-end IC. Microelectron. J. 107, 104950 (2021)
Laskar, N.M., et al.: Design of high gain, high bandwidth neural amplifier IC considering noise-power trade-off. Microsyst. Technol. 27(2), 585–599 (2021)
Zijlmans, M.; Jacobs, J.; Zelmann, R.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J.: High frequency oscillations and seizure frequency in patients with focal epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 85(2–3), 287–292 (2009)
Bihr, U.; Ortmanns, M.: A front-end circuit with active spike and LFP separation via a switched capacitor filter structure for neural recording applications. In: 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 2231–2234 (2012)
Veldandi, H.; Shaik, R.A.: A 0.3–v pseudo-differential bulk-input OTA for low-frequency applications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(12), 5199–5221 (2018)
Lee, C.; Jeon, T.; Jang, M.; Park, S.; Kim, J., et al.: A 6.5-μW 10-kHz BW 80.4-dB SNDR G m-C-based CT∆∑ modulator with a feedback-assisted G m linearization for artifact-tolerant neural recording. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 55(11), 2889–2901 (2020)
Namdari, A.; Dolatshahi, M.: Design of a low-voltage and low-power, reconfigurable universal OTA-C filter. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 111(2), 169–188 (2022)
Funding
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, S., Nath, S., Guha, K. et al. Design and Analysis of a Fifth Order Low Pass Gm-C Filter for Seizure Detection. Arab J Sci Eng 49, 2935–2944 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07824-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07824-7