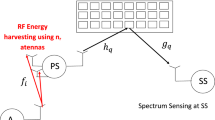
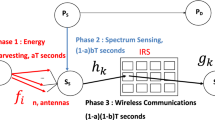
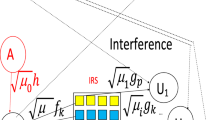
Abstract
In this paper, we derive a tight lower bound of the detection probability of the energy detector when intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) are used. The secondary source uses the energy detector to detect primary source activity. There is IRS between primary source and secondary source. The secondary sources compute the energy of the received signal from primary source and reflected on IRS. The proposed spectrum sensing algorithm using IRS offers 15, 21, 27, 33 dB gain with respect to conventional sensing without IRS for a number of reflectors \(K=8,16,32,64\). We also used IRS for data communication between primary source and destination as well as the communication between secondary nodes. The proposed primary and secondary networks of cognitive radio network (CRN) using IRS offer 23, 29, 36, 43, 49 and 56 dB gain with respect to conventional CRN without IRS for a number of reflectors \(K=8,16,32,64,128,256\). We show that the use of \(N=20,10,5\) symbols in energy detection offers up to 8.5, 7.7 and 4.7 dB gain with respect to a single symbol. We plot the miss detection probability \(P_\mathrm{md}\) versus the false alarm probability \(P_f\). For \(K=16\) reflectors, average SNR per bit \(E_b/N_0=-10\) dB and \(P_f=0.01\), \(P_\mathrm{md}=2 10^{-3}, 7 10^{-3}, 2.5 10^{-2}\) when \(N=20,10,5\) symbols are used in energy detection, whereas \(P_\mathrm{md}=0.45\) when a single symbol is used.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryan G.; Pourranjbar A.; Kaddoum G.: Collaborative spectrum sensing in tactical wireless networks. ICC—IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (2020)
Xiangyue M.; Hazer I.; Brian K.: End-to-end deep learning-based compressive spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. ICC 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), 21–24 (2020)
Runze, W.; Mou, W.; Luokai, H.; Haijun, W.: Energy-efficient cooperative spectrum sensing scheme based on spatial correlation for cognitive. IEEE Access Internet Things 8(1), 139501–139511 (2020)
Mehran, G.; Fakharzadeh, M.: A fast soft decision algorithm for cooperative spectrum sensing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 68(1), 241–245 (2020)
Patel, D.; Brijesh, S.; López-Benítez, M.: Improved likelihood ratio statistic-based cooperative spectrum sensing for cognitive radio. IET Commun. 14(11), 101–112 (2020)
Qingqing, W.; Rui, Z.: Beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts. ICASSP (2019)
Hongliang, Z.; Boya, D.; Lingyang, S.; Zhu, H.: Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces assisted communications with limited phase shifts: how many phase shifts are enough? IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(4), 4498–4502 (2020)
Ertugrul, B.; Di Renzo, M.; De Rosny, J.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.S.; Zhang, R.: Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Access 7(1), 116753–116773 (2019)
Qingqing, W.; Rui, Z.: Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network. IEEE Commun. Mag. 58(1), 106–112 (2020)
Ertugrul, B.: Reconfigurable intelligent surface-based index modulation: a new beyond mimo paradigm for 6G. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68(5), 3187–3196 (2020)
Di Renzo M.: 6G wireless: wireless networks empowered by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. In: Proceedings of the 2019 25th Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC)
Chongwen, H.; Zappone, A.; Alexandropoulos, G.; Debbah, M.; Yuen, C.: Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 18(8), 4157–4170 (2019)
Huayan, G.; Ying-Chang, L.; Jie, C.; Larsson, E.: Weighted sum-rate maximization for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 19(5), 3064–3076 (2020)
Alexandropoulos G.; Vlachos E.: A hardware architecture for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with minimal active elements for explicit channel estimation. ICASSP IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (2020)
Thirumavalavan V.C.; Jayaraman T.S.: BER analysis of reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted downlink power domain NOMA system. In: Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on COMmunication Systems and NETworkS (COMSNETS) (2020)
Pradhan, C.; Li, A.; Song, L.; Vucetic, B.; Li, Y.: Hybrid precoding design for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided mmWave communication systems. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett. 9(7), 1041–1045 (2020)
Ying, K.; Gao, Z.; Lyu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Alouini, M.S.: GMD-based hybrid beamforming for large reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted millimeter-wave massive MIMO. IEEE Access 8(1), 19530–19539 (2020)
Yang, L.; Guo, W.; Ansari, I.S.: Mixed dual-hop FSO-RF communication systems through reconfigurable intelligent surface. IEEE Commun. Lett. 24(7), 1558–1562 (2020)
Di, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.: Practical hybrid beamforming with finite-resolution phase shifters for reconfigurable intelligent surface based multi-user communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(4), 4565–4570 (2020)
Zhao, W.; Wang, G.; Atapattu, S.; Tsiftsis, T.A.; Tellambura, C.: Is backscatter link stronger than direct link in reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted system? IEEE Commun. Lett. 24(6), 1342–1346 (2020)
Nadeem, Q.; Kammoun, A.; Chaaban, A.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.S.: Asymptotic max–min SINR analysis of reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted miso systems. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 19(12), 7748–7764 (2020)
Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Tan, J.; Shuangkaisheng, B.; Shenheng, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhi, C.; Di Renzo, M.; Chan-Byoung, C.; Hanzo, L.: Reconfigurable intelligent surface-based wireless communications: antenna design, prototyping, and experimental results. IEEE Access 8(1), 45913–45923 (2020)
Makarfi, A.U.; Kharel, R.; Rabie, K.M.; Kaiwartya, O.; Li, X.; Do, D.T.: Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (2021)
He, J.; Kaiqiang, Y.; Yong, Z.; Yuanming, S.: Reconfigurable intelligent surface enhanced cognitive radio networks. In: IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall) (2020)
Jie, Y.; Ying-Chang, L.; Jingon, J.; Gang, F.; Larsson, E. G.: Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-enhanced cognitive radio system. ICC, IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (2020)
Jie, Y.; Ying-Chang, L.; Jingon, J.; Gang, F.; Larsson, E.G.: Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted cognitive radio system. IEEE Trans. Commun. 69(1), 675–687 (2021)
Lei, Z.; Yu, W.; Weige, T.; Ziyan, J.; Tiecheng, S.; Cunhua, P.: Intelligent reflecting surface aided MIMO cognitive radio systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(10), 11445–11457 (2020)
Dongfang, X.; Xianghao, Y.; Robert, S.: Resource allocation for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted cognitive radio networks. In: IEEE 21st International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC) (2020)
Fatemeh, Z.; Mohammad, R.S.; Qingqing, W.: Vertical beamforming in intelligent reflecting surface-aided cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, Early access article (2021)
Lei, Z.; Cunhua, P.; Yu, W.; Hong, R.; Kezhi, W.; Arumugam, N.: Robust beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface aided cognitive radio networks. GLOBECOM, IEEE Global Communications Conference (2020)
Dong, L.; Hui-Ming, W.; Haitao, X.: Secure cognitive radio communication via intelligent reflecting surface. IEEE Trans. Commun. 69(7), 4678–4690 (2021)
Limeng, D.; Hui-Ming, W.; Haitao, X.; Jiale, B.: Secure intelligent reflecting surface assisted MIMO cognitive radio transmission. Presented at the (2021)
Proakis, J.: Digital Communications, 5th edn Mac Graw-Hill, New York (2007)
Alhamad, R.; Boujemaa, H.: Cooperative spectrum sensing with energy harvesting for Nakagami fading channels. Int. J. Sens. Netw. IJSNET 33(1), 1–7 (2020)
Xi, Y.; Burr, A.; Wei, J.B.; Grace, D.: A general upper bound to evaluate packet error rate over quasi-static fading channels. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 10(5), 1373–1377 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhamad, R. Throughput and Detection Probability of Interweave Cognitive Radio Networks Using Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 3281–3292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06211-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06211-4