Abstract
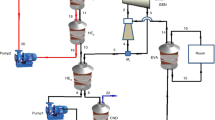
In this study, a new method for the LNG has been proposed based on the SMR process. In the proposed process, an ORC is added to the conventional SMR process and the BOG is used as a coolant in the main heat exchanger. ASPEN HYSYS software utilizing the Peng–Robinson equation of state is used to simulate the SMR and SMR-ORC. The specific energy consumption, total exergy efficiency, and carbon dioxide emissions of the proposed method are compared with the conventional SMR process. Finally, an economic evaluation was performed on both processes. The simulation results showed that in the conventional process the total exergy efficiency and specific energy consumption are 34% and 647 \(\frac{{{\text{kWh}}}}{{{\text{ton}}}}\), respectively, while in the proposed process the total exergy efficiency has reached 39% and the energy consumption is reduced to 472 \(\frac{{{\text{kWh}}}}{{{\text{ton}}}}\). Also, the environmental assessment of carbon dioxide emissions from the production of electrical energy required by pumps and compressors showed that the proposed process has 28.51% less carbon dioxide emissions than the conventional SMR method.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APEA:
-
Aspen Process Economic Analyzer
- ACC:
-
Annual capital cost
- BOG:
-
Boil-off gas
- CEPCI:
-
Chemical engineering price cost index
- CWC:
-
Cold warehouse cooling
- C3MR:
-
Propane precooling mixed refrigerant
- DMR:
-
Dual-mixed refrigerant
- FCI:
-
Total Fixed Capital Investment
- h:
-
Specific enthalpy
- IEA:
-
International energy agency
- LNG:
-
Liquefied natural gas
- LHS:
-
Light hydrocarbon separation
- MSMR:
-
Modified mixed refrigerant liquefaction process
- MSMR:
-
Modified single mixed refrigerant
- MR:
-
Mixed refrigerant
- \(n_{{\text{co2,net}}}\) :
-
Net of carbon dioxide emission
- ORC:
-
Organic Rankine cycle
- PNEC:
-
Parallel nitrogen expansion liquefaction process
- SEC:
-
Specific energy consumption
- SMR:
-
Single mixed refrigerant
- s:
-
Specific entropy
- TCOP:
-
Total cost of production
- TAC:
-
Total annual cost
- TEC:
-
Total major equipment’s purchase cost
- VSO:
-
Vortex search optimization
- \(\dot{X}_{{{\text{des}}}}\) :
-
Exergy destruction
- \(\dot{E}_{{\text{D}}}^{{{\text{total}}}}\) :
-
Total exergy destruction
- \(\dot{W}_{{{\text{used}}}}^{{{\text{total}}}}\) :
-
Tal power consumed
- \(\eta_{{{\text{ex}}}}\) :
-
Exergy efficiency
- 0 (zero):
-
Ambient conditions
- \(\dot{E}_{{{\text{NG}}}}\) :
-
Exergy of natural gas
References
Nawaz, A.; Qyyum, M.A.; Qadeer, K.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, A.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.: Optimization of mixed fluid cascade LNG process using a multivariate Coggins step-up approach: overall compression power reduction and exergy loss analysis. Int. J. Refrig. 104, 189–200 (2019)
Fahmy, M.; Nabih, H.; El-Nigeily, M.: Enhancement of the efficiency of the Open Cycle Phillips Optimized Cascade LNG process. Energy Convers. Manag. 112, 308–318 (2016)
Song, C.; Tan, S.; Qu, F.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.: Optimization of mixed refrigerant system for LNG processes through graphically reducing exergy destruction of cryogenic heat exchangers. Energy 168, 200–206 (2019)
Mokhatab, S.; Poe, W.A.; Mak, J.: Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing: Principles and Practices. Gulf Professional Publishing, Houston (2018)
Moein, P.; Sarmad, M.; Ebrahimi, H.; Zare, M.; Pakseresht, S.; Vakili, S.Z.: APCI-LNG single mixed refrigerant process for natural gas liquefaction cycle: analysis and optimization. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 26, 470–479 (2015)
Nguyen, T.-V.; Elmegaard, B.: Assessment of thermodynamic models for the design, analysis and optimisation of gas liquefaction systems. Appl. Energy 183, 43–60 (2016)
WEO, I., IEA World Energy Outlook 2008. 2008, OECD/IEA Paris, France.
Tak, K.; Choi, J.; Ryu, J.-H.; Moon, I.: Sensitivity analysis of effects of design parameters and decision variables on optimization of natural gas liquefaction process. Energy 206, 118132 (2020)
He, T.; Mao, N.; Liu, Z.; Qyyum, M.A.; Lee, M.; Pravez, A.M.: Impact of mixed refrigerant selection on energy and exergy performance of natural gas liquefaction processes. Energy 199, 117378 (2020)
He, T.; Karimi, I.A.; Ju, Y.: Review on the design and optimization of natural gas liquefaction processes for onshore and offshore applications. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 132, 89–114 (2018)
Mortazavi, A.; Somers, C.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Rodgers, P.; Al-Hashimi, S.: Performance enhancement of propane pre-cooled mixed refrigerant LNG plant. Appl. Energy 93, 125–131 (2012)
Hatcher, P.; Khalilpour, R.; Abbas, A.: Optimisation of LNG mixed-refrigerant processes considering operation and design objectives. Comput. Chem. Eng. 41, 123–133 (2012)
Vatani, A.; Mehrpooya, M.; Palizdar, A.: Energy and exergy analyses of five conventional liquefied natural gas processes. Int. J. Energy Res. 38, 1843–1863 (2014)
Xiong, X.; Lin, W.; Gu, A.: Design and optimization of offshore natural gas liquefaction processes adopting PLNG (pressurized liquefied natural gas) technology. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 30, 379–387 (2016)
Remeljej, C.W.; Hoadley, A.F.A.: An exergy analysis of small-scale liquefied natural gas (LNG) liquefaction processes. Energy 31, 2005–2019 (2006)
Lim, W.; Lee, I.; Tak, K.; Cho, J.H.; Ko, D.; Moon, I.: Efficient configuration of a natural gas liquefaction process for energy recovery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 1973–1985 (2014)
Jin, C.; Son, H.; Lim, Y.: Optimization and economic analysis of liquefaction processes for offshore units. Appl. Therm. Eng. 163, 114334 (2019)
Khan, M.S.; Lee, S.; Getu, M.; Lee, M.: Knowledge inspired investigation of selected parameters on energy consumption in nitrogen single and dual expander processes of natural gas liquefaction. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 23, 324–337 (2015)
Wu, J.; Ju, Y.: Design and optimization of natural gas liquefaction process using brazed plate heat exchangers based on the modified single mixed refrigerant process. Energy 186, 115819 (2019)
He, T.; Liu, Z.; Ju, Y.; Parvez, A.M.: A comprehensive optimization and comparison of modified single mixed refrigerant and parallel nitrogen expansion liquefaction process for small-scale mobile LNG plant. Energy 167, 1–12 (2019)
Nguyen, T.-V.; Rothuizen, E.D.; Markussen, W.B.; Elmegaard, B.: Thermodynamic comparison of three small-scale gas liquefaction systems. Appl. Therm. Eng. 128, 712–724 (2018)
Qyyum, M.A.; Lee, M.: Hydrofluoroolefin-based novel mixed refrigerant for energy efficient and ecological LNG production. Energy 157, 483–492 (2018)
Qyyum, M.A.; Ali, W.; Long, N.V.D.; Khan, M.S.; Lee, M.: Energy efficiency enhancement of a single mixed refrigerant LNG process using a novel hydraulic turbine. Energy 144, 968–976 (2018)
Rehman, A.; Qyyum, M.A.; Qadeer, K.; Zakir, F.; He, X.; Nawaz, A.; Lee, M.; Wang, L.: Single mixed refrigerant LNG process: investigation of improvement potential, operational optimization, and real potential for further improvements. J. Clean. Prod. 284, 125379 (2021)
Rehman, A.; Qyyum, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Nawaz, S.; Lee, M.; Wang, L.: Performance enhancement of nitrogen dual expander and single mixed refrigerant LNG processes using jaya optimization approach. Energies 13, 3278 (2020)
Qyyum, M.A.; Yasin, M.; Nawaz, A.; He, T.; Ali, W.; Haider, J.; Qadeer, K.; Nizami, A.-S.; Moustakas, K.; Lee, M.: Single-solution-based vortex search strategy for optimal design of offshore and onshore natural gas liquefaction processes. Energies 13, 1732 (2020)
Almeida-Trasvina, F.; Smith, R.; Jobson, M.: Development of an energy-efficient single mixed refrigerant cycle for small-scale LNG production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60(32), 12049–12067 (2021)
Pan, J.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Tang, L.; Bai, J.: Design and analysis of LNG cold energy cascade utilization system integrating light hydrocarbon separation, organic Rankine cycle and direct cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 213, 118672 (2022)
Kim, S.; Cho, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, M.: Characteristics and optimization of supercritical CO2 recompression power cycle and the influence of pinch point temperature difference of recuperators. Energy 147, 1216–1226 (2018)
Kim, S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, M.: Parametric study and optimization of closed Brayton power cycle considering the charge amount of working fluid. Energy 198, 117353 (2020)
Astolfi, M.; Fantolini, A.M.; Valenti, G.; De Rinaldis, S.; Inglese, L.D.; Macchi, E.: Cryogenic ORC to enhance the efficiency of LNG regasification terminals. Energy Procedia 129, 42–49 (2017)
Xue, X.; Guo, C.; Du, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.: Thermodynamic analysis and optimization of a two-stage organic Rankine cycle for liquefied natural gas cryogenic exergy recovery. Energy 83, 778–787 (2015)
He, T.; Ma, H.; Ma, J.; Mao, N.; Liu, Z.: Effects of cooling and heating sources properties and working fluid selection on cryogenic organic Rankine cycle for LNG cold energy utilization. Energy Convers. Manag. 247, 114706 (2021)
Bao, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, N.; He, G.: Effects of stage number of condensing process on the power generation systems for LNG cold energy recovery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 126, 566–582 (2017)
Una, D.; Oduola, M.; Odagme, B.: Sensitivity analysis of a single mixed refrigerant liquefaction process of natural gas. In: SPE Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition. OnePetro (2016).
Hajji, A.; Chahartaghi, M.; Kahani, M.: Thermodynamic analysis of natural gas liquefaction process with propane pre-cooled mixed refrigerant process (C3MR). Cryogenics 103, 102978 (2019)
Sabbagh, O.; Fanaei, M.A.; Arjomand, A.; Ahmadi, M.H.: Multi-objective optimization assessment of a new integrated scheme for co-production of natural gas liquids and liquefied natural gas. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 47, 101493 (2021)
Nikkho, S.; Abbasi, M.; Zahirifar, J.; Saedi, M.; Vatani, A.: Energy and exergy investigation of two modified single mixed refrigerant processes for natural gas liquefaction. Comput. Chem. Eng. 140, 106854 (2020)
Tahmasebi, S.; Abbasabadi, A.B.; Ghasemi, N.; Javadian, H.; Mashhadi, S.; Fattahi, M.; Arian, Y.R.; Maddah, H.: Investigation of various feed conditions on NGL recovery plant energy and exergy performance: a case study. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 22, 83–89 (2015)
Darvish, K.; Ehyaei, M.A.; Atabi, F.; Rosen, M.A.: Selection of optimum working fluid for organic Rankine cycles by exergy and exergy-economic analyses. Sustainability 7, 15362–15383 (2015)
Ding, H.; Sun, H.; Sun, S.; Chen, C.: Analysis and optimisation of a mixed fluid cascade (MFC) process. Cryogenics 83, 35–49 (2017)
Jin, C.; Yuan, Y.; Son, H.; Lim, Y.: Novel propane-free mixed refrigerant integrated with nitrogen expansion natural gas liquefaction process for offshore units. Energy 238, 121765 (2022)
Shamsi, M.; Obaid, A.A.; Farokhi, S.; Bayat, A.: A novel process simulation model for hydrogen production via reforming of biomass gasification tar. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 47, 772–781 (2022)
Shamsi, M.; Moghaddas, S.; Naeiji, E.; Farokhi, S.: Techno-economic, energy, exergy, and environmental comparison of hydrogen production from natural gas, biogas, and their combination as feedstock. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2023)
Kotas, T.J.: The Exergy Method of Thermal Plant Analysis. Paragon Publishing, Trowbridge (2012)
Shamsi, M.; Farokhi, S.; Pourghafari, M.; Bayat, A.: Tuning the natural gas dew point by Joule–Thomson and mechanical refrigeration processes: a comparative energy and exergy analysis. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 212, 110270 (2022)
Qyyum, M.A.; Ahmed, F.; Nawaz, A.; He, T.; Lee, M.: Teaching-learning self-study approach for optimal retrofitting of dual mixed refrigerant LNG process: energy and exergy perspective. Appl. Energy 298, 117187 (2021)
Marmolejo-Correa, D.; Gundersen, T.: A comparison of exergy efficiency definitions with focus on low temperature processes. Energy 44, 477–489 (2012)
Nguyen, T.B.; Zondervan, E.: Methanol production from captured CO2 using hydrogenation and reforming technologies environmental and economic evaluation. J. Util. 34, 1–11 (2019)
Alipour, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Omidvarborna, H.; Karimi, A.: Techno-economic assessment of the AHP based selected method for separating formic acid from an aqueous effluent. J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 56, 105–121 (2022)
Peters, M.S.; Timmerhaus, K.D.; West, R.E.: Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers. McGraw-Hill, New York (2003)
Sinnott, R.; Towler, G.: Chemical Engineering Design, SI Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2019)
Smith, R.: Chemical Process: Design and Integration. Wiley, Hoboken (2005)
Mofid, H.; Jazayeri-Rad, H.; Shahbazian, M.; Fetanat, A.: Enhancing the performance of a parallel nitrogen expansion liquefaction process (NELP) using the multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) algorithm. Energy 172, 286–303 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shamsi, M., Rahimi, M., Sheidaei, M. et al. A New Integrated Process for LNG Production Based on the Single Mixed Refrigerant: Energy, Exergy, Environmental and Economic Analysis. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 15805–15821 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07659-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07659-2