Abstract
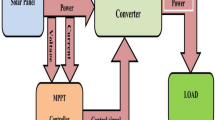
Individual users are increasingly employing photovoltaic (PV) arrays on a commercial and small scale, and they are all attempting to obtain the maximum available power from the panels. The P-V characteristic of the PV module changes after every small-time duration because of the highly fluctuating atmospheric conditions. However, in such cases, it is indispensable to track the Maximum Power Point (MPP), and this becomes a strong nonlinear issue with a time-bounded solution. Therefore, this paper proposes a Logarithmic Seagull Artificial Neural Network-based Improved Perturb and Observe Maximum Power Point Tracking (LSANN-IPOMPPT) algorithm to acquire maximum power from the PV system. The temperature and irradiance are the input variables and the optimal current and voltages to trace the MPP are computed by using the LSANN method. Then, the IPOMPPT algorithm is built for the DC–DC converter, which functions as an interface connecting solar modules and the load for transferring maximum power. The DC–DC converter is tuned by an LSANN-IPOMPPT controller to exploit the solar array at a maximal power point. The tracking ability of the proposed LSANN-IPOMPPT is evaluated with current state-of-the-art approaches for differing irradiance and temperature levels. The simulation outcomes depicted that the implementation of LSANN-based IPOMPPT algorithm with a zeta converter exhibited a more efficient output power range than the existing methods.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(J_{{PV\left( {cur} \right)}} ,J_{{PV\left( {nom} \right)}}\) :
-
Current by incident light, photovoltaic current in nominal conditions
- \(r_{SR} ,r_{PR}\) :
-
Series, shunt resistance
- \(l,k_{BC}\) :
-
Ideality factor, Boltzmann constant
- \(T_{tmp} ,T_{{v\left( {tmp} \right)}}\) :
-
Module temperature, cell reference temperature
- \(Q_{E} ,w\) :
-
Semiconductor bandgap energy, charge of an electron
- \(F_{irr} ,F_{{irr\left( {nom} \right)}}\) :
-
Solar irradiance, nominal value of irradiance
- \(J_{shc} ,P_{opc}\) :
-
Short circuit current, open-circuit voltage
- \(J_{shc\left( \kappa \right)} ,J_{rev}\) :
-
Short circuit current per temperature factor \(\kappa\), reverse saturation current
- \(PW_{max}\) :
-
Maximum power
- \(J_{{L_{ind\left( 1 \right)} }} ,J_{{L_{ind\left( 2 \right)} }}\) :
-
Ripple current of inductors in Zeta converter
- \(P_{Vt}^{i/p} , P_{Vt}^{o/p}\) :
-
Input, output voltage of Zeta converter
- \(L_{ind\left( 1 \right)} , L_{ind\left( 2 \right)}\) :
-
Inductors of Zeta converter
- \(C_{cap}^{i/p} , C_{cap}^{o/p}\) :
-
Input, output capacitor of Zeta converter
- \(J_{cur}^{o/p} ,P c_{cap}^{o/p}\) :
-
Output current, output ripple voltage of Zeta converter
- \(St_{f} , \varphi_{D}\) :
-
Switching frequency, duty cycle of Zeta converter
- \(\Delta_{tmp,irr}\) :
-
Temperature, irradiance of PV panel
- \(\Omega_{wt\left( n \right)} , \wp_{bias} , \hbar_{AF}\) :
-
Assigned weight, bias values, activation function of neural network
- \(J_{max} , P_{max}\) :
-
Maximum current, maximum voltage
- \(err,Tar,Obs\) :
-
Error, target, and observed values in neural network
- \({\text{Popsize}},max_{k}\) :
-
Seagull population size, maximum iteration
- \(G_{nw\left( \Psi \right)} , \chi_{cur\left( \Psi \right)}\) :
-
New, current location of the search agent
- \(\varpi_{\Psi } ,\,{\text{e}}\) :
-
Control frequency, motion behaviour of the search
- \(\chi_{best\left( \Psi \right)} , \chi_{\Psi } \left( k \right)\) :
-
Best-fit search agent, best solution
- \(r_{\Psi ,best\left( \Psi \right)}\) :
-
Range between best-fit search agent and other search agents
- \(a,b,c\) :
-
Motion behaviour of seagull
- \(d, q \,{\text{and}}\,f\) :
-
Radius of each turn of spiral, correlation constants
- \(I_{ita}\) :
-
Inertia factor
- \(opt\Psi_{hid\left( n \right),neu\left( n \right)}\) :
-
Optimal number of neurons and hidden layers
References
Sulman, M.; Ali, M.: Impact of environmental factor’s on solar photovoltaic module and different material employed on it. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 9(8), 623–630 (2020)
Peng, F.Z.; Gebbenand M.L.; Ge, B.: A compact nX DC–DC converter for photovoltaic power systems. In: IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, 15–19 September 2013, Denver, CO, USA (2013)
Kroeger, K.P.; Choi, S.; Bazzi, A.M.; Johnson, B.B., Krein, P.T.: A digital implementation of continuous-time ripple correlation control for photovoltaic applications. In: Power and Energy Conference at Illinois (PECI), 12–13 February 2010, Urbana, IL, USA (2010)
Abdallatif, H.; Abdel-Qader, I.; Harb, A.: A fast MPPT algorithm for smart grid-PV connected system based on multiple sparse-aware time-varying step size adaptation technique. In: 10th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), 26–28 March 2019, Sousse, Tunisia (2019)
Cao, G.; Sun, K.; Jiang, S.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.: A modular DC/DC photovoltaic generation system for HVDC grid connection. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 4(2), 56–64 (2018)
Khallat, M.A.; Rahman, S.: A probabilistic approach to photovoltaic generator performance prediction. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1(3), 34–40 (1986)
Chy, D.K., Khaliluzzaman, M., Karim, R.: Analysing efficiency of DC–DC converters joined to PV system run by intelligent controller. In: International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), February 16–18, 2017, Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh (2017)
Panagea, I.S.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.G.; Grillakis, M.G.: Climate change impact on photovoltaic energy output the case of Greece. Adv. Meteorol. 2014(4), 1–11 (2014)
Dhahri, Y.; Ghedira, S.; Zrafi, R.; Besbes, K.: Design of an integrated inductor in micro-converter DC–DC for photovoltaic applications. In: International Conference on Engineering & MIS (ICEMIS), 8–10 May 2017, Monastir, Tunisia (2017)
Demirtas, M.; Tamyurek, B.; Kurt, E.; Cetinbas, I.; Ozturk, M.K.: Effects of aging and environmental factors on performance of CdTe and CIS thin-film photovoltaic modules. J. Electron. Mater. 48(11), 6890–6900 (2019)
Sasidharan, N.; Ongsakul, W.; Varghese, M.P.; Anooja, V.S.; Akhila R.: Efficient improvement of solar photovoltaic system using artificial cooling methods. In: International Conference on Power, Signals, Control and Computation (EPSCICON), 6–10 January 2018, Thrissur, India (2018)
Amara, K.; Fekik, A.; Hocine, D.; Hamida, M.L.; Bourennane, E.-B.; Malek, T.A.; Malek, A.: Improved performance of a PV solar panel with adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system ANFISm based MPPT. In: 7th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), 14–17 October 2018, Paris, France (2018)
Elgendy, M.; Zahawi, B.; Atkinson, D.: Assessment of perturb and observe MPPT algorithm implementation techniques for PV pumping applications. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy. 3, 21–33 (2012)
Sera, D.; Mathe, L.; Kerekes, T.; Spataru, S.V.; Teodorescu, R.: On the perturb-and-observe and incremental conductance MPPT methods for PV systems. IEEE J. Photovolt. 3(3), 1070–1078 (2013)
Gonzalez-Castano, C.; Marulanda, J.; Restrepo, C.; Kouro, S.; Alzate, A.; Rodriguez, J.: Hardware-in-the-loop to test an MPPT technique of solar photovoltaic system: a support vector machine approach. Sustainability 13(6), 3000 (2021)
Yilmaz, U.; Kircay, A.; Borekci, S.: PV system fuzzy logic MPPT method and PI control as a charge controller. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 994–1001 (2018)
Kumar, N.; Hussain, I.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K.: Rapid MPPT for uniformly and partial shaded PV system by using jaya DE algorithm in highly fluctuating atmospheric conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 13(5), 2406–2416 (2017)
Priyadarshi, N.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Blaabjerg, F.; Bhaskar, M.S.: An experimental estimation of hybrid ANFIS–PSO-based MPPT for PV grid integration under fluctuating sun irradiance. IEEE Syst. J. 14, 1218–1229 (2019)
Titri, S.; Larbes, C.; Toumi, K.; Benatchba, K.: A new MPPT controller based on the ant colony optimization algorithm for photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions. Appl. Soft Comput. 58, 465–479 (2017)
Tao, H.; Ghahremani, M.; Ahmed, F.W.; Jing, W.; Nazir, M.S.; Ohshima, K.: A novel MPPT controller in PV systems with hybrid whale optimization-PS algorithm based ANFIS under different conditions. Control. Eng. Pract. 112, 1–12 (2021)
Behera, M.K.; Saikia, L.C.: A new combined extreme learning machine variable steepest gradient ascent MPPT for PV system based on optimized PI-FOI cascade controller under uniform and partial shading conditions. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 42(1), 1–17 (2020)
Villegas-Mier, C.G.; Rodriguez-Resendiz, J.; Álvarez-Alvarado, J.M.; Rodriguez-Resendiz, H.; Herrera-Navarro, A.M.; Rodríguez-Abreo, O.: Artificial neural networks in MPPT algorithms for optimization of photovoltaic power systems: a review. Micromachines 12, 1260 (2021)
Lappalainen, K.; Valkealahti, S.: Effects of irradiance transition characteristics on the mismatch losses of different electrical PV array configurations. IET Renew Power Gener 11, 248–254 (2017)
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial and non-financial interests to disclose.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Divyasharon, R., Narmatha Banu, R. Design and Analysis of LSANN-IPOMPPT with Zeta Converter in PV Systems for Fluctuating Atmospheric Circumstances. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 6053–6065 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07196-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07196-4