Abstract
The indirect vector control (IVC) technique for stand-alone self-excited induction generator (SEIG)-based wind energy system (WES) is presented in this work. IVC regulates the SEIG speed, torque, and DC voltage independently. Further, the proposed technique is analyzed with back-to-back two-level converter such as generator side converter (GSC) and load side converter (LSC) using space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) strategy. Two-level and three-level space vector pulse width modulation inverters are used, and the performance comparison between the two schemes is also discussed during step change of wind speed. The three-level inverter exhibits enhancement of SEIG voltage along with current, speed, DC voltage and torque in contrast to those obtained from two-level inverter. IVC for SEIG-based WES is implemented in MATLAB/SIMULINK software, and the experimental environment is set up for 4 kW system.



































Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\rho\) :
-
Air density
- \(A\) :
-
Turbine swept area
- \(R\) :
-
Length of the blade in meter
- \(V_{w}\) :
-
Wind speed
- \(\omega_{t}^{ * }\) :
-
Mechanical speed of turbine
- \(\beta\) :
-
Pitch angle in degree
- \(s\) :
-
Laplace operator
- \(\omega_{r}\) :
-
Generator speed
- \(p\) :
-
Pole pairs
- \(T_{e}\) :
-
Torque developed
- \(\omega_{{{\text{sl}}}}\) :
-
Slip speed
- \(v_{{{\text{sd}}}}\), \(v_{{{\text{sq}}}}\) :
-
Stator voltages
- \(i_{{{\text{sd}}}}\), \(i_{{{\text{sq}}}}\) :
-
Stator currents
- \(i_{{{\text{rd}}}}\), \(i_{{{\text{rq}}}}\) :
-
Rotor currents
- \(i_{{{\text{sm}}}}\) :
-
Magnetizing stator current
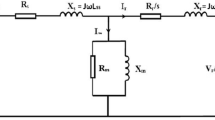
- \(R_{s}\),\(R_{r}\) :
-
Winding resistances
- \(L_{s}\) , \(L_{r}\) :
-
Self-inductances
- L m :
-
Mutual inductance
- \(\lambda_{{{\text{sd}}}} ,\lambda_{{{\text{sq}}}} ,\lambda_{{{\text{rd}}}} ,\lambda_{{{\text{rq}}}}\) :
-
Stator and rotor fluxes
- \(i_{{{\text{ed}}}}\), \(i_{{{\text{eq}}}}\) :
-
Excitation capacitor currents
- \(C_{{{\text{ed}}}}\), \(C_{{{\text{eq}}}}\) :
-
The value of excitation capacitor in \(d - q\) axes
- \(\theta\) :
-
Transformation angle
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Leakage factor
- \(\tau_{r}\) :
-
Rotor time constant
- GSC:
-
Generator side converter
- IVC:
-
Indirect vector control
- LSC:
-
Load side converter
- MLI:
-
Multilevel inverter
- PI:
-
Proportional integral
- SEIG:
-
Self-excited induction generator
- TLI:
-
Two-level load side inverter
- WES:
-
Wind energy system
References
Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, S.: Review on the techno-commercial aspects of wind energy conversion system. IET Renew. Power Gener. Rev. 12(14), 1581–1608 (2018)
Sener, S.E.C.; Sharp, J.L.; Anctil, A.: Factors impacting diverging paths of renewable energy: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 2335–2342 (2019)
Xu, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, B.: Wind energy generation technological paradigm diffusion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 59, 436–449 (2016)
Li, Z.; Wong, S.-C.; Tse, C.K.; Liu, X.: Controller saturation nonlinearity in doubly fed induction generator- based wind turbines under unbalanced grid conditions. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 44(8), 1–18 (2015)
Dewangan, S.; Dyanamina, G.; Kumar, N.: Performance improvement of wind-driven self-excited induction generator using fuzzy logic controller. Int. Trans. Elect. Energy Syst. 29(8), 1–20 (2019)
Ko, D.H.; Jeong, S.T.; Kim, Y.C.: Assessment of wind energy for small-scale wind power in Chuuk State, Micronesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 52, 613–622 (2015)
Saha, S.; Haque, M.E.; Mahmud, M.A.: Diagnosis and mitigation of sensor malfunctioning in a permanent magnet synchronous generator based wind energy conversion system. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv. 33(3), 938–948 (2018)
Chandramohan, K.; Padmanaban, S.; Kalyanasundaram, R.; Blaabjerg, F.: Modeling of five-phase, self-excited induction generator for wind mill application. Elect. Power Comp. Syst. 46(3), 353–363 (2018)
Ejiofor, O.S.; Candidus, E.U.; Victory, M.C.; Ugochukwu, E.C.: Wind energy dynamics of the separately excited induction generator. Int. J. Appl. Sci. 2(1), 22–32 (2019)
Fernandes, J.F.P.; Perez-Sanchez, M.; da Silva, F.F.; Lopez-Jimenez, P.A.; Ramos, H.M.; Branco, P.J.C.: Optimal energy efficiency of isolated PAT sytems by SEIG excitation tuning. Energy Conv. Manag. 183(1), 391–405 (2019)
Jha, D.; Thakur, A.: Novel control strategy for standalone wind energy conversion system supplying power to isolated DC Load. Majlesi J. Elect. Eng. 13(1), 19–29 (2019)
Kalla, U.K.; Singh, B.; Murthy, S.S.: Modified electronic load controller for constant frequency operation with voltage regulation of small hydro-driven single-phase SEIG. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 52(4), 2789–2800 (2016)
Mosaad, M.I.: Model reference adaptive control of STATCOM for grid integration of wind energy systems. IET Elect. Power Appl. 12(5), 605–613 (2018)
Chilipi, R.R.; Singh, B.; Murthy, S.S.: Performance of a self-excited induction generator with DSTATCOM-DTC drive-based voltage and frequency controller. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv. 29(3), 545–557 (2014)
Chauhan, P.J.; Chatterjee, J.K.: A Novel speed adaptive stator current compensator for voltage and frequency control of standalone SEIG feeding three-phase four-wire system. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 10(1), 248–256 (2019)
Arthishri, K.; Kumaresan, N.; Gounden, N.A.: Analysis and application of three-phase SEIG with power converters for supplying single-phase grid from wind energy. IEEE Syst. J. 13(2), 1813–1822 (2019)
dos Santos, T.H.; Goedtel, A.; da Silva, S.A.O.; Suetake, M.: Scalar control of an induction motor using a neural sensorless technique. Elect. Power Syst. Res. 108, 322–330 (2014)
Jaladi, K.K.; Sandhu, K.S.: DC-link transient improvement of SMC-based hybrid control of DFIG-WES under asymmetrical grid faults. Int. Trans. Elect. Energy Syst. 28(12), 1–27 (2018)
Jaladi, K.K.; Sandhu, K.S.: A new hybrid control scheme for minimizing torque and flux ripple for DFIG-based WES under random change in wind speed. Int. Trans. Elect. Energy Syst. 29(4), 1–15 (2019)
Bašić, M.; Vukadinović, D.; Grgić, I.: Compensation of stray load and iron losses in small vector-controlled induction generators. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv. 1, 9 (2019)
Baˇ, M.; Vukadinović, D.: Online efficiency optimization of a vector controlled self-excited induction generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv. 31(1), 373–380 (2016)
Pal, A.; Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.K.: An improved rotor flux space vector based MRAS for field oriented control of induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Elect. 33(6), 5131–5141 (2018)
Chinmaya, K.A.; Singh, G.K.: Performance evaluation of multiphase induction generator in stand-alone and grid-connected wind energy conversion system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 12(7), 823–831 (2018)
Tatte, Y.N.; Aware, M.V.: Torque ripple and harmonic current reduction in a three-level inverter-fed direct-torque-controlled five-phase induction motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Elect. 64(7), 5265–5275 (2017)
Maswood, A.I.; Gabriel, O.H.P.; Al, A.E.: Comparative study of multilevel inverters under unbalanced voltage in a single DC link. IET Power Elect. 6(8), 1530–1543 (2013)
Azeem, H.; Yellasiri, S.; Jammala, V.; Naik, B.S.; Panda, A.K.: A Fuzzy logic based switching methodology for a cascaded H-bridge multi-level inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Elect. 34(10), 9360–9364 (2019)
Boulouiha, H.M.; Allali, A.; Laouer, M.; Tahri, A.; Denaï, M.; Draou, A.: Direct torque control of multilevel SVPWM inverter in variable speed SCIG-based wind energy conversion system. Renew. Energy 80, 140–152 (2015)
Bandy, K.; Stumpf, P.: Model predictive torque control for multilevel inverter fed induction machines using sorting networks. IEEE Access 9, 13800–13813 (2021)
Xiao, D.; Alam, K.S.; Osman, I.; Akter, M.P.; Shakib, S.M.S.I.; Rahman, M.F.: Low complexity model predictive flux control for three-level neutral-point clamped inverter-fed induction motor drives without weighting factor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 56(6), 6496–6506 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The current work is supported by the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India, through a Ph.D. scholarship grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Parameters of induction machine | Parameters of IGBT inverter | Parameters of converter |
|---|---|---|
P = 4000 W | Ron = 1 mΩ | Ron = 0.001 Ω |
V = 400 V | RS = 105 Ω | Vf = 0.8 V |
f = 50 Hz | Lon = 1 mH | |
RS = 0.035 pu | ||
N = 1430 rpm | ||
H.P = 5.4 | ||
Lls = 0.045 pu |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dewangan, S., Vadhera, S. Performance Evaluation of Multilevel Inverter in Variable Speed SEIG-Based Wind Energy System. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 3311–3324 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06197-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06197-z