Abstract
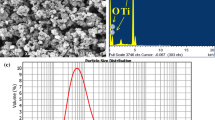
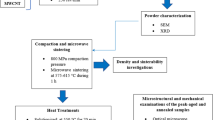
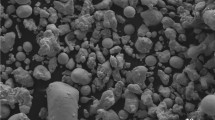
In this work, an investigation was conducted into the microstructure and mechanical characteristics of friction stir processed aluminum matrix composites (AMCs) reinforced with exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets (xGnPs). The microstructure was characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), respectively. In addition, microhardness and tensile tests were performed to evaluate the differentiation of mechanical properties for all the samples. Field emission scanning electron microscopy was employed to reveal the fractographic features of all the samples. The results illustrated that the grains of the AMCs consist of equiaxed crystals with an average grain size of 3.2 µm, forming an ultrafine-grained microstructure. Additionally, the ratio of high angle grain boundaries in AMCs was higher than that of FSPed sample. The mechanical performance of AMCs was improved significantly as a result of Al4C3 generated in the solid-phase chemical reaction between the xGnPs and the Al matrix during FSP in combination with the fine grain strengthening. The microhardness, yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of AMCs reached 80 HV, 110 MPa and 210 MPa, respectively, which were 47, 69 and 20% higher than those of the base metal, respectively. The preferred orientation of the base metal transformed from < 200 > toward < 111 > , < 220 > and < 311 > owing to the combination effect of FSP and xGnPs. The incorporation of xGnPs ameliorated the mechanical properties of the AMCs dramatically, and the fracture surface of the AMCs was indicative of a combined ductile–brittle failure behavior.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta, M.K.: Analysis of tribological behavior of Al/Gr/MoS 2 surface composite fabricated by friction stir process. Carbon Lett. 30, 399–408 (2020)
Jain, V.K.S.; Varghese, J.; Muthukumaran, S.: Effect of first and second passes on microstructure and wear properties of titanium dioxide-reinforced aluminum surface composite via friction stir processing. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 949–957 (2019)
Mehrian, S. M.; Rahsepar, M.; Khodabakhshi, F.; Gerlich, A.: Effects of friction stir processing on the microstructure, mechanical and corrosion behaviors of an aluminum-magnesium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. (405) 126647 (2021).
Maji, P.; Nath, R.K.; Paul, P.; Meitei, R.; Ghosh, S.K.: Effect of processing speed on wear and corrosion behavior of novel MoS 2 and CeO 2 reinforced hybrid aluminum matrix composites fabricated by friction stir processing. J. Manuf. Process 69, 1–11 (2021)
Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, B.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Dong, P.; Wang, W.: Microstructural, Microhardness and tribological analysis of cooling-assisted friction stir processing of high-entropy alloy particles reinforced aluminum alloy surface composites. Surf. Topogr-Metrol (8) 035012 (2020).
Kheirkhah, S.; Imani, M.; Aliramezani, R.; Zamani, M.; Kheilnejad, A.: Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Al6061/BN surface composite prepared by friction stir processing. Surf. Topogr-Metrol (7) 035002 (2019).
Sharma, A.; Narsimhachary, D.; Sharma, V.M.; Sahoo, B.; Paul, J.: Surface modification of Al6061-SiC surface composite through impregnation of graphene, graphite & carbon nanotubes via FSP: a tribological study. Surf. Coat. Technol. 368, 175–191 (2019)
Suryanarayana, C.; Al-Aqeeli, N.: Mechanically alloyed nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 58, 383–502 (2013)
Kannan, C.; Ramanujam, R.; Balan, A.: Machinability studies on Al 7075/BN/Al2O3 squeeze cast hybrid nanocomposite under different machining environments. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 587–595 (2018)
Khodabakhshi, F.; Simchi, A.: The role of microstructural features on the electrical resistivity and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy Al-SiC-Al2O3 nanocomposites. Mater. Design 130, 26–36 (2017)
Khdair, A.I.; Fathy, A.: Enhanced strength and ductility of Al-SiC nanocomposites synthesized by accumulative roll bonding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 478–489 (2020)
Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y.; Charit, I.: Friction stir processing: a novel technique for fabrication of surface composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 341, 307–310 (2003)
Khodabakhshi, F.; Arab, S.M.; Švec, P.; Gerlich, A.P.: Fabrication of a new Al-Mg/graphene nanocomposite by multi-pass friction-stir processing: Dispersion, microstructure, stability, and strengthening. Mater. Charact. 132, 92–107 (2017)
Sharma, V.; Prakash, U.; Kumar, B.: Surface composites by friction stir processing: A review. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 224, 117–134 (2015)
Mishra, R.S.; De, P.S.; Kumar, N.: Friction stir welding and processing. Springer International Publishing (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07043-8
Khodabakhshi, F.; Nosko, M.; Gerlich, A.P.: Dynamic restoration and crystallographic texture of a friction-stir processed Al–Mg–SiC surface nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34(14), 1773–1791 (2018)
Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Shi, Q.: In situ exfoliation of graphite for fabrication of graphene/aluminum composites by friction stir processing. Mater. Lett. (301) 130280 (2021).
Dixit, S.; Mahata, A.; Mahapatra, D.R.; Kailas, S.V.; Chattopadhyay, K.: Multi-layer graphene reinforced aluminum–manufacturing of high strength composite by friction stir alloying. Compos. B Eng. 136, 63–71 (2018)
Jain, V.K.S.; Yazar, K.; Muthukumaran, S.: Development and characterization of Al5083-CNTs/SiC composites via friction stir processing. J. Alloys Compd. 798, 82–92 (2019)
Sharma, A.; Fujii, H.; Paul, J.: Influence of reinforcement incorporation approach on mechanical and tribological properties of AA6061-CNT nanocomposite fabricated via FSP. J. Manuf. Process 59, 604–620 (2020)
Khodabakhshi, F.; Gerlich, A.; Švec, P.: Reactive friction-stir processing of an Al-Mg alloy with introducing multi-walled carbon nano-tubes (MW-CNTs): microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties. Mater. Charact. 131, 359–373 (2017)
Fustes, J.; Gomes, A.; da Silva Pereira, M.: Electrodeposition of Zn–TiO 2 nanocomposite films—effect of bath composition. J. Solid State Electrochem. (12) 1435–1443 (2008).
Berube, L. P.; L'Espérance, G.: A quantitative method of determining the degree of texture of zinc electrodeposits. J. Electrochem. Soc. (136) 2314 (1989).
Nasir, E.M.: Texture coefficient and conductivity dependence on the annealing and thicknesses of thin CdS films. Int. Rev. Phys. 7(1), 22–25 (2013)
Sakai, T.; Belyakov, A.; Kaibyshev, R.; Miura, H.; Jonas, J.J.: Dynamic and post-dynamic recrystallization under hot, cold and severe plastic deformation conditions. Prog. Mater. Sci. 60, 130–207 (2014)
McNelley, T.; Swaminathan, S.; Su, J.: Recrystallization mechanisms during friction stir welding/processing of aluminum alloys. Scr. Mater. 58, 349–354 (2008)
Khodabakhshi, F.; Simchi, A.; Kokabi, A.; Gerlich, A.; Nosko, M.: Effects of stored strain energy on restoration mechanisms and texture components in an aluminum–magnesium alloy prepared by friction stir processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 642, 204–214 (2015)
Jiang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, D.-B.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.: Nucleation and growth mechanisms of interfacial carbide in graphene nanosheet/Al composites. Carbon 161, 17–24 (2020)
Khodabakhshi, F.; Simchi, A.; Kokabi, A.; Nosko, M.; Simanĉik, F.; Švec, P.: Microstructure and texture development during friction stir processing of Al–Mg alloy sheets with TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 605, 108–118 (2014)
Khodabakhshi, F.; Simchi, A.; Kokabi, A.; Švec, P.; Simančík, F.; Gerlich, A.: Effects of nanometric inclusions on the microstructural characteristics and strengthening of a friction-stir processed aluminum–magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 642, 215–229 (2015)
Ammouri, A.; Kridli, G.; Ayoub, G.; Hamade, R.: Relating grain size to the Zener-Hollomon parameter for twin-roll-cast AZ31B alloy refined by friction stir processing. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 222, 301–306 (2015)
Hansen, N.: Hall-Petch relation and boundary strengthening. Scr. Mater. 51, 801–806 (2004)
Khodabakhshi, F.; Gerlich, A.; Simchi, A.; Kokabi, A.: Cryogenic friction-stir processing of ultrafine-grained Al–Mg–TiO2 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 620, 471–482 (2015)
Kim, C.; Lee, J.; Plichta, M.: Plastic relaxation of thermoelastic stress in aluminum/ceramic composites. Metall. Trans. A 21, 673–682 (1990)
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Changchun University of Technology, Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials of Ministry of Education for providing the necessary facilities to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Gong, W., Wu, H. et al. Mechanical and Microstructural Analysis of Exfoliated Graphite Nanoplatelets-Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites Synthesized via Friction Stir Processing. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 3009–3019 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07051-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07051-6