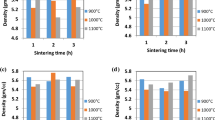
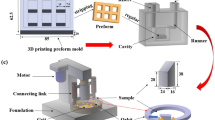
Abstract
For decades, the demand for thermally stable wear and corrosion-resistant materials has been met by surface boriding of ferrous materials. Issues associated with the surface boriding, such as boride layer–host material interface instabilities, could be avoided by the in situ synthesis of iron borides. However, attempts to fabricate bulks of iron matrix reinforced with iron borides using casting have inherent drawbacks. The requirement of elevated temperatures and less control over the microstructure can be given as examples. This study uses an in situ approach to manufacture iron matrix microcomposite wires reinforced with controlled morphology and ratio of iron borides. Powder mixtures of 5, 10, and 15 vol. %~B4C in Fe are compacted in steel tubes which are cold rolled to turn the iron particles into extended fibers. Wires are later treated at 1100 °C for 2 h to assist the B diffusion into elongated Fe particles, consequently resulting in the synthesis of iron borides. The influence of the processing parameters on the microstructure is evaluated using microhardness, SEM, EDS, tensile testing, and fractographic analyses. Results showed that the iron borides’ morphology and relative ratio in the iron matrix can be controlled by employing an appropriate combination of plastic deformation and powder mixture ratios in the pre-sinter wires.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zafar, H.M.N.; Nair, F.: Deformation processed high strength high conductivity Cu and Al matrix composite wires: an introductory review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. L. 236, 1927–1948 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/14644207221090534
Sahin, S.; Meric, C.; Saritas, S.: Production of ferroboron powders by solid boronizing method. Adv. Powder Technol. 21, 483–487 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2010.01.011
Montealegre-Melendez, I.; Arévalo, C.; Ariza, E.; Pérez-Soriano, E.M.; Rubio-Escudero, C.: Analysis of the microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium-based composites reinforced by secondary phases and B4C particles produced via direct hot pressing. Materials. 10, 1240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111240
Fattahi, M.; Pazhouhanfar, Y.; Delbari, S.A.; Shaddel, S.; Namini, S.: A Strengthening of novel TiC–AlN ceramic with in-situ synthesized Ti3Al intermetallic compound. Ceram. Int. 46, 14105–14113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.213
Balaji, V.S.; Kumaran, S.: Densification and microstructural studies of titanium–boron carbide (B4C) powder mixture during spark plasma sintering. Powder Technol. 264, 536–540 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.05.050
Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liao, H.; Zeng, M.; Ma, S.: A review on relationship between morphology of boride of Fe-B alloys and the wear/corrosion resistant properties and mechanisms. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 6308–6320 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.09.004
Allaoui, O.; Bouaouadja, N.; Saindernan, G.: Characterization of boronized layers on a XC38 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 201, 3475–3482 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.07.238
Kayali, Y.; Büyüksaǧiş, A.; Yalçin, Y.: Corrosion and wear behaviors of boronized AISI 316L stainless steel. Met. Mater. Int. 19, 1053–1061 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-5019-x
Nair, F.; Zafar, H.M.N.; Cerit, A.A.; Karamış, M.B.: Analyzing the influence of simultaneously austenitization and multi-directional boriding on the surface and subsurface of H13 tool steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07036-4
Ohtani, H.; Hasebe, M.; Ishida, K.; Nishizawa, T.: Calculation of Fe-C-B Ternary phase diagram. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 28, 1043–1050 (1988). https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational1966.28.1043
Aizenshtein, M.; Mizrahi, I.; Froumin, N.; Hayun, S.; Dariel, M.: Interface interaction in the B4C/(Fe–B–C) system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 495, 70–74 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.06.100
Medvedovski, E., Chinski, FA & Stewart, J., Thermal diffusion coatings for wear-resistant components for oil and gas industry, In: P. C. Tatsuki Ohji, Makio Naito, Javier E. Garay, Hua-Tay Lin. pp. 13–29. Wiley, Coronado, California (2014)
Lentz, J.; Röttger, A.; Theisen, W.: Hardness and modulus of Fe2B, Fe3 (C, B), and Fe23 (C, B) 6 borides and carboborides in the Fe-CB system. Mater. Charact. 135, 192–202 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2017.11.012
Delai, O.; Xia, C.; Shiqiang, L.: Growth kinetics of the FeB/Fe2B boride layer on the surface of 4Cr5MoSiV1 steel: experiments and modelling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 11, 1272–1280 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.01.109
García-León, R.A.; Martínez-Trinidad, J.; Campos-Silva, I.: Historical review on the boriding process using bibliometric analysis. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 74, 541–557 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02174-6
Sireli, GK., Molten salt baths: electrochemical boriding, In: G. E. T. Rafael Colas. (1st), pp. 2284–2300. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, USA (2016)
Martini, C.; Palombarini, G.; Poli, G.; Prandstraller, D.: Sliding and abrasive wear behaviour of boride coatings. Wear 256, 608–613 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2003.10.003
Campos-Silva, I.; Martinez-Trinidad, J.; Doñu-Ruíz, M.; Rodríguez-Castro, G.; Hernandez-Sanchez, E.: Interfacial indentation test of FeB/Fe2B coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 206, 1809–1815 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.08.017
Bagliuk, G., Properties and structure of sintered boron containing carbon steels, In: V. Shatokha. pp. 249–266. InTechOpen, Rijeka, Croatia (2012)
Bindal, C.; Ucisik, A.: Characterization of boriding of 0.3% C, 0.02% P plain carbon steel. Vacuum. 82, 90–94 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2007.04.039
Sen, U.; Sen, S.; Yilmaz, F.: An evaluation of some properties of borides deposited on boronized ductile iron. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 148, 1–7 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.01.015
Bindal, C.; Üçisik, A.H.: Characterization of borides formed on impurity-controlled chromium-based low alloy steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 122, 208–213 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(99)00294-7
Simonenko, A.N.; Poroshin, V.V.; Antia, P.K.: Aging of salt baths with electrolysis-free liquid boriding. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 27, 13–16 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00741880
Bartsch, K.; Leonhardt, A.: Formation of iron boride layers on steel by d.c.-plasma boriding and deposition processes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 116–119, 386–390 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(99)00078-X
Kulka, M.; Makuch, N.; Piasecki, A.: Nanomechanical characterization and fracture toughness of FeB and Fe2B iron borides produced by gas boriding of Armco iron. Surf. Coat. Technol. 325, 515–532 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.07.020
Matiašovský, K.; Chrenková-Paučírová, M.; Fellner, P.; Makyta, M.: Electrochemical and thermochemical boriding in molten salts. Surf. Coat. Technol. 35, 133–149 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0257-8972(88)90064-3
Lyakhovich, L.S.; Protasevich, G.F.; Voroshnin, L.G.; Suprunovich, A.S.; Shabashova, N.D.: Liquid boriding. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 18, 647–648 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703830
Jamali, G.; Nourouzi, S.; Jamaati, R.: Manufacturing of gradient Al/SiC composite wire by friction stir back extrusion. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 35, 735–743 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.09.004
Mindivan, H.: A Study on the corrosion and Tribocorrosion behavior of Al-30 Vol.% B4C composite produced by mechanical milling and hot pressing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 9140–9148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06127-y
Hamamcı, M.; Cerit, A.A.; Nair, F.: Effect of sintering parameters on the microstructure and micromechanical properties of in-situ synthesized boride phases (Fe2B-FeB) in iron matrix composites reinforced with B4C particles. Mater. Charact. 191, 112075 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112075
Fiedler, H.C.; Hayes, W.J.: The formation of a soft layer in borided hot work die steels. Metall. Trans. 1, 1071–1073 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811810
Ma, Y.; Gao, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.: Fabrication and characterization of iron pnictide wires and bulk materials through the powder-in-tube method. Physica C: Supercond. 469, 651–656 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.2009.03.024
Huang, Z.; Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Wang, B.: Bulk Fe2B crystal fabricated by mechanical ball milling and plasma activated sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 196–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.07.205
Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; He, Y.; Bai, Y.: Interface characteristics and corrosion behaviour of oriented bulk Fe2B alloy in liquid zinc. Corros. Sci. 78, 71–80 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2013.08.033
Li, K.; Huang, Z.; Jian, Y.; Min, T.; Lou, X.: Friction and wear behavior of single-phase Fe2B Bulk under dry sliding condition. Tribol. Trans. 61, 513–521 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2017.1363929
Ma, S.; Xing, J.; He, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, Y.: Effect of orientation and lamellar spacing of Fe2B on interfaces and corrosion behavior of Fe-B alloy in hot-dip galvanization. Acta Mater. 115, 392–402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.06.016
Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Xing, J.; Wei, X.; Ma, S.: Effect of hot forging on microstructure and abrasion resistance of Fe-B Alloy. Tribol. Trans. 56, 461–468 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2012.759304
Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.: Abrasion wear behavior of a forged and unforged Fe-B alloy. Mater. Test. 58, 127–132 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3139/120.110834
Yi, D.; Xing, J.; Ma, S.; Fu, H.; Chen, W.: Three-body abrasive wear behavior of low carbon Fe–B cast alloy and its microstructures under different casting process. Tribol. Lett. 42, 67–77 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9748-z
Shi, X.L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Zhou, R.: Effects of rare earth, titanium, and magnesium additions on microstructures and properties of high-boron medium-carbon alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23, 1226–1233 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30180-7
Chen, X.; Li, Y.: Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of high boron white cast iron. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528, 770–775 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.09.092
Chang, K.-C.; Zhao, J.-R.; Hung, F.-Y.: Microstructure, mechanical properties, and fatigue fracture characteristics of high-fracture-resistance selective laser melting Al-Ni-Cu alloys. Metals. 11, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010087
Yu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xin, R.; Liu, R.: Study on properties of SLM-NiTi shape memory alloy under the same energy density. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 13, 241–250 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.04.058
Konovalov, S.; Osintsev, K.; Golubeva, A.; Smelov, V.; Ivanov, Y.: Surface modification of Ti-based alloy by selective laser melting of Ni-based superalloy powder. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 8796–8807 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.06.016
Nair, F.; Hamamcı, M.: Effect of In-Situ synthesized boride phases on the impact behavior of iron-based composites reinforced by B4C particles. Metals. 10, 554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050554
Pantsyrny, V.I.; Khlebova, N.E.; Sudyev, S.V.; Kukina, O.V.; Beliakov, N.A.: Thermal stability of the high strength high conductivity Cu–Nb, Cu–V, and Cu–Fe nanostructured microcomposite wires. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 24, 1–4 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASC.2013.2293655
Manchili, S.K.; Wendel, J.; Zehri, A.; Liu, J.; Hryha, E.: Effect of nanopowder addition on the sintering of water-atomized iron powder. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 51, 4890–4901 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-05891-1
Turov, Y.V.; Khusid, B.; Voroshnin, L.; Khina, B.; Kozlovskii, I.: Structure formation in sintering iron-boron carbide powder composite. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 30, 465–470 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795069
Turov, Y.V.; Khusid, B.; Voroshnin, L.; Khina, B.; Kozlovskii, I.: Gas transport processes in sintering of an iron-boron carbide powder composite. Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 28, 618–622 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00794577
Sezgin, C.T.; Hayat, F.: The effects of boriding process on tribological properties and corrosive behavior of a novel high manganese steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 300, 117421 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117421
Ozdemir, O.; Usta, M.; Bindal, C.; Ucisik, A.H.: Hard iron boride (Fe2B) on 99.97wt% pure iron. Vacuum. 80, 1391–1395 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2006.01.022
Ebrahimi, S.; Heydari, M.S.; Baharvandi, H.R.; Ehsani, N.: Effect of iron on the wetting, sintering ability, and the physical and mechanical properties of boron carbide composites: a review. Int. J. Refract. Hard Met. 57, 78–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.02.007
Marr, T.; Freudenberger, J.; Kauffmann, A.; Romberg, J.; Okulov, I.: Processing of intermetallic Titanium aluminide wires. Metals. 3, 188–201 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/met3020188
Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y.; He, J.; Yao, Y.; Sun, Z.: Effect of cold drawing on microstructure and properties of the invar alloy strengthened by carbide-forming elements. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 13, 1012–1019 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.05.026
Hardwick, D.A.; Rhodes, C.G.; Fritzemeier, L.G.: The effect of annealing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-X microcomposites. Metall. Trans. A. 24, 27–34 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02669599
Dudrová, E.; Kabátová, M.: Fractography of sintered steels. Powder Metall. Prog. 8, 59–75 (2004)
Vidal, V.; Thilly, L.; Lecouturier, F.; Renault, P.O.: Effects of size and geometry on the plasticity of high-strength copper/tantalum nanofilamentary conductors obtained by severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 54, 1063–1075 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2005.10.031
Rodriguez, J.A.; Goodman, D.W.J.S.: The nature of the metal-metal bond in bimetallic surfaces. Science 257, 897–903 (1992)
Özturk, T.; Poole, W.J.; Embury, J.D.: The deformation of Cu·W laminates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 148, 175–178 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(91)90819-9
Vassileva, V.; Danninger, H.; Strobl, S.; Gierl-Mayer, C.; de Oro Calderon, R.: The role of the atmosphere on boron-activated sintering of ferrous powder compacts. Powder Metall. Prog. 18, 6–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/pmp-2018-0002
Rokebrand, P.; Sigalas, I.: Fe–B–C composites produced using spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Refract. Hard Met. 49, 320–326 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.07.039
Tkachenko, V.F.; Kogan, Y.I.: Structural characteristics and mechanical properties of sintered Fe-B4C materials. Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 17, 384–388 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795022
Funding
This study did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fehmi Nair was involved in conceptualization, materials and experimental setup preparation, resources, and supervision. Hafiz Muhammad Numan Zafar was involved in conceptualization, data curation, manuscript preparation, validation, and visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors confirm that they have no competing interests associated with the publication of this study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zafar, H.M.N., Nair, F. Fabrication and Microscale Characterization of Iron Matrix Composite Wires Reinforced by in situ Synthesized Iron Boride Phases. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 3909–3930 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07320-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07320-4