Abstract
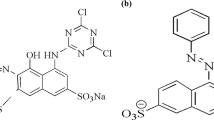
Removal of negatively charged acid blue 25 (AB25) and acid red 1 (AR1) from their aqueous single and binary solute solutions by adsorption onto raw Indonesian kaolin was investigated. The effect of contact time, initial concentration, temperature, and the molar ratio of AB25 and AR1 in batch adsorption mode was determined. It was found that the individual and co-adsorption of AB25 and AR1 followed pseudo-second-order kinetics with mass transport being a combination of intraparticle and film diffusion. The adsorption isotherm data were consistent with the Langmuir model, implying that the adsorption of the synthetic dyes occurs on a homogeneous monolayer of the basal surfaces of kaolinite particles. Thermodynamic parameters suggested that the adsorption is spontaneous and exothermic. The maximum capacity of the co-adsorption of AB25 and AR1 was 9.02 and 7.67 mg g−1 lower compared to their individual adsorption (16.5 and 12.8 mg g−1, respectively). This confirms that adsorption of the two anionic synthetic dyes is competitive during co-adsorption. This competitive effect is important to consider in the simultaneous removal of multiple synthetic dyes from wastewater.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drumond Chequer, F.M.; de Oliveira, G.A.R.; Anastacio Ferraz, E.R.; Carvalho, J.; Boldrin Zanoni, M.V.; de Oliveir, D.P.: Textile dyes: dyeing process and environmental impact. In: Eco-Friendly Textile Dyeing and Finishing. IntechOpen: London, UK, pp. 151–176 (2013)
Křížová, H.: Natural dyes: their past, present, future and sustainability. Recent Dev. Fibrous Mater. Sci. 12, 59–71 (2015)
Chiu, Y.H.; Chang, T.F.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Sone, M.; Hsu, Y.J.: Mechanistic insights into photodegradation of organic dyes using heterostructure photocatalysts. Catalysts 9, 430 (2019)
Popli, S.; Patel, U.D.: Destruction of azo dyes by anaerobic–aerobic sequential biological treatment: a review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 405–420 (2015)
Ardila-Leal, L.D.; Poutou-Piñales, R.A.; Pedroza-Rodríguez, A.M.; Quevedo-Hidalgo, B.E.: A brief history of colour, the environmental impact of synthetic dyes and removal by using laccases. Molecules 26, 3813 (2021)
Ghodke, S.A.; Sonawane, S.H.; Bhanvase, B.A.; Potoroko, I.: Advanced engineered nanomaterials for the treatment of wastewater, p. 959–970. Elsevier, Handbook of nanomaterials for industrial applications (2018)
Forgacs, E.; Cserháti, T.; Oros, G.: Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ. Int. 30, 953–971 (2004)
Piaskowski, K.; Świderska-Dąbrowska, R.; Zarzycki, P.K.: Dye removal from water and wastewater using various physical, chemical, and biological processes. J. AOAC Int. 10, 1371–1384 (2018)
Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N.: Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 17, 195–213 (2019)
Okoniewska, E.: Removal of selected dyes on activated carbons. Sustainability 13, 4300 (2021)
Mouni, L.; Belkhiri, L.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Bouzaza, A.; Assadi, A.; Tirri, A.; Dahmoune, F.; Madani, K.; Remini, H.: Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by adsorption on kaolin: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 153, 38–45 (2018)
Shahrin, E.W.; Narudin, N.A.; Padmosoedarso, K.M.; Kusrini, E.; Mahadi, A.H.; Shahri, N.N.; Usman, A.: Pectin derived from pomelo pith as a superior adsorbent to remove toxic acid blue 25 from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2, 100116 (2021)
Silva, F.; Nascimento, L.; Brito, M.; da Silva, K.; Paschoal, W.; Fujiyama, R.: Biosorption of methylene blue dye using natural biosorbents made from weeds. Materials 12, 1–16 (2019)
Lim, L.B.L.; Usman, A.; Hassan, M.H.; Zaidi, N.A.H.M.: Tropical wild fern (Diplazium esculentum) as a new and effective low-cost adsorbent for removal of toxic crystal violet dye. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 14, 621–627 (2020)
Jawad, A.H.; Ngoh, Y.S.; Radzun, K.A.: Utilization of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) rinds as a natural low-cost biosorbent for adsorption of methylene blue: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 12, 371–381 (2018)
Sánchez-Jiménez, N.; Sevilla, M.T.; Cuevas, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Procopio, J.R.: Interaction of organic contaminants with natural clay type geosorbents: potential use as geologic barrier in urban landfill. J. Environ. Manag. 95, S182–S187 (2012)
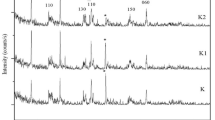
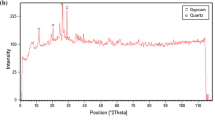
Yahaya, S.; Jikan, S.S.; Badarulzaman, N.A.; Adamu, A.D.: Chemical composition and particle size analysis of kaolin. Path Sci. 3, 1001–1004 (2017)
Babu Valapa, R.; Loganathan, S.; Pugazhenthi, G.; Thomas, S.; Varghese, T.O.: An overview of polymer-clay nanocomposites, p. 29–81. Elsevier, Clay-polymer nanocomposites (2017)
Shao, G.N.; Engole, M.; Imran, S.M.; Jeon, S.J.; Kim, H.T.: Sol-gel synthesis of photoactive kaolinite-titania: effect of the preparation method and their photocatalytic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 331, 98–107 (2015)
Mustapha, S.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Tijani, J.O.; Mohammed, A.K.; Shuaib, D.T.: Potential of using kaolin as a natural adsorbent for the removal of pollutants from tannery wastewater. Heliyon 5, e02923 (2019)
Rida, K.; Bouraoui, S.; Hadnine, S.: Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by kaolin and zeolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 83–84, 99–105 (2013)
Harris, R.G.; Wells, J.D.; Johnson, B.B.: Selective adsorption of dyes and other organic molecules to kaolinite and oxide surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 180, 131–140 (2001)
Ziółkowska, D.; Shyichuk, A.; Karwasz, I.; Witkowska, M.: Adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes onto commercial kaolin. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 27, 205–214 (2009)
Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M.: Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: a critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 1193–1226 (2019)
Turabik, M.: Adsorption of basic dyes from single and binary component systems onto bentonite: simultaneous analysis of basic red 46 and basic yellow 28 by first order derivative spectrophotometric analysis method. J. Hazard. Mater. 158, 52–64 (2008)
Dávila-Jiménez, M.M.; Elizalde-González, M.P.; Hernández-Montoya, V.: Performance of mango seed adsorbents in the adsorption of anthraquinone and azo acid dyes in single and binary aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 6199–6206 (2009)
Sismanoglu, T.; Kismir, Y.; Karakus, S.: Single and binary adsorption of reactive dyes from aqueous solutions onto clinoptilolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 184, 164–169 (2010)
Adeyi, A.A.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Abdullah, L.C.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Lau, K.L.; Abdullah, M.: Simultaneous adsorption of cationic dyes from binary solutions by thiourea-modified poly (acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid): detailed isotherm and kinetic studies. Materials 12, 2903 (2019)
Adeyi, A.A.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Abdullah, L.C.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Lau, K.L.; Alias, N.H.: Simultaneous adsorption of malachite green and methylene blue dyes in a fixed-bed column using poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid) modified with thiourea. Molecules 25, 2650 (2020)
Li, Y.; Xiao, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Y.: Thermal and pH dual-responsive cellulose microfilament spheres for dye removal in single and binary systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 377, 88–97 (2019)
Rehman, M.Z.U.; Aslam, Z.; Shawabkeh, R.A.; Hussein, I.A.; Mahmood, N.: Concurrent adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes from environmental water on amine functionalized carbon. Water Sci. Technol. 81, 466–478 (2020)
Asbollah, M.A.; Mahadi, A.H.; Kusrini, E.; Usman, A.: Synergistic effect in concurrent removal of toxic methylene blue and acid red-1 dyes from aqueous solution by durian rind: kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics, and mechanism. Int. J. Phytoremediation 23, 1432–1443 (2021)
Simonin, J.-P.: On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 300, 254–263 (2016)
Robati, D.: Pseudo-second-order kinetic equations for modeling adsorption systems for removal of lead ions using multi-walled carbon nanotube. J. Nanostructure Chem. 3, 55 (2013)
Ho, Y.S.; Ng, J.C.Y.; McKay, G.: Kinetics of pollutant sorption by biosorbents: review. Sep. Purif. Methods 29, 189–232 (2000)
Viegas, R.M.C.; Campinas, M.; Costa, H.; Rosa, M.J.: How do the HSDM and Boyd’s model compare for estimating intraparticle diffusion coefficients in adsorption processes. Adsorption 20, 737–746 (2014)
Ghaffari, H.R.; Pasalari, H.; Tajvar, A.; Dindarloo, K.; Goudarzi, B.; Alipour, V.; Ghanbarneajd, A.: Linear and nonlinear two-parameter adsorption isotherm modeling: a case-study. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 6, 1–11 (2017)
Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.-J.: Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 61, 229–242 (2008)
Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Anastopoulos, I.: A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 273, 425–434 (2019)
Saikia, B.J.; Parthasarathy, G.: Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic characterization of kaolinite from Assam and Meghalaya, Northeastern India. J. Mod. Phys. 1, 206–210 (2010)
Castellano, M.; Turturro, A.; Riani, P.; Montanari, T.; Finocchio, E.; Ramis, G.; Busca, G.: Bulk and surface properties of commercial kaolins. Appl. Clay Sci. 48, 446–454 (2010)
Bukalo, N.N.; Ekosse, G.I.E.; Odiyo, J.O.; Ogola, J.S.: Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of clay size fraction of Cretaceous-Tertiary kaolins in the Douala Sub-Basin, Cameroon. Open Geosci. 9, 407–418 (2017)
Tironi, A.; Trezza, M.A.; Irassar, E.F.; Scian, A.N.: Thermal treatment of kaolin: effect on the pozzolanic activity. Procedia Mater. Sci. 1, 343–350 (2012)
Ivanović, M.D.; Kljajević, L.M.; Nenadović, M.; Bundaleski, N.; Vukanac, I.; Todorović, B.Ž; Nenadović, S.S.: Physicochemical and radiological characterization of kaolin and its polymerization products. Mater. Constr. 68, e155 (2018)
Güneyisi, E.; Gesoǧlu, M.; Özturan, T.; Mermerdaş, K.: Microstructural properties and pozzolanic activity of calcined kaolins as supplementary cementing materials. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 39, 1274–1284 (2012)
Agarwal, P.; Huang, D.; Thakur, S.S.; Rupenthal, I.D.: Chapter 4—Nanotechnology for ocular drug delivery. In: Design of Nanostructures for Versatile Therapeutic Applications, pp. 137–188 (2018)
El-Khaiary, M.I.; Malash, G.F.: Common data analysis errors in batch adsorption studies. Hydrometallurgy 105, 314–320 (2011)
Sharma, P.; Das, M.R.: Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solution using graphene oxide nanosheets: investigation of adsorption parameters. J. Chem. Eng. Data 58, 151–158 (2013)
Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A.: Analysis of mass transfer kinetics in the biosorption of synthetic dyes onto spirulina platensis nanoparticles. Biochem. Eng. J. 68, 85–90 (2012)
Samat, J.H.; Shahri, N.N.M.; Asbollah, M.A.; Suhaimi, N.A.A.; Padmosoedarso, K.M.; Kusrini, E.; Mahadi, A.H.; Hobley, J.; Usman, A.: Adsorption of acid blue 25 on agricultural wastes: efficiency, kinetics, mechanism and regeneration. Air. Soil Water Res. 14, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/11786221211057496
Hanafiah, M.A.K.M.; Ngah, W.S.W.; Zolkafly, S.H.; Teong, L.C.; Majid, Z.A.A.: Acid blue 25 adsorption on base treated Shorea dasyphylla sawdust: kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic and spectroscopic analysis. J. Environ. Sci. 24, 261–268 (2012)
Ferrero, F.: Dye removal by low cost adsorbents: hazelnut shells in comparison with wood sawdust. J. Hazard. Mater. 142, 144–152 (2006)
Dahri, M.K.; Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Chan, C.M.: Removal of acid blue 25 using cempedak durian peel from aqueous medium: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Int. Food Res. J. 23, 1154–2116 (2016)
Khalid, K.; Ngah, W.S.W.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M.; Malek, N.S.A.; Khazaai, S.N.M.: Acid blue 25 adsorption onto phosphoric acid treated rubber leaf powder. Am. J. Environ. Eng. 5, 19–25 (2015)
Lakkaboyana, S.K.; Khantong, S.; Kabir, M.A.; Ali, Y.; Yaacob, W.Z.W.: Removal of acid blue 25 dye from wastewater using rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum Linn.) seed as an efficient natural biosorbent. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 6, 111–117 (2018)
Kooh, M.R.R.; Dahri, M.K.; Lim, L.B.L.; Lim, L.H.: Batch adsorption studies on the removal of acid blue 25 from aqueous solution using Azolla pinnata and soya bean waste. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 2453–2464 (2016)
Alizadeh, S.; Seyyedi, K.: Removal of C.I. acid red 1 (AR1) dye pollutant from contaminated waters by adsorption method using sunflower seed shells and pine cone as agro-waste materials. J. Appl. Chem. Res. 13, 93–105 (2019)
Khanna, S.; Rattan, V.K.: Removal of acid red 1 from aqueous waste streams using peel of Cucumis sativus fruit. Equilibrium studies. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 52, 803–811 (2017)
Juang, L.-C.; Lee, C.-K.; Wang, C.-C.; Hung, S.-H.; Lyu, M.-D.: Adsorptive removal of acid red 1 from aqueous solution with surfactant modified titanate nanotubes. Environ. Eng. Sci. 25, 519–528 (2008)
Su, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, Q.; Yu, Q.; Meng, R.; Yao, J.: Efficient removal of cationic and anionic dyes using cellulose-g-p(AA-co-AM) bio-adsorbent. BioResources 12, 3413–3424 (2017)
Kılıç, M.; Janabi, A.S.K.: Investigation of dyes adsorption with activated carbon obtained from Cordia Myxa. Bilge Int. J. Sci. Technol. 1, 87–104 (2017)
Kumar, N.; Andersson, M.P.; van den Ende, D.; Mugele, F.; Siretanu, I.: Probing the surface charge on the basal planes of kaolinite particles with high-resolution atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 33, 14226–14237 (2017)
Jaradat, K.A.; Darbari, Z.; Elbakhshwan, M.; Abdelaziz, S.L.; Gill, S.K.; Dooryhee, E.; Ecker, L.E.: Heating-freezing effects on the orientation of kaolin clay particles. Appl. Clay Sci. 150, 163–174 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Dr. Eny Kusrini is thankful to Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education of the Republic of Indonesia through PTUPT Grant No. NKB-281/UN2.RST/HKP.05.00/2021 and Dr. Jonathan Hobley is grateful to National Cheng Kung University’s NCKU90 distinguished visiting scholar program for hosting his research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashrul Asbollah, M., Sahid, M.S.M., Padmosoedarso, K.M. et al. Individual and Competitive Adsorption of Negatively Charged Acid Blue 25 and Acid Red 1 onto Raw Indonesian Kaolin Clay. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 6617–6630 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06498-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06498-3