Abstract
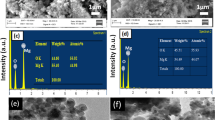
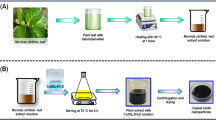
Magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs) have received considerable attention from researchers these days because of their wide-ranging applications in areas such as pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and dermatology. Therefore, in the present study, we have synthesized MgO-NPs with a green approach. The MgO-NPs from aqueous leaf extract of Mariposa christia vespertilionis have been successfully synthesized and checked its resistance to antimicrobial activity. The green-synthesized MgO-NPs samples were calcined at three different calcination temperatures (400 °C, 600 °C, and 900 °C) and subjected to characterization. The antimicrobial activity of the MgO-NPs against gram-positive (S. aureus) bacteria and gram-negative (E. coli) bacteria was also established. UV–Vis spectroscopy was used to confirm the formation of the nanoparticles. Based on Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, the Mg–O stretching is found in the range of 400 cm−1 to 500 cm−1. The scanning electron microscopy showed the spherical shape of the MgO-NPs and transmission electron microscopy revealed that the smallest crystallite size of MgO-NPs calcined at 600 °C was found to be around 17 nm which is less than the size of the MgO-NPs calcined at 400 °C (90 nm) and 900 °C (158 nm). X-ray diffractometer diffractograms show highly crystalline with hexagonal wurtzite structure. Finally, the antimicrobial activities of MgO-NPs showed an efficient effect against gram-positive bacteria, but a negative effect against gram-negative bacteria. The study revealed that the prepared MgO-NPs have shown a promising result as antibacterial agents.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat, I.U.H., Anwar, S.J., Subramaniam, E., Shalla, A.H.: Nanoparticles; Their Use as Antibacterial and DNA Cleaving Agents. In: Nanomaterials for Healthcare, Energy and Environment, Adv. Struct. Mater. Pp. 71-85. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. (2019).https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9833-9_4
Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I.: Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 12(7), 908–931 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Agrawal, S.; Bhatt, M.; Rai, S.K.; Bhatt, A.; Dangwal, P.; Agrawal, P.K.: Silver nanoparticles and its potential applications: a review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 7(2), 930–937 (2019)
Essien, E.R.; Atasie, V.N.; Okeafor, A.O.; Nwude, D.O.: Biogenic synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Manihot esculenta (Crantz) leaf extract. Int. Nano Lett. 10, 43–48 (2020)
Abinaya, S.; Kavitha, H.P.; Prakash, M.; Muthukrishnaraj, A.: Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles and its applications: a review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 19, 100368 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100368
Bandeira, M.; Gionavela, M.; Roesch-Ely, M.; Devine, D.M.: Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: a review of the synthesis methodology and mechanism or formation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 15, 100223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100223
Prasanth, R.; Kumar, S.D.; Jayalakshmi, A.; Singaravelu, G.; Govindaraju, K.; Kumar, V.G.: Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Indian. J. Geo. Mar. Sci. 48, 1210–1215 (2019)
Duong, T.H.Y.; Nguyen, T.N.; Oanh, H.T.; Thi, T.A.D.; Giang, L.N.T.; Phuong, H.T.; Anh, N.T.; Nguyen, B.M.; Quang, V.T.; Le, G.T.; Nguyen, T.V.: Synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoplates and their application in nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide adsorption. J. Chem. 2, 1–9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4376429
Saidi, N.S.M.; Yusoff, H.M.; Bhat, I.U.H.; Appalasamy, S.; Hassim, A.D.M.; Yusoff, F.; Asari, A.; Wahab, N.H.A.: Stability and antibacterial properties of green synthesis silver nanoparticles using Nephelium lappaceum peel extract. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 24(6), 940–953 (2020)
Yusoff, H.M.; Idris, N.H.; Hipul, N.F.; Yusof, N.F.M.; Izham, N.Z.M.; Bhat, I.U.H.: Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using black tea extract and its potential as anode material in sodium-ion batteries. Malays. J. Chem. 22(20), 43–51 (2020)
Malhotra, B.D.; Ali, M.A.: Nanomaterials in biosensors: fundamentals and applications. Nanomater. Biosens. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-44923-6.00001-7
Munjal, S.; Singh, A.; Kumar, V.: Synthesis and characterization of MgO nanoparticles by orange fruit waste through green method. Int. J. Adv. Chem. 4(9), 36–42 (2017). https://doi.org/10.20431/2349-0403.0409005
Yusoff, H.M.; Chandran, P.D.B.; Sayuti, F.A.; Kan, S.-U.; Radzi, S.A.M.; Yong, F.-S.J.; Lee, O.J.; Chia, P.W.: Highly efficient, recyclable and alternative method of synthesizing phenols from phenylboronic acids using non-endangered metal: samarium oxide. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 130, 108749 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108749
Velmurugan, R., Incharoensakdi, A.: Nanoparticles and organic matter. In: Nanomaterials in Plants, Algae, and Microorganisms, pp.407-428. Academic Press, United States (2018)
Yusoff, H.M.; Hazwani, N.U.; Hassan, N.; Izwani, F.: Comparison of sol gel and dehydration magnesium oxide (MgO) as a catalyst in Michael addition reaction. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 7(3), 43–50 (2015)
Marina, B.; Possan, A.L.; Pavin, S.S.; Raota, C.S.; Vebber, M.C.; Giovanela, M.; Roesch-Ely, M.; Devine, D.M.: Crespo JS Mechanism of formation, characterization and cytotoxicity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles obtained from Ilex paraguariensis leaves extract. Nano-Struct Nano-Objects (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2020.100532
Anwar, S.J.; Bhat, I.U.H.; Yusoff, H.M.; Razali, M.H.; Kadir, M.A.; Ern, L.K.: Brown algae-based preparation, characterization and application of Pd nanocatalyst for enhanced reductive azo dye degradation. Clean. Eng. Technol. 4, 100172 (2021)
Vergheese, M.; Vishal, S.K.: Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. J. pharmacogn. Phytochem. 7, 1193–1200 (2018)
Palanisamy, G.; Pazhanivel, T.: Green synthesis of MgO nanoparticles for antibacterial activity. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 4, 137–141 (2017)
Suresh, J.; Yuvakkumar, R.; Sundrarajan, M.; Hong, S.I.: Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Res. 952, 141–144 (2014)
Lee, J.J., Yazan, L.S., Kassim, N.K., Che, Abdullah, C.A., Esa, N., Lim, P.C.: Tan DC. Cytotoxic activity of christia vespertilionis root and leaf extract and fractions against breast cancer cell lines. Molecules. 25 (11), 2610 (2020). Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112610
Murugesu, S.; Perumal, V.; Balan, T.; Hamzan, N.A.S.; Shahrim, N.S.S.; Sharrizal, N.S.R.; Hin, L.W.: A review on Christia vespertilionis: a new emerging medicinal plant. Fabad J. Pharm. Sci. 45(3), 269–277 (2020)
Ariff, M.A.M.; Tukiman, S.; Razak, N.A.A.; Osman, M.S.; Jaapar, J.: Optimization of supercritical fluid extraction of Mariposa Christia vespertilionis leaves towards antioxidant using response surface methodology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1349, 012054 (2019)
Ravindran, M.; Dash, G.K.; Sengamalam, R.; Vignesh, R.: Red Butterfly wing (Christia vespertilionis (L. f) Bakh F.): a potential anticancer and antiplasmodial herb under threat of survival in Malaysia. Malays. J. Med. Health. Sci. 15(3), 154 (2019)
Mutalib, N.A.; Latip, N.A.: Synergistic interactions between Christia vespertilionis leaves extract and chemotherapy drug cyclophosphamide on WRL-68 cell line. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 7(3), 109–113 (2019). https://doi.org/10.22270/ajprd.v7i3.488
Smitha, S.; Jain, R.: Anatomical profiling and phytochemical analysis of Christia Vespertilionis (L. F.) Bakh F. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 9(1), 40–50 (2019)
Osman, M.S.; Bashah, N.A.A.; Amri, N.; Kasmir, S.I.; Safri, A.I.D.; Ariff, M.A.M.; Yaakob, N.: Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using aqueous extracts of Mariposa Cristia Vespertillonis: influence of pH on its colloidal stability. Mater. Today: Proceedings. 5, 22050–22055 (2018)
Yusoff, H.M.; Rafit, F.A.; Mohamad, F.I.; Hassan, N.; Daud, A.I.: The effects of calcination temperatures in the synthesis of nanocrystalline magnesium oxide via Sol-Gel technique. Appl. Mech. Mater. 865, 36–42 (2017)
Saleh, T.A.: Protocols for synthesis of nanomaterials, polymers, and green materials as adsorbents for water treatment technologies. Environ. Technol. Innov. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101821
Balraj, B.; Senthilkumar, N.; Potheher, I.V.; Arulmozhi, M.: Characterization, antibacterial, anti-arthritic and in-vitro cytotoxic potentials of biosynthesized magnesium oxide nanomaterial. Mater. Sci. Eng. 231, 121–127 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2018.10.011
Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Habib, S.S.; Memic, A.: Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria: a comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 6003–6009 (2012)
El-Seedi, H.R.; El-Shabasy, R.M.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; Saeed, A.; Shah, A.; Shah, R.; Iftikhar, F.J.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Omri, A.; Hajrahand, N.H.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Zou, X.; Halabi, M.F.; Sarhann, W.; Guo, W.: Metal nanoparticles fabricated by green chemistry using natural extracts: biosynthesis, mechanisms, and applications. RSC Adv. 9(42), 24539 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA02225B
Pugazhendhi, A.; Prabhu, R.; Muguganantham, K.; Shanmuganathan, R.; Natarajan, S.: Anticancer, antimicrobial and photocatalytic activities of green synthesized magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO NPs) using aqueous extract of Sargassum wightii. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 195, 86–97 (2018)
Wunderlich, B.: Thermal Analysis. In: Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology. pp. 9134–9141. Elsevier (2001) https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-08-043152-6/01648-X
Diaz, R.M.; Cardoso-Avila, P.E.; Tavares, J.A.P.; Patakfalvi, R.; Cruz, V.V.; Guevara, H.P.L.; Coronado, O.G.; Garibay, R.I.A.; Arroyo, Q.E.S.; Maranon-Ruiz, V.F.; Contreras, J.C.: Two-step triethylamine-based synthesis of MgO nanoparticles and their antibacterial effect against pathogenic bacteria. Nanomaterials 11(2), 410 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020410
Preethika, M.; Sobana, P.T.: Synthesis and characterisation of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum and its application. World J. Pharm. Res. 7, 285–294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100368
Alswat, A.A., Ahmad, M.B., Saleh, T.A.: Preparation and Characterization of Zeolite\Zinc Oxide-Copper Oxide Nanocomposite: Antibacterial Activities Colloid and Interface Science Communications. 16, 19–24 (2017) doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2016.12.003
Alavi, M.A.; Morsali, A.: Syntheses and characterization of Mg(OH)2 and MgO nanostructures by ultrasonic method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 17(2), 441–446 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.08.013
Karthikeyan, C.; Sisubalan, N.; Sridevi, M.; Varaprasad, K.; Basha, M.H.G.; Shucai, W.; Sadiku, R.: Biocidal chitosan-magnesium oxide nanoparticles via a green precipitation process. J. Hazardous Mater. 411, 124884 (2021)
Vijayakumar, S.; Punitha, V.N.; Parameswari, N.: Phytonanosynthesis of MgO nanoparticles: green synthesis characterization and antimicrobial evaluation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06107-3
Prado, D.C.; Fernández, I.; Rodríguez-Páez, J.E.: MgO nanostructures: synthesis, characterization and tentative mechanisms of nanoparticles formation. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects. 23, 100482 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2020.100482
Arabi, M., Ostovan,A., Bagheri, A.R., Guo, X., Li, J., Ma, J., Chen, L.: Hydrophilic molecularly imprinted nanospheres for the extraction of rhodamine B followed by HPLC analysis: A green approach and hazardous waste elimination. Talanta, 120933 (2020)
Ostovan, A., Ghaedi, M., Arabi, M., Chen, L.: Hydrophilic multitemplate molecularly imprinted biopolymers based on a green synthesis strategy for determination of B-Family vitamins, Source: ACS APPLIED MATERIALS & INTERFACES. 10, 4 : 4140–4150 (2018). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b17500
Ibrahim, H., Klarner, A.D., Poorganji, B., Dean, D., Luo, A.A., Elahinia, M.: Microstructural, mechanical and corrosion characteristics of hear-treated Mg-1.2Zn-O.5Ca (wt%) alloy for use as resorbable bone fixation material. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 69, 203–212 (2017). doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.01.005
Baby, J.N., Sriram, B., Wang, S., George, M.: Effect of various deep eutectic solvents on the sustainable synthesis of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles for simultaneous electrochemical determination of nitrofurantoin and 4-Nitrophenol. Source: ACS sustainable chemistry & engineering. 8, 3: 1479–1486 (2020). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05755
Sharmila, G.; Muthukumaran, C.; Sangeetha, E.; Saraswathi, H.; Soundarya, S.; Kumar, N.M.: Green fabrication, characterization of Pisonia alba leaf extract derived MgO nanoparticles and its biological applications. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects. 20, 100380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2019.100380
Jhansi, K., Jayarambabu, N., Reddy, K. P., Reddy, N. M., Suvarna, R. P., Rao, K. V., Kumar, V. R., Rajendar, V.: Biosynthesis of MgO nanoparticles using mushroom extract: effect on peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seed germination. 3 Biotech. 7: 263–274 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0894-3
Ahmed, T., Noman, M., Manzoor, N., Shahid, M., Hussaini, K.M., Rizwan, M, Ali, S., Maqsood, A., Li, B.: Green magnesium oxide nanoparticles-based modulation of cellular oxidative repair mechanisms to reduce arsenic uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants. Environmental pollution. 288, 117785 (2021). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117785
Bagheri, A.R.; Arabi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L.: Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers based on a green synthesis strategy for magnetic solid-phase extraction of acrylamide in food samples. Talanta 195, 390–400 (2019)
Ibrahem, E.J.; Thalij, K.M.; Badawy, A.S.: Antibacterial potential of magnesium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol. J. Int. 18(1), 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.9734/BJI/2017/29534
Osman, M.S.; Ghani, Z.A.; Ismail, N.F.; Razak, N.A.A.; Jaapar, J.; Ariff, M.A.M.: qualitative comparison of active compounds between red and green Mariposa christia vespertilionis leaves extracts. AIP Conf Proc. 1885, 020282–020287 (2017)
Abdallah, Y., Ogunyemi, S.O., Abdelazez, A., Zhang, M., Hong, X., Ibrahim, E., Hossain, A., Fouad, H., Li, B., Chen, J.: The green synthesis of MgO nano-flowers using Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Rosemary) and the antibacterial activities against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. Biomed. Res. Int. (2019). 1–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5620989
Ghindan, A.Y.; Al-Antary, T.W.; Awwad, A.M.; Akash, M.W.: Aphidicidal potential of green synthesized magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles using Olea europaea leaves extract. ARPN J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 12(10), 293–301 (2017)
Tang, Z.X.; Lv, B.F.: MgO nanoparticles as antibacterial agent: preparation and activity. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 31(3), 591–601 (2014)
Kadhem, E.A.; Zhgair, M.H.; Mahdi, S.S.; Tizkam, H.H.; Alahmad, S.: Antibacterial activity of magnesium oxide nanoparticles prepared by calcination method. Int. J. Pharm. Qual. Assur. 10(3), 73–76 (2019)
Bindhu, M.R., Umadevi, M., Micheal, M.K., Arasu, M.V., Al-Dhabi, N.A.: Structural, morphological and optical properties of MgO nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. Mater. Lett. 166, 19–22 (2016). doi; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.12.020
Khan, A.; Shabbier, D.; Ahmad, P.: Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of MgO-NPs produced from camellia-sinensis leaves extract. Mater. Res. Express. 8(1), 015402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abd421
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the research fund University Malaysia Terengganu (UMT), Talent and Publication Enhancement Research Grant (TAPE-RG Vot: 55259), Faculty of Science and Marine Environment, and Institute of Marine Biotechnology for the facilities provided throughout this study. The authors would also like to thank the Centre for Functional Materials and Nanotechnology, Institute of Science, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Malaysia, for their support in completing this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Farizan, A.F., Yusoff, H.M., Badar, N. et al. Green Synthesis of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles Using Mariposa christia vespertilionis Leaves Extract and Its Antimicrobial Study Toward S. aureus and E. coli. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 7373–7386 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07282-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07282-7