Abstract
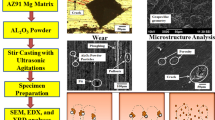
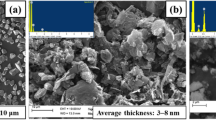
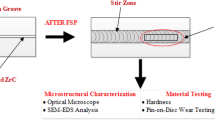
The current research work presents a detailed study of the development and wear performance of Al2O3 reinforced AZ91 Magnesium metal matrix composites. The fabrication of composites was performed using the ultrasonic-assisted stir casting process with optimized parameters. The Al2O3 reinforcement powder was varied in wt% of 0.75, 1.5, and 2.25, respectively. Different parametric combinations of stirrer speed, ultrasonic power, and reinforcement concentration were used to fabricate the composites as per the Taguchi L9 design matrix. These parameters were found to influence the distribution of the reinforcement particulates, resulting in the varying microstructure and wear resistance of the composites. The wear behaviour of composites was examined against the rotating EN-32 counterface steel disc of a pin-on-disc tribometer. The SEM, XRD, and EDX analyses were performed to analyze their surface morphologies, microstructures, phases, and elemental compositions. The enhancement in wear resistance was attributed to the uniform dispersion of particulates owing to the ultrasonic agitations. The microstructural images of the worn-out specimens elucidated the formation of wear tracks on the composite surface, which were caused by adhesion, micro-cutting of the soft matrix, oxidation, and delamination during sliding wear testing. The material removal has also occurred due to the pull-out of Al2O3 reinforcement particles and eruption of soft AZ91 Mg matrix. The composite developed at higher reinforcement concentration has shown a relatively smoother surface with light wear tracks and small agglomerations.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aatthisugan, I.; Razal Rose, A.; Selwyn Jebadurai, D.: Mechanical and wear behaviour of AZ91D magnesium matrix hybrid composite reinforced with boron carbide and graphite. J. Magnes. Alloy. 5, 20–25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2016.12.004
Rahmani, K.; Majzoobi, G.H.; Bakhtiari, H.; Sadooghi, A.: On the effect of compaction velocity, size, and content of reinforcing particles on corrosion resistance of Mg–B4C composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 271, 124946 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124946
Mert, F.: A comparison of the dry sliding wear behavior of As-cast and hot rolled Az31B magnesium alloy. Omer Halisdemir Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 7, 1–10 (2018)
James, S.; Annamalai, A.; Kuppan, P.; Oyyaravelu, R.: Fabrication of hybrid metal matrix composite reinforced with SiC/Al2O3/TiB2. Mech. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.2412/MMSE.66.73.476
Toozandehjani, M.; Kamarudin, N.; Dashtizadeh, Z.; Lim, E.Y.: Conventional and advanced composites in aerospace industry : technologies revisited. Am. J. Aerosp. Eng. 5(1), 9–15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajae.20180501.12
King, D.; Inderwildi, O.; Carey, C.: Advanced aerospace materials: past, present and future. Aviat. Environ. 3(9), 22–27 (2009)
Uvaraja, V.C.; Natarajan, N.; Rajendran, I.; Sivakumar, K.: Tribological behavior of novel hybrid composite materials using Taguchi technique. J. Tribol. 135, 1–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4023147
Kannan, C.; Ramanujam, R.; Balan, A.S.S.: Mathematical modeling and optimization of tribological behaviour of Al 7075 based hybrid nanocomposites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650120965781
Ravichandran, M.; Veerappan, G.; Dhinakaran, V.; Katiyar, J.K.: Optimization of tribo-mechanical properties of boron carbide reinforced magnesium metal matrix composite. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/13506501211030070
Hira, J.; Mangal, S.K.; Manna, A.: Fabrication of hybrid Mg/(Al2O3p + SiCp + Grp) metal matrix composite on developed gas injection liquid stir casting setup. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40, 2729–2738 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1755-1
Sadooghi, A.; Rahmani, K.; Hashemi, S.J.: Effects of nano and micro size of MgO on mechanical properties, wear, and corrosion of magnesium matrix composite. Strength Mater. 53, 983–997 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-022-00366-7
Habibnejad-Korayem, M.; Mahmudi, R.; Ghasemi, H.M.; Poole, W.J.: Tribological behavior of pure Mg and AZ31 magnesium alloy strengthened by Al2O3 nano-particles. Wear 268, 405–412 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.08.031
Tarasasanka, C.; Ravindra, K.: Application of taguchi techniques to study dry sliding wear behaviour of magnesium matrix composites reinforced with alumina nano particles. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 12, 2855–2865 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2006.01.006
Podymova, N.B.; Karabutov, A.A.: Combined effects of reinforcement fraction and porosity on ultrasonic velocity in SiC particulate aluminum alloy matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 113, 138–143 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.01.017
Suresh, S.; Gowd, G.H.; Deva Kumar, M.L.S.: Mechanical properties of AA 7075/Al2O3/SiC Nano-metal matrix composites by stir-casting method. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. D 100(1), 43–53 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-019-00178-1
Gao, Q.; Wu, S.; Lü, S.; Xiong, X.; Du, R.; An, P.: Improvement of particles distribution of in-situ 5 vol% TiB2particulates reinforced Al-4.5Cu alloy matrix composites with ultrasonic vibration treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 692, 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.09.013
Wang, C.R.; Deng, K.K.; Bai, Y.: Microstructure, and mechanical and wear properties of Grp/AZ91 magnesium matrix composites. Materials 12, 1–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071190
Girish, B.M.; Satish, B.M.; Sarapure, S.: Optimization of wear behavior of magnesium alloy AZ91 hybrid composites using taguchi experimental design. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 3193–3200 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3447-1
Tarasasanka, C.; Snehita, K.; Ravindra, K.; Sameerkumar, D.: Optimization of dry sliding wear properties ofAZ91E/ nano Al2O3 reinforced metal matrix composite with grey relational analysis. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 11, 41 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4314/ijest.v11i4.4
Das, B.; Roy, S.; Rai, R.N.; Saha, S.C.: Multiobjective optimization of in situ process parameters in preparation of Al-4.5% Cu–TiC MMC using a grey relation based teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 232(4), 393–407 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408917710555
Ravichandran, M.; Anandakrishnan, V.: Optimization of powder metallurgy parameters to attain maximum strength coefficient in Al-10 wt% MoO3 composite. J. Mater. Res. 30, 2380–2387 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.211
Ekka, K.K.; Chauhan, S.R.: Varun: dry sliding wear characteristics of SiC and Al2O3 nanoparticulate aluminium matrix composite using taguchi technique. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40, 571–581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1528-2
Rahmani, K.; Majzoobi, G.H.; Ebrahim-Zadeh, G.; Kashfi, M.: Comprehensive study on quasi-static and dynamic mechanical properties and wear behavior of Mg—B4C composite compacted at several loading rates through powder metallurgy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31, 371–381 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65502-4
Rahmani, K.; Majzoobi, G.H.: The effect of particle size on microstructure, relative density and indentation load of Mg-B4C composites fabricated at different loading rates. J. Compos. Mater. 54, 2297–2311 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998319896009
Gušin, A.Z.; Žužk, B.; Podgornik, B.; Kevorkijan, V.: The uncertainty of hardness measurements related to the measurement method, surface preparation and range of the measurements. Mater. Technol. 53, 897–904 (2019). https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2019.098
Gnanavelbabu, A.; Sunu Surendran, K.T.; Kumar, S.: Influence of ultrasonication power on grain refinement, mechanical properties and wear behaviour of AZ91D/nano-Al2O3 composites. Mater. Res. Express. 7, 016544 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab64d7
Sindhu, D.; Thakur, L.; Chandna, P.: parameter optimization of rotary ultrasonic machining on quartz glass using response surface methodology (RSM). Silicon 12, 629–643 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00160-2
Pazhouhanfar, Y.; Eghbali, B.: Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of TiB2 reinforced Al6061 matrix composites produced using stir casting process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 710, 172–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.10.087
Contacts, S.; Encounters, M.: Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 24, 981 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1721448
Rahmani, K.; Nouri, A.; Wheatley, G.; Malekmohammadi, H.; Bakhtiari, H.; Yazdi, V.: Determination of tensile behavior of hot-pressed Mg–TiO2 and Mg–ZrO2 nanocomposites using indentation test and a holistic inverse modeling technique. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 14, 2107–2114 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.090
Sahoo, B.N.; Panigrahi, S.K.: Effect of in-situ (TiC-TiB2) reinforcement on aging and mechanical behavior of AZ91 magnesium matrix composite. Mater. Charact. 139, 221–232 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.03.002
Kumar, D.; Thakur, L.: Recent studies on the fabrication of magnesium based metal matrix nano-composites by using ultrasonic stir casting technique—a review. Mater. Sci. Forum 969, 889–894 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.969.889
Ahamad, N.; Mohammad, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Gupta, P.: Wear, optimization and surface analysis of Al-Al2O3-TiO2 hybrid metal matrix composites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 235(1), 93–102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650120970432
Selvakumar, N.; Narayanasamy, P.: Optimization and Effect of Weight Fraction of MoS2 on the Tribological Behavior of Mg-TiC-MoS2 Hybrid Composites. Tribol. Trans. 59(4), 733–747 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2015.1110866
Muley, S.V.; Singh, S.P.; Sinha, P.; Bhingole, P.P.; Chaudhari, G.P.: Microstructural evolution in ultrasonically processed in situ AZ91 matrix composites and their mechanical and wear behavior. Mater. Des. 53, 475–481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.056
Lai, M.O.; Lu, L.; Chung, B.Y.: Formation of Mg-Al-Ti/MgO composite via reduction of TiO2. Compos. Struct. 57, 183–187 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8223(02)00082-X
Kawamori, S.; Kuroda, K.; Kasuga, Y.; Yokouchi, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Ameyama, K.: Effect of alumina content on the mechanical properties of alumina particle dispersion magnesium. Mater. Trans. 51, 1893–1900 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2010060
Rashad, M.; Pan, F.; Asif, M.; She, J.; Ullah, A.: Improved mechanical proprieties of “magnesium based composites” with titanium-aluminum hybrids. J. Magnes. Alloy. 3, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2014.12.010
Hassan, S.F.; Gupta, M.: Effect of type of primary processing on the microstructure, CTE and mechanical properties of magnesium/alumina nanocomposites. Compos. Struct. 72, 19–26 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.10.008
Xiao, P.; Gao, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.: Microstructure, mechanical properties and strengthening mechanisms of Mg matrix composites reinforced with in situ nanosized TiB2 particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 710, 251–259 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.10.107
Torabi Parizi, M.; Ebrahimi, G.R.; Ezatpour, H.R.: Effect of graphene nanoplatelets content on the microstructural and mechanical properties of AZ80 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 742, 373–389 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.025
Malaki, M.; Xu, W.; Kasar, A.K.; Menezes, P.L.; Dieringa, H.; Varma, R.S.; Gupta, M.: Advanced metal matrix nanocomposites. Metals 9, 330 (2019)
Czerwinski, F.: The oxidation behaviour of an AZ91D magnesium alloy at high temperatures. Acta Mater. 50, 2639–2654 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00094-0
Ghosh, P.K.; Ray, S.: Effect of porosity and alumina content on the high temperature mechanical properties of compocast aluminium alloy-alumina particulate composite. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 4077–4086 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01133361
Aydin, F.; Sun, Y.: Investigation of wear behaviour and microstructure of hot-pressed TiB2 particulate-reinforced magnesium matrix composites. Can. Metall. Q. 57, 455–469 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00084433.2018.1478491
Bhingole, P.P.; Chaudhari, G.P.; Nath, S.K.: Processing, microstructure and properties of ultrasonically processed in situ MgO-Al2O3-MgAl2O4 dispersed magnesium alloy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 66, 209–217 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.08.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, D., Thakur, L. A Study of Development and Sliding Wear Behavior of AZ91D/Al2O3 Composites Fabricated by Ultrasonic-Assisted Stir Casting. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 2951–2967 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07032-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07032-9