Abstract
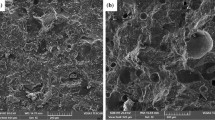
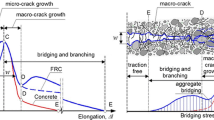
Abundant research on geopolymer concrete in the last two decades has provided worldwide acceptability in conventional structural applications. The high-impact applications of geopolymers are mostly limited because they are quasi-brittle in nature and show moderate crack resistance; hence, they require suitable reinforcing materials such as fibers. This paper reports a study to assess the strength and durability properties of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete (FA-GPC) prepared with novel C-glass fibers. The binder mix was comprised of Fly Ash (FA), Lime (L), Silica Fume (SF) and was activated by sodium hydroxide (12 M) and sodium silicate solution, followed by curing under ambient conditions. Glass fibers were utilized in varying proportions (0.125, 0.25, 0.375, 0.5, 0.625, and 0.75%), by weight of the binder mix. It was found that the incorporation of 0.5% glass fiber significantly increased the compressive strength, split tensile strength, and flexural strength properties. From the durability perspective, the samples exhibited good resistance against seawater, MgSO4 solution, and H2SO4 when compared with the control mix. Further, the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis was employed to explore the nature of the geopolymer–fiber matrix. It was revealed that excellent interfacial bonding existed between fiber and the geopolymer matrix. The results indicate that addition of C-glass fibers significantly improves the overall mechanical performance of FA-GPC. The research presented here establishes the advantages of using C-glass fibers-based geopolymer concrete, thus encouraging its broader utilization.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Alkali resistance
- BIS:
-
Bureau of Indian Standards
- C:
-
Chemical or corrosion
- CAgg:
-
Coarse aggregates
- CTM:
-
Compression testing machine
- E:
-
Electrical
- FA:
-
Fly ash
- FAgg:
-
Fine aggregates
- FA-GPC:
-
Fly ash-based geopolymer concrete
- FCA:
-
Ferrochrome ash
- FTM:
-
Flexural testing machine
- GFRFGC:
-
Glass fiber reinforced fly ash based geopolymer concrete
- GGBFS:
-
Ground granulated blast furnace slag
- GPC:
-
Geopolymer concrete
- Kg:
-
Kilogram
- L:
-
Lime
- M:
-
Molarity
- MPa:
-
Megapascal
- Na2SiO3 :
-
Sodium silicate
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- OPC:
-
Ordinary Portland Cement
- RHA:
-
Rice husk ash
- Rs.:
-
Rupee
- SCBA:
-
Sugarcane bagasse ash
- SEM:
-
Scanning Electron Microscope
- SF:
-
Silica fume
- SP:
-
Superplasticizer
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- XRF:
-
X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy
References
Mustakim, S.M.; Das, S.K.; Mishra, J.; Aftab, A.; Alomayri, T.S.; Assaedi, H.S.; Kaze, C.R.: Improvement in fresh, mechanical, and microstructural properties of fly ash-blast furnace slag based geopolymer concrete by addition of nano and micro silica. Silicon, pp.1–14 (2020).
Das, S.K.; Mishra, J.; Singh, S.K.; Mustakim, S.M.; Patel, A.; Das, S.K.; Behera, U.: Characterization and utilization of rice husk ash (RHA) in fly ash–Blast furnace slag based geopolymer concrete for sustainable future. Mater. Today: Proc. 33, 5162–5167 (2020)
Rashad, A.M.: A comprehensive overview about the influence of different admixtures and additives on the properties of alkali-activated fly ash. Mater. Des. 53, 1005–1025 (2014)
Vignesh, P.; Krishnaraja, A.R.; Nandhini, N.: Study on mechanical properties of geopolymer concrete using m-sand and glass fibers. Int. J. Innovative Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3(2), 110 (2014)
Bashar, I.I.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Islam, A.; Santhi, H.; Sharmin, A.: Engineering properties and fracture behaviour of high volume palm oil fuel ash based fibre reinforced geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 111, 286–297 (2016)
Madheswaran, C.K.; Ambily, P.S.; Rajamane, N.P.; Arun, G.: Studies on flexural behaviour of reinforced geopolymer concrete beams with lightweight aggregates. Int. J. Civ. Struct. Eng. 4(3), 295–305 (2014)
Reed, M.; Lokuge, W.; Karunasena, W.: Fibre-reinforced geopolymer concrete with ambient curing for in situ applications. J. Mater. Sci. 49(12), 4297–4304 (2014)
Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.E.; Sumajouw, D.M.J.; Rangan, B.V.: August. Introducing fly ash-based geopolymer concrete: manufacture and engineering properties. In 30th conference on our world in concrete & structures (Vol. 24) (2005)
Das, S.K.; Mishra, J.; Mustakim, S.M.; Adesina, A.; Kaze, C.R.; Das, D.: Sustainable utilization of ultrafine rice husk ash in alkali-activated concrete: Characterization and performance evaluation. J. Sustain. Cement-Based Mater., pp.1–19 (2021).
Krishna, R.S.; Shaikh, F.; Mishra, J.; Lazorenko, G.; Kasprzhitskii, A.: Mine tailings-based geopolymers: Properties, applications and industrial prospects. Ceram. Int. 47(13), 17826–17843 (2021)
Sikder, A.; Saha, P.: Effect of different types of Waste as Binder on Durability Properties of Geopolymer Concrete: A Review. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 796, No. 1, p. 012018). Bristol: IOP Publishing (2021).
Uma, K.; Anuradha, R.; Venkatasubramani, R.: Experimental investigation and analytical modeling of reinforced geopolymer concrete beam. Int. J. Civ. Struct. Eng. 2(3), 817–827 (2012)
Vijai, K.; Kumutha, R.; Vishnuram, B.G.: Properties of glass fibre reinforced geopolymer concrete composites. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 13(4), 511–520 (2012)
Al-Majidi, M.H.; Lampropoulos, A.; Cundy, A.B.: Tensile properties of a novel fibre reinforced geopolymer composite with enhanced strain-hardening characteristics. Compos. Struct. 168, 402–427 (2017)
Samal, S.; Marvalová, B.; Petríková, I.; Vallons, K.A.; Lomov, S.V.; Rahier, H.: Impact and post impact behavior of fabric reinforced geopolymer composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 127, 111–124 (2016)
Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Chai, J.X.H.; Lu, T.M.: Properties of fresh and hardened glass fiber reinforced fly ash based geopolymer concrete. In Key Engineering Materials (Vol. 594, pp. 629–633). Switzerland: Trans Tech Publications Ltd (2014).
Mishra, J.; Das, S.K.; Krishna, R.S.; Nanda, B.; Patro, S.K.; Mustakim, S.M.: Synthesis and characterization of a new class of geopolymer binder utilizing ferrochrome ash (FCA) for sustainable industrial waste management. Mater. Today: Proc. 33, 5001–5006 (2020)
Korniejenko, K.; Mikula, J.; Lach, M.: Characterization of mechanical properties of short glass fiber reinforced geopolymer composites. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Composite Science and Technology, Lisboa, Portugal (pp. 2–4) (2015).
Mermerdaş, K.; MulapeeR, E.S.; Oleiwi, S.M.: Effect of glass fiber addition on the strength properties and pore structure of fly ash based geopolymer composites. Eskişehir Tech. Univ. J. Sci. Technol. A-Appl. Sci. Eng. 20(4), 427–435 (2019)
Al-Mashhadani, M.M.; Canpolat, O.; Aygörmez, Y.; Uysal, M.; Erdem, S.: Mechanical and microstructural characterization of fiber-reinforced fly ash based geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 167, 505–513 (2018)
Shinde, B.H.; Kadam, K.N.: Properties of fly ash based geopolymer mortar with ambient curing. Int. J. Eng. Res. 5(1), 203–206 (2016)
Alomayri, T.; Shaikh, F.U.A.; Low, I.M.: Effect of fabric orientation on mechanical properties of cotton fabric reinforced geopolymer composites. Mater. Des. 57, 360–365 (2014)
Li, W.; Xu, J.: Impact characterization of basalt fiber reinforced geopolymeric concrete using a 100-mm-diameter split Hopkinson pressure bar. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 513, 145–153 (2009)
Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Behnia, A.; Javadi Pordsari, A.; Mehrali, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.: A comprehensive study of the polypropylene fiber reinforced fly ash based geopolymer. PLoS ONE 11(1), e0147546 (2016)
Midhun, M.S.; Rao, T.G.; Srikrishna, T.C.: Mechanical and fracture properties of glass fiber reinforced geopolymer concrete. Adv. Concrete Const. 6(1), 29 (2018)
Ganesh, A.C.; Muthukannan, M.: Development of high performance sustainable optimized fiber-reinforced geopolymer concrete and prediction of compressive strength. J. Clean. Prod. 282, 124543 (2021)
Sufian, S.: The microstructural and mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced geopolymer composites. Malaysian J. Microscopy, 15(1) (2019).
Chawla, K.K.: Glass fibers. In: Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, pp. 3541–3545 (2001)
Funke, H.; Gelbrich, S.; Kroll, L.: The durability and performance of short fibers for a newly developed alkali-activated binder. Fibers 4(1), 11 (2016)
Ghugal, Y.M.; Deshmukh, S.B.: Performance of alkali-resistant glass fiber reinforced concrete. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 25(6), 617–630 (2006)
Iskender, M.; Karasu, B.: Glass fibre reinforced concrete (GFRC). El-Cezerî Fen ve Mühendislik Dergisi 5, 136–162 (2018)
Madhava Perumal, R.; Jasper Daniel, J.; Suriya, S.; Vignesh, R.: Experimental study on glass fiber reinforced geopolymer concrete. J. Appl. Sci. Comput. (JASC) 6(5), 135–141 (2019)
Alizade, E.; Jandaghi, A.F.; Zabihi, S.: Effect of steel fiber corrosión on mechanical properties of steel fiber reinforced concrete (2016).
Lakshmi, K.; Rao, M.S.N.: Experimental study on geopolymer concrete by using glass fibres. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 6(11), 1693–1698 (2019)
Rautray, S.S.; Mohanty, B.N.; Das, M.R.: Performance of self-compacting geopolymer concrete using Bacillus Licheniformis. Mater. Today: Proc. 26, 2817–2824 (2020)
BIS 383: 1970, 1970, Coarse and fine aggregate from natural sources of concrete 9th Revision, BIS, New Delhi.
IS 10086-1982, Indian Standard specification for moulds for use in tests of cement and concrete-V Reprint December 1995, Bureau of Indian Standard, New Delhi-110 002
IS: 516-1959, Indian standard methods of tests for strength of concrete, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi, India.
Jain, M.N.N.; Hake, S.L.; Shirsath, M.N.: Geopolymer concrete with lime addition at normal room temperature. JournalNX 2(8), 13–16 (2016)
Adam, A.A.; Amiri, N.H.; Suarnita, I.W.; Rupang, N.: The effect of lime addition on the setting time and strength of ambient cured fly ash based geopolymer binder. In MATEC web of conferences (Vol. 47, p. 01015). EDP Sciences (2016).
Okoye, F.N.; Durgaprasad, J.; Singh, N.B.: Effect of silica fume on the mechanical properties of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. Ceram. Int. 42(2), 3000–3006 (2016)
Das, S.K.; Mustakim, S.M.; Adesina, A.; Mishra, J.; Alomayri, T.S.; Assaedi, H.S.; Kaze, C.R.: Fresh, strength and microstructure properties of geopolymer concrete incorporating lime and silica fume as replacement of fly ash. J. Build. Eng. 32, 101780 (2020)
Raval, V.; Nisarg, P.; Digvijaysinh, M.; Umang, G.; Mistry, J.: Improving structure integrity with fibre reinforced concrete. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 06(04), 2920–2924 (2019)
Kumar, R.; Suman, S.K.; Sharma, M.: Laboratory investigation on the synthesis and mechanical characterization of fiber-reinforced geopolymer concrete. Mater. Today: Proc. 32, 268–273 (2020)
Rao, K.J.; Ramlal, C.S.S.B.; Sandeep, D.; Rao, M.V.S.: A Study on the Fresh and Hardened Properties of Fly-Ash Based Glass Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 9(2), 560–567 (2016)
Ravichandran, G.; Sivaraja, M.; Jegan, M.; Harihanandh, M.; Krishnaraja, A.: Performance of glass fiber reinforced geopolymer concrete under varying temperature effect. Technology 9(4), 1316–1323 (2018)
Ganesh, C.; Muthukannan, M.: Investigation on the glass fiber reinforced geopolymer concrete made of M-sand. J. Mater. Eng. Struct. 6(4), pp.501–512 (2019).
Shaikh, F.U.A.: Deflection hardening behaviour of short fibre reinforced fly ash based geopolymer composites. Mater. Des. 50, 674–682 (2013)
Sikder, A.; Bera, D.; Rath, A.: Bamboo as a green building material in construction industry—a review. In International Conference on Recent Advances in Mechanics and Materials (ICRAMM-2016). pp.269–273 (2016).
Abbas, R.; Khereby, M.A.; Ghorab, H.Y.; Elkhoshkhany, N.: Preparation of geopolymer concrete using Egyptian kaolin clay and the study of its environmental effects and economic cost. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 22(3), 669–687 (2020)
Thaarrini, J.; Dhivya, S.: Comparative study on the production cost of geopolymer and conventional concretes. Int. J. Civil Eng. Res. 7(2), 117–124 (2016)
Shah, N.A.; Khandare, M.; Comparative study of strength & cost of fiber reinforced geopolymer concrete and conventional (OPC) concrete. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 5(6), 1724–1729 (2018)
Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R.: Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development: a review. J. Mater. Sci. 42(3), 729–746 (2007)
Saral, J.A.; Gayathri, S.; Tamilselvi, M.; Raj, B.R.: An experimental study on fibre reinforced geopolymer concrete composites-glass fibre, Copper Slag. Int. J. Eng. Technolo., 7(3.34), 433–435 (2018).
Sathanandam, T.; Awoyera, P.O.; Vijayan, V.; Sathishkumar, K.: Low carbon building: Experimental insight on the use of fly ash and glass fibre for making geopolymer concrete. Sustain. Environ. Res. 27(3), 146–153 (2017)
Sathish, K.; Blessen, S.T.; Alex, C.: An experimental study of the properties of glass fiber reinforced geopolymer concrete. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2(6), 722–726 (2012)
Bhalchandra, S.A.; Bhosle, A.Y.: Properties of glass fibre reinforced geopolymer concrete. Int. J. Modern Eng. Res. (IJMER) 3(4), 2007–2010 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the faculties from KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India: Dr. Ashoke Ku. Rath and Dr. Dillip Ku. Bera, Dr. Purnachandra Saha, and faculties from VSSUT, Burla, Odisha, India: Dr. Sanjaya Ku. Patro and Dr. Bharadwaj Nanda for their guidance during the experimental investigations and proofreading of the manuscript. The authors also acknowledge the support from Dr. S.M. Mustakim and the laboratory staff of CSIR—Institute of Minerals and Materials Technology, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India, for their help in completing this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sikder, A., Mishra, J., Krishna, R.S. et al. Evaluation of the Mechanical and Durability Properties of Geopolymer Concrete Prepared with C-Glass Fibers. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 12759–12774 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07558-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07558-y