Abstract
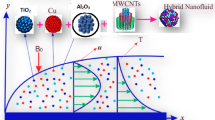
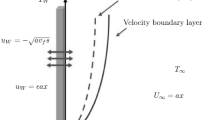
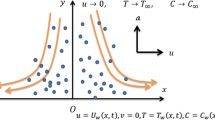
The current study investigates the flow of viscous nanofluids over the stretching surface with variable thickness in the presence of heterogeneous and homogeneous reactions. Comparison is made for water-based nanofluids with copper (Cu), silver (Ag), copper oxide (CuO), aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and titanium oxide (TiO2) as nanoparticles. The heat transfer phenomenon is characterized by nonlinear thermal radiation. The formulation of the model consists of partial differential equations with convective boundary conditions, which are converted into ordinary differential equations with the help of boundary layer approximation. The convergent series solution is computed with the help of an efficient analytical method, namely the Optimal Homotopy technique. For the validation of the suggested approach, the convergence of the obtained results is illustrated for different values of involved parameters. Moreover, residual errors for the varied number of terms in the derived series solution are displayed graphically. To validate the accuracy of the present results, a comparison with previously published results is presented. The influence of various variables on the velocity profile, the distribution profiles of temperature, and concentration is graphically discussed. Heat transfer rate (or local Nusselt number) and skin friction coefficient are estimated through the Tables. It is observed that temperature rises for higher radiation parameter and the temperature of aluminum oxide nanofluid is more because of its higher thermal conductivity as compared to other four nanoparticles. The study also reveals that with an improvement in the volume fraction of nanoparticles, the degree of the heat transfer rate and the coefficient of skin friction also increases.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- u, v :
-
Velocity components
- T :
-
Temperature
- b :
-
Stretched sheet constant
- \((\rho c_{p} )_{nf}\) :
-
Heat capacitance
- \(\mu_{f}\) :
-
Base fluid dynamic viscosity
- \(h_{f}\) :
-
Non-uniform heat transfer coefficient
- \(\alpha_{nf}\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(\rho_{nf}\) :
-
Effective density of nanofluid
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient temperature
- \(K^{ * }\) :
-
Heterogeneous rate constant
- \(K_{r}\) :
-
Homogeneous rate constant
- \(C_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient concentration
- \(q_{r}\) :
-
Thermal radiation
- \(k_{f}\) :
-
Mean adsorption coefficient
- \(q_{w}\) :
-
Wall heat flux
- \(D_{A}\) :
-
Coefficient of diffusion specie A
- \(D_{B}\) :
-
Coefficient of diffusion specie B
- \(\theta_{w}\) :
-
Temperature ratio parameter
- c p :
-
Specific heat
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- w :
-
Wall notation
- U w :
-
Stretching velocity
- \(a_{ \circ } ,\,b_{ \circ } ,\lambda\) :
-
Dimensionless constant
- \(T_{f}\) :
-
Wall temperature
- \(\mu_{nf}\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity of nanofluid
- \(U_{ \circ }\) :
-
Dimensional constant
- \(\rho_{f}\) :
-
Density of the base fluid
- \(B_{t}\) :
-
Thermal Biot number
- n :
-
Power-law index
- Sc:
-
Schmidt number
- a, b :
-
Reaction rate species
- \(k_{nf}\) :
-
Effective thermal conductivity of nanofluid
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Variable wall thickness
- \(E_{c}\) :
-
Eckert number
- R :
-
Radiation parameter
- \(\Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
References
Choi, S.U.S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles developments and applications of non-Newtonian fluid flow. ASME FED 66, 99–105 (1995)
Si, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.: A mixed convection flow and heat transfer of pseudo-plastic power law nanofluids past a stretching vertical plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 105, 350–358 (2017)
Hayat, T.; Qayyum, S.; Imtiaz, M.; Alsaedi, A.: Comparative study of silver and copper water nanofluids with mixed convection and nonlinear thermal radiation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 102, 723–732 (2016)
Khan, W.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Ismail, A.I.M.: Hydrodynamic and thermal slip effect on double-diffusive free convective boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a flat vertical plate in the moving free stream. PLoS ONE 8(3), e54024 (2013)
Shehzad, S.A.; Abdullah, Z.; Abbasi, F.M.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.: Magnetic field effect in three-dimensional flow of an Oldroyd-B nanofluid over a radiative surface. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 399, 97–108 (2016)
Lu, D.; Ramzan, M.; N. ul Huda, J. D. Chung, U. Farooq. : Nonlinear radiation effect on MHD Carreau nanofluid flow over a radially stretching surface with zero mass flux at the surface. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–17 (2018)
Hayat, T.; Tanveer, A.; Alsaadi, F.: Simultaneous effects of radial magnetic field and wall properties on peristaltic flow of Carreau–Yasuda fluid in curved flow configuration. AIP Adv. 5, 127–234 (2015)
Hayat, T.; Khan, M.I.; Waqas, M.; Alsaedi, A.: Newtonian heating effect in nanofluid low by a permeable cylinder. Results Phys. 7, 256–262 (2017)
Qayyum, S.; Khan, M.I.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.: Comparative investigation of five nanoparticles in flow of viscous fluid with Joule heating and slip due to rotating disk. Physica B: Cond. Matter. 534, 173–183 (2018)
Hayat, T.; Qayyum, S.; Alsaedi, A.; Shafiq, A.: Inclined magnetic field and heat source/sink aspects in flow of nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 103, 99–107 (2016)
Abid, N.; Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Kadry, S.; Chu, Y.M.: Comparative analysis of magnetized partially ionized copper, copper oxide–water and kerosene oil nanofluid flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–14 (2020)
Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Kadry, S.; Chu, Y.M.; Akhtar, M.: Nanofluid flow containing carbon nanotubes with quartic autocatalytic chemical reaction and Thompson and Troian slip at the boundary. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–13 (2020)
Ramzan, M.; Gul, H.; Chung, J.D.; Kadry, S.; Chu, Y.M.: Significance of Hall effect and Ion slip in a three-dimensional bioconvective Tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow subject to Arrhenius activation energy. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–15 (2020)
Ramzan, M.; Rafiq, A.; Chung, J.D.; Kadry, S.; Chu, Y.M.: Nanofluid flow with autocatalytic chemical reaction over a curved surface with nonlinear thermal radiation and slip condition. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–13 (2020)
Lv, Y.P.; Gul, H.; Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Bilal, M.: Bioconvective Reiner-Rivlin nanofluid flow over a rotating disk with Cattaneo–Christov flow heat flux and entropy generation analysis. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–18 (2021)
Riasat, S.; Ramzan, M.; Sun, Y.L.; Malik, M.Y.; Chinram, R.: Comparative analysis of Yamada-Ota and Xue models for hybrid nanofluid flow amid two concentric spinning disks with variable thermophysical characteristics. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 26, 101039 (2021)
Yu, B.; Ramzan, M.; Riasat, S.; Kadry, S.; Chu, Y.M.; Malik, M.Y.: Impact of autocatalytic chemical reaction in an Ostwald-de-Waele nanofluid flow past a rotating disk with heterogeneous catalysis. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–17 (2021)
Gul, H.; Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Chu, Y.M.; Kadry, S.: Multiple slips impact in the MHD hybrid nanofluid flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux and autocatalytic chemical reaction. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–14 (2021)
Shaheen, N.; Ramzan, M.; Alshehri, A.; Shah, Z.; Kumam, P.: Soret-Dufour impact on a three-dimensional Casson nanofluid flow with dust particles and variable characteristics in a permeable media. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–21 (2021)
Zhang, Y.; Shahmir, N.; Ramzan, M.; Alotaibi, H.; Aljohani, H.M.: Upshot of melting heat transfer in a Von Karman rotating flow of gold–silver/engine oil hybrid nanofluid with cattaneo-christov heat flux. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 26, 101149 (2021)
Ahmad, M.; Taj, M.; Abbasi, A.; Ahmad, I.: Time-dependent 3D flow of Maxwell nanofluid due to an unsteady stretching surface through porous space. J Braz Soc Mech Sci. 41(10), 1–13 (2019)
Ahmad, M.; Muhammad, T.; Ahmad, I.; Aly, S.: Time-dependent 3D flow of viscoelastic nanofluid over an unsteady stretching surface. Phys. A 551, 124004 (2020)
Ahmad, M.; Shehzad, S.A.; Iqbal, A.; Taj, M.: Time-dependent three-dimensional Oldroyd-B nanofluid flow due to bidirectional movement of surface with zero mass flux. Adv. Mech. Eng. 12(4), 1687814020913783 (2020)
Ahmad, M.; Mabood, F.; Shehzad, S.A.; Taj, M.; Magmood, F.M.: Convective heat and zero-mass flux conditions in the time-dependent second-grade nanofluid flow by unsteady bidirectional surface movement. Chin. J. Phys. 72, 448 (2021)
Herisanu, N.; Marinca, V.; Dordea, T.; Madescu, G.: A new analytical approach to nonlinear vibration of an electric machine. Proc. Rom. Acad. Ser. A: Math. Phys. Technol. Sci. Inf. Sci. 9(3), 229–236 (2008)
Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M.; Sajid, M.: Heat transfer analysis of MHD flow due to unsteady bi-directional stretching sheet through porous space. Therm. Sci. 20(6), 1913–1925 (2016)
Shehzad, S.A.; Sheikholeslami, M.; Ambreen, T.; Shafee, A.; Babazadeh, H.; Ahmad, M.: Heat transfer management of hybrid nanofluid including radiation and magnetic source terms within a porous domain. Appl. Nanosci. 10(12), 5351–5359 (2020)
Khan, N.S.; Shah, Q.; Sohail, A.; Ullah, Z.; Kaewkhao, A.; Kumam, P.; Thounthong, P.: Rotating flow assessment of magnetized mixture fluid suspended with hybrid nanoparticles and chemical reactions of species. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–18 (2021)
Bashir, S.; Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Chu, Y.M.; Kadry, S.: Analyzing the impact of induced magnetic flux and Fourier’s and Fick’s theories on the Carreau–Yasuda nanofluid flow. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–18 (2021)
Hayat, T.; Khan, M.I.; Farooq, M.; Alsaedi, A.; Waqas, M.; Yasmeen, T.: Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model in flow of variable thermal conductivity fluid over a variable thicked surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 99, 702–710 (2016)
Ramesh, G.K.; Kumara, B.C.P.; Gireesha, B.J.; Rashidi, M.M.: Casson fluid flow near the stagnation point over a stretching sheet with variable thickness and radiation. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 9(3), 1115–1122 (2016)
Hayat, T.; Hussain, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Asghar, A.: Carbon nanotubes effects in the stagnation point flow towards a nonlinear stretching sheet with variable thickness. Adv. Powder Technol. 27, 1677–1688 (2016)
Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.: Bending collapse of square tubes with variable thickness. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 106, 107–116 (2016)
Xun, S.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.: Flow and heat transfer of Ostwald-de Waele fluid over a variable thickness rotating disk with index decreasing. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 103, 1214–1224 (2016)
Hayat, T.; Bashir, G.; Waqas, M.; Alsaedi, A.: MHD 2D flow of Williamson nanofluid over a nonlinear variable thicked surface with melting heat transfer. J. Mol. Liq. 223, 836–844 (2016)
Fang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.: Boundary layer flow over a stretching sheet with variable thickness. Appl. Math. Comput. 218, 7241–7252 (2012)
Hayat, T.; Bashir, Z.; Qayyum, S.; Alsaedi, A.: Investigation of double diffusion Cattaneo–Christov model in mixed convection flow by variable thickness surface. Results Phys. 7, 3873–3881 (2017)
Suleman, M.; Ramzan, M.; Ahmad, S.; Lu, D.; Muhammad, T.; Chung, J.D.: A numerical simulation of silver–water nanofluid flow with impacts of newtonian heating and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions past a nonlinear stretched cylinder. Symmetry. 11(2), 295 (2019)
Falodun, B.O.; Ayegbusi, F.D.: Soret-Dufour mechanism on an electrically conducting nanofluid flow past a semi-infinite porous plate with buoyancy force and chemical reaction influence. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Eqn. 37(2), 1419–1438 (2021)
Ramzan, M.; Bilal, M.; Chung, J.D.: Influence of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions on MHD 3D Maxwell fluid flow with Cattaneo-Christov heat flux and convective boundary condition. J. Mol. Liqds. 230, 415–422 (2017)
Agunbiade, A.S.; Dada, S.M.: Effects of viscous dissipation on convective rotatory chemically reacting Rivlin–Ericksen flow past a porous vertical plate. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 13(1), 402–413 (2019)
Ramzan, M.; Shaheen, N.: Thermally stratified Darcy–Forchheimer nanofluid flow comprising carbon nanotubes with effects of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. Phys. Scrip. 95(1), 701–715 (2019)
Raju, C.S.K.; Sandeep, N.; Saleem, S.: Effects of induced magnetic field and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions on stagnation flow of a Casson fluid. Eng. Sci. Tech. Int. J. 19(2), 875–887 (2016)
Mishra, R.: Slip Effect on MHD flow and heat transfer of Jeffrey Nanofluid over a Streching sheet in the presence of nonlinear thermal radiation and chemical reaction. Int. J. Eng. & Sci. Res. Tech. 6(4), 2017 (2017)
Ramzan, M.; Shaheen, N.; Kadry, S.; Ratha, Y.; Nam, Y.: Thermally Stratified Darcy Forchheimer Flow on a Moving Thin Needle with Homogeneous heterogeneous reactions and non-uniform heat source/sink. Appl. Sci. 10(2), 432 (2020)
Vaidya, H.; Prasad, K.V.; Setty, S.: Significances of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions on casson fluid over a slippery stretchable rotating disk with variable thickness. CFD Lett. 4, 41–63 (2019)
Sheikh, M.; Abbas, Z.: Homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in stagnation point flow of Casson fluid due to a stretching/shrinking sheet with uniform suction and slip effects. Ain Shams Eng. J. 8, 467–474 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Abha 61413, Saudi Arabia for funding this work through research groups program under Grant Number R.G.P-1/36/42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR supervised and conceived the idea; SB wrote the manuscript; and MYM and HA helped in the revised draft and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, S., Ramzan, M., Malik, M.Y. et al. Comparative Analysis of Five Nanoparticles in the Flow of Viscous Fluid with Nonlinear Radiation and Homogeneous–Heterogeneous Reaction. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 8129–8140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06094-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06094-5