Abstract
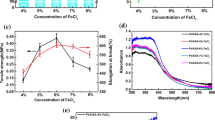
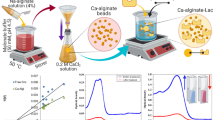
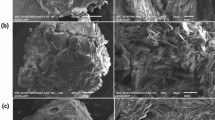
A novel catalyst made of zero-valent iron (Fe0) well dispersed and immobilized on alginate beads and coated using CuO-Fe3O4 (CuO-Fe3O4-Fe0/Abs) was designed and fabricated as a sustainable catalyst to degrade oxytetracycline using a heterogeneous photo-Fenton process. The CuO-Fe3O4 component was incorporated as a thin layer to cover the beads during the cross-linking reaction to allow immobilization of Fe0 inside the bead structure. Characterization analyses such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirmed the successful immobilization of Fe0 on the thin layer of CuO-Fe3O4 on the beads. The performance test of the catalysts showed that they effectively removed OTC from water through the Fenton and photo-Fenton process at a wide range of pH values (pH 3–8) under visible irradiation. The optimum conditions to completely degrade 20 mg/L antibiotics were achieved at pH 3.0 in the presence of 200 mg/L (CuO-Fe3O4-Fe0/Abs) catalyst within 60 min of reaction time because of the synergic effect associated with Fe0 Fenton reaction in the presence of CuO-Fe3O4. These results proved the high performance of the catalyst for the OTC degradation in wastewater satisfactorily fits the pseudo-first-order kinetic model. The k value increases from 0.0476 for Cycle 1 to 0.0831 min−1 for Cycle 4 to indicate that chemical reaction indeed played the predominant role in the OTC degradation. It also had high stability with the controlled release of Fe0 into the solution to enhance its catalytic activity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fouad, K.; Bassyouni, M.; Alalm, M.G.; Saleh, M.Y.: Recent developments in recalcitrant organic pollutants degradation using immobilized photocatalysts. Appl. Phys. A 127(8), 1–28 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04724-1
King, S.T.; Sylvander, M.; Kheperu, M.; Racz, L.; Harper, W.F., Jr.: Detecting recalcitrant organic chemicals in water with microbial fuel cells and artificial neural networks. Sci. Total Environ. 497, 527–533 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.108
O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Song, Y.; Sarmah, A.K.; Li, X.; Tack, F.M.: Sustainable in situ remediation of recalcitrant organic pollutants in groundwater with controlled release materials: a review. J. Control. Release 283, 200–213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.06.007
Klein, E.Y.; van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R.: Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 115(15), E3463–E3470 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.171729511
Hassouna, M.; Amin, R.R.; Ahmed-Anwar, A.A.; Mahmoud, R.K.: Efficient removal of oxytetracycline and some heavy metals from aqueous solutions by Mg-Al layered double hydroxide nanomaterial. Egypt. J. Chem. 62, 177–195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21608/EJCHEM.2019.6102.1510
Leal, J.; Esteves, V.; Santos, E.: Use of sunlight to degrade oxytetracycline in marine aquaculture’s waters. Environ. Pollut. 213, 932–939 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.040
Ferreira, L.; Salmerón, I.; Peres, J.; Tavares, P.; Lucas, M.; Malato, S.: Advanced oxidation processes as sustainable technologies for the reduction of elderberry agro-industrial water impact. Water Resour. Ind. 24, 100137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2020.100137
Hitam, C.; Jalil, A.: A review on exploration of Fe2O3 photocatalyst towards degradation of dyes and organic contaminants. J. Environ. Manage 258, 110050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.110050
Le, T.T.; Murugesan, K.; Lee, C.-S.; Vu, C.H.; Chang, Y.-S.; Jeon, J.-R.: Degradation of synthetic pollutants in real wastewater using laccase encapsulated in core–shell magnetic copper alginate beads. Bioresour. Technol. 216, 203–210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.077
Hassandoost, R.; Pouran, S.R.; Khataee, A.; Orooji, Y.; Joo, S.W.: Hierarchically structured ternary heterojunctions based on Ce3+/Ce4+ modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles anchored onto graphene oxide sheets as magnetic visible-light-active photocatalysts for decontamination of oxytetracycline. J. Hazard. Mater. 376, 200–211 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.035
Liu, M.; Yu, S.; Hou, L.-A.; Hu, X.: Removal of oxytetracycline by Fe2O3–TiO2/modified zeolite composites under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(10), 9087–9096 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01052-2
Lei, Y.; Chen, C.-S.; Tu, Y.-J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Zhang, H.: Heterogeneous degradation of organic pollutants by persulfate activated by CuO-Fe3O4: mechanism, stability, and effects of pH and bicarbonate ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(11), 6838–6845 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00623
Dong, Y.; Dong, W.; Cao, Y.; Han, Z.; Ding, Z.: Preparation and catalytic activity of Fe alginate gel beads for oxidative degradation of azo dyes under visible light irradiation. Catal. Today 175(1), 346–355 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.035
Kim, H.; Hong, H.-J.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.-H.; Yang, J.-W.: Degradation of trichloroethylene (TCE) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) immobilized in alginate bead. J. Hazard. Mater. 176(1–3), 1038–1043 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.145
Kang, Y.-G.; Vu, H.C.; Le, T.T.; Chang, Y.-S.: Activation of persulfate by a novel Fe (II)-immobilized chitosan/alginate composite for bisphenol a degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 353, 736–745 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.175
Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.: Lignin peroxidase immobilization on Ca-alginate beads and its dye degradation performance in a packed bed reactor system. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 20, 101205 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101205
Lee, C.-S.; Gong, J.; Huong, C.V.; Oh, D.-S.; Chang, Y.-S.: Macroporous alginate substrate-bound growth of Fe0 nanoparticles with high redox activities for nitrate removal from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 298, 206–213 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.113
Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.: Novel characteristics of horseradish peroxidase immobilized onto the polyvinyl alcohol-alginate beads and its methyl orange degradation potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 105, 328–335 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.042
Pullin, H.; Springell, R.; Parry, S.; Scott, T.: The effect of aqueous corrosion on the structure and reactivity of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 308, 568–577 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.088
Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-G.; Shin, H.-S.: Effects of synthesis conditions on the characteristics and reactivity of nano scale zero valent iron. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 105(1–2), 144–150 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.04.005
Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B.; Takriff, M.S.; Sopian, K.: Synthesis and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical oxidation of concentrated chlorophenols under direct solar radiation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 7(6), 4871–4888 (2012)
Jiang, Y.; Ran, J.; Mao, K.; Yang, X.; Zhong, L.; Yang, C.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.: Recent progress in Fenton/Fenton-like reactions for the removal of antibiotics in aqueous environments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 236, 113464 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113464
Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Jin, C.; Kang, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; You, M.; Wu, Z.: Synthesis of novel Co3O4 hierarchical porous nanosheets via corn stem and MOF-Co templates for efficient oxytetracycline degradation by peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 392, 123789 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123789
Zhao, N.; Liu, K.; He, C.; Gao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, T.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Qiu, R.: Singlet oxygen mediated the selective removal of oxytetracycline in C/Fe3C/Fe0 system as compared to chloramphenicol. Environ. Int. 143, 105899 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105899
Wang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Xing, S.: Comparative study of Cu-based bimetallic oxides for Fenton-like degradation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 203, 450–456 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.013
Wu, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xin, S.; Lu, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Cui, Y.; Fu, R.; Wang, S.: CuxNiyCo-LDH nanosheets on graphene oxide: An efficient and stable Fenton-like catalyst for dual-mechanism degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 434, 134574 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134574
Pham, V.L.; Kim, D.-G.; Ko, S.-O.: Cu@Fe3O4 core-shell nanoparticle-catalyzed oxidative degradation of the antibiotic oxytetracycline in pre-treated landfill leachate. Chemosphere 191, 639–650 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.090
Pereira, J.H.; Queirós, D.B.; Reis, A.C.; Nunes, O.C.; Borges, M.T.; Boaventura, R.A.; Vilar, V.J.: Process enhancement at near neutral pH of a homogeneous photo-Fenton reaction using ferricarboxylate complexes: application to oxytetracycline degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 253, 217–228 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.037
Masschelein, C.A.; Ryder, D.S.; Simon, J.-P.: Immobilized cell technology in beer production. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 14(2), 155–177 (1994). https://doi.org/10.3109/07388559409086966
Kessler, A.; Hedberg, J.; Blomberg, E.; Odnevall, I.: Reactive oxygen species formed by metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in physiological media—a review of reactions of importance to nanotoxicity and proposal for categorization. Nanomaterials 12(11), 1922 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111922
Hu, X.; Li, C.; Song, J.; Zheng, S.; Sun, Z.: Multidimensional assembly of oxygen vacancy-rich amorphous TiO2-BiOBr-sepiolite composite for rapid elimination of formaldehyde and oxytetracycline under visible light. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 574, 61–73 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.035
Li, N.; Zhou, L.; Jin, X.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z.: Simultaneous removal of tetracycline and oxytetracycline antibiotics from wastewater using a ZIF-8 metal organic-framework. J. Hazard. Mater. 366, 563–572 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.047
Priya, B.; Raizada, P.; Singh, N.; Thakur, P.; Singh, P.: Adsorptional photocatalytic mineralization of oxytetracycline and ampicillin antibiotics using Bi2O3/BiOCl supported on graphene sand composite and chitosan. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 479, 271–283 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.067
Raizada, P.; Kumari, J.; Shandilya, P.; Singh, P.: Kinetics of photocatalytic mineralization of oxytetracycline and ampicillin using activated carbon supported ZnO/ZnWO. Desalination 79, 204–213 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20831
Raizada, P.; Kumari, J.; Shandilya, P.; Dhiman, R.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, P.: Magnetically retrievable Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 immobilized on graphene sand composite for investigation of photocatalytic mineralization of oxytetracycline and ampicillin. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 106, 104–116 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.12.012
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Long-term Research Grant Scheme (LRGS/1/2018/USM/01/1/3) provided by the Ministry of Higher Education of Malaysia.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support received from the Ministry of Higher Education (MoHE) of Malaysia (LRGS Grant, Project number LRGS/1/2018/USM/01/1/3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alrebaki, M.A., Ba-Abbad, M.M. & Abdullah, A.Z. Novel Fe0 Embedded Alginate Beads and Coated with CuO-Fe3O4 as a Sustainable Catalyst for Photo-Fenton Degradation of Oxytetracycline in Wastewater. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 8957–8969 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07577-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07577-9