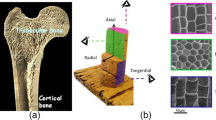
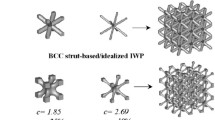
Abstract
Micro-lattice structure is a modern concept in cellular materials, which merges valuable mechanical attributes of material with smart geometrical directions. It is light in weight and consists of high energy absorption capacity, high strength and less vibration than other cellular materials. The micro-lattice structure is another type of cellular solid’s materials containing slender lattice parts known as strut and is categorized according to their cell arrangement. Due to the above properties nowadays, it is very popular for industrial applications like medical and bioengineering, aviation, automation and robotics. There are various techniques available for manufacturing micro-lattice structure. The simple, rapid and scalable fabrication of micro-lattice structure is achieved using additive manufacturing. Even geometrically intricate parts, complex assemblies can easily accommodate this lightweight technology. This paper presents an overall view of the micro-lattice structure concerning different topologies, various manufacturing methods, and different materials used. This paper also discusses how the variation of the above parameters can perk up the micro-lattices working notably, from a mechanical and application outlook. The attributes of micro-lattice structures and the foremost later finite element analysis models developed by different researchers for analyses of different properties have been also discussed here. This paper surveys the challenges confronted by various researchers and proposes future insight about micro-lattice structures required to progress their utilization in lightweight applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A.; Ashby, M.F.: Effective properties of the octet-truss lattice material. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 49(8), 1747–1769 (2001)
Köhnen, P.; Haase, C.; Bültmanna, J.; Ziegler, S.: Johannes Henrich Schleifenbaum, Wolfgang Bleck, “Mechanical properties and deformation behavior of additively manufactured lattice structures of stainless steel.” Mater. Des. 145, 205–217 (2018)
https://3dprinting.com/tips-tricks/3d-printed-lattice-structures/)
https://techxplore.com/news/2016-07-lattice-absorbs-vibrations.html
https://www.wardsauto.com/engines/iav-sees-huge-potential-3d-printed-pistons
Narkhede, S.; Sur, A.: Performance prediction of hollow micro-lattice cross-flow heat exchanger using a numerical approach. Int. J. Ambient Energy (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2021.1927835
Dong, L.; King, W.P.; Raleigh, M.; Wadley, H.N.: A microfabrication approach for making metallic mechanical metamaterials. Mater Des, 160, 147−168 (2018)
Tabatabaei, M.; Atluri, S.N.: Ultra-light cellular composite materials with architected geometrical structure. Comp. Struct. 196, 181–198 (2018)
QuanLaia, C.; Daraiob, C.: Highly porous MLS as ultrathin and efficient impact absorbers. Int. J. Impact Eng 120, 138–149 (2018)
Clough, E.C.; Plaisted, T.A.; Eckel, Z.C.; Cante, K.; Hundley, J.M.; Schaedler, T.A.: Elastomeric microlattice impact attenuators. Matter 1(6), 1519−1531 (2019)
Rosa, F.; Manzoni, S.; Casati, R.: Damping behavior of 316L lattice structures produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 160, 1010–1018 (2018)
Erdeniz, D.; Schaedler, T.A.; Dunand, D.C.: Deposition-based synthesis of nickel-based super-alloy MLS. ScriptaMaterialia 138, 28–31 (2017)
Smith, M.: The Compressive Response of Novel Lattice Structures Subjected to Static and Dynamic Loading, PhD thesis, University of Liverpool (2012)
Yong Liu, Y.; Schaedler, T.A.; Chen, X.: Dynamic energy absorption characteristics of hollow MLS. Mech. Mater. 77, 1–13 (2014)
Salari-Sharif, L.; Godfrey, S.W.; Tootkaboni, M.; Valdevit, L.: The effect of manufacturing defects on compressive strength of ultralight hollow microlattices: a data-driven study. Addit. Manuf., 19, 51−61 (2018)
Kessler, J.; Bâlc, N.; Gebhardt, A.; Abbas, K.: Basic research on lattice structures focused on the strut shape and welding beads. Phys. Procedia 83, 833−838 (2016)
Sharma, M.; Dobbelsteina, H.; Thielea, M.; Ostendorf, A.: Laser metal deposition of lattice structures by columnar built. Procedia CIRP 74, 218–221 (2018)
Laakso, P.; Riipinen, T.; Laukkanen, A.; Andersson, T.; Jokinen, A.; Revuelta, A.; Ruusuvuori, K.: Optimization and simulation of SLM process for high density H13 tool steel parts. Phys. Procedia 83, 26−35 (2016)
Ascari, A.; Fortunato, E.; Liverani, A.; Gamberoni, L.: Tomesani, “New Possibilities in the fabrication of hybrid components with big dimensions utilizing SLM.” Phys. Procedia 83, 839–846 (2016)
Dai, D.: DongdongGu, Influence of scan strategy and molten pool configuration on microstructures and tensile properties of selective laser melting additive manufactured aluminum based part. Opt. Laser Technol. 99, 91–100 (2018)
TheresaJuarez, AlmutSchroer; Schwaiger, R.; Hodge, A.M.: Evaluating sputter deposited metal coatings on 3D printed polymer micro-truss structures. Mater. Des. 140, 442–450 (2018)
Carluccio, D. : Challenges and opportunities in the selective laser melting of biodegradable metals for load-bearing bone Scaffold applications. Minerals Metals Mater Soc. ASM Int. 51, 3311−3334 (2020)
Schaedler, T.A.; Jacobsen, A.J.; Torrents, A.; Sorensen, A.E.; Lian, J.; Greer, J.R., et al.: Ultralight metallic microlattices. Science 334, 962–965 (2011)
Ryu, W.; Choi, Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.: Development of a lightweight prosthetic hand for patients with amputated fingers. Appl. Sci., 10(10), 3536 (2020)
Patrick Köhnen, C.H.: Mechanical properties and deformation behavior of additively manufactured lattice structures of stainless steel. Mater. Des. 14 (2018)
source: https://www.researchgate.net
Liang Donga, W.P.: A micro-fabrication approach for making metallic mechanical meta-materials. Mater. Des., pp. 147–168 (2018)
Nelissena, W.E.D.; C. A. : Journal of mechanics and physics solids. Lattice Mater. Architect. Actuat. 2D, 30472–30481 (2018)
Francesco Rosa, S.M.: Damping behavior of 316L lattice structures produced by Selective. Mater. Des., pp. 1010–1018 (2018)
Thomas Tancogne, D.; Mohr, D.: Elastically-isotropic truss lattice materials of re duce d plastic anisotropy. Int. J.Solids Struct. 138, 24–39 (2018)
Geng, X.; Yahui, Lu.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Yue, Z.: Fracture characteristic analysis of cellular lattice structures under tensile load. Int. J. Solids Struct. 7683(19), 30015 (2019)
R. Hasan, R.M.: Comparison of the drop weight impact performance of sandwich panels with aluminiumhoneycomb and titanium alloy micro lattice cores. Appl. Mech. Mater., pp. 24–25 (2010)
Tankasala, H.C.; Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A.: Tensile response of elastoplastic lattices at finite strain. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 109, 307–330 (2017)
SadeqSaleha, M.; LibParkbPanata, J.J.R.: 3D printed hierarchically-porous microlattice electrode materials for exceptionally high specific capacity and areal capacity lithium ion batteries. Addit. Manuf. 23, 70–78 (2018)
Krödel, S.; Li, L.; Constantinescu, A.; Daraio, C.: Stress relaxation in polymeric MLS materials. Mater. Des. 130, 433–441 (2017)
Shi, J.; Liu, L.: Creating hollow micro-lattice materials reinforced by carbon nano-tubes for improved mechanical properties. Mater. Lett. 240, 205–208 (2019)
Abueidda, D.W.: Elhebeary, M.; Shiang, C.-S.A.; Al-Rub, R.K.A.; Jasiuk, I.M.: Compression and buckling of micro-architectured Neovius-lattice. Extreme Mech. Lett., 30059, 1–25 (2020)
Cao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, D.; Fang, D.: Compression experiment and numerical evaluation on mechanical responses of the lattice structures with stochastic geometric defects originated from additive manufacturing. Compos. B 36513–8, 1–31 (2020)
Portela, C.M.; Greer J.R.; Kochmann D.M.: Mechanical behavior of additively-manufactured polymeric octet-truss lattice structures under quasi-static and dynamic compressive loading (2019)
Panesara A.; Meisam Abdia, C.; Hickmana, D.; Ashcroft, I.: Strategies for functionally graded lattice structures derived using topology optimisation for Additive Manufacturing (2018)
Liu, Y.; Schaedler, T.A.; Jacobsen, A.J.; Chen, X :Quasi-static energy absorption of hollow MLS. Comp. Part B 67, 39–49 (2014)
Gillard, F.; Boardman, R.; Mavrogordato, M.; Hollis, D.; Sinclair, I.; Pierron, F., et al.: The application of digital volume correlation (DVC) to study the micro-structural behaviour of trabecular bone during compression. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 29, 480–499 (2014)
Yang, K.; Wang J.; Jia, L.; Yang, G.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.: Additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V lattice structures with high structural integrity under large compressive deformation. J. Mater.Sci. Technol. (2018)
Yan Wu, L.Y.: Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium (2018)
Zefeng Xiao, Y.Y.: Evaluation of topology-optimized lattice structures manufactured via selective laser melting. Mater Des, pp 27–37 (2018)
Maloney, K.J.; Roper, C.S.; Jacobsen, A.J.; Carter, W.B.; Valdevit, L. ; Schaedler, T.A.: MLS as architected thin films: analysis of mechanical properties and high strain elastic recovery (2013)
Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Zenga, H.; Yang, H.; Lei, H.; LI, X.; Wang, Y.: Lightweight structure of a phase-change thermal controller based on lattice cells manufactured by SLM. Chin. J. Aeronaut. (2018)
Jin, Z.-H.: A MSL material with negative or zero thermal expansion. Comp. Commun., pp. 48–51 (2017)
Abigail Orange, Y.W.: An investigation of the fatigue strength of multiple cellular structures fabricated by electron beam powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. In: Solid Freeform Fabrication :Proceedings of the 29th Annual International (2018)
Huynh, L.; Rotella, J.; Sangid, M.D.: Fatigue behavior of IN718 MLS produced via additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 105, 278–289 (2016)
Zefeng Xiao, Y.Y.: Evaluation of topology-optimized lattice structures manufactured via selective laser melting. Mater. Des., pp. 27–37
Hongshuai Lei, C.L.: Evaluation of compressive properties of SLM fabricated multi-layer lattice structures by experimental test and μ-CT-based finite element analysis. Mater. Des. (2019)
Yan, X; Li, Q.; Yin, S.; Chen, Z.; Jenkins, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, J; Ma, W.Y.; Bolot, R.; Lupoi, R.; Ren, Z.; Liao, H.; Liu, M .: Mechanical and in vitro study of anisotropic Ti6Al4V lattice structure fabricated using selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd., 782, 209e223 (2019)
Ling, A.C.; Cernicchi B.A.; Gilchrist, M.D.; Cardiff, P.: Mechanical behaviour of additively-manufactured polymeric octet-truss lattice structures under quasi-static and dynamic compressive loading. Mater. Des., 162, 106–118 (2019)
Chen, X.Y.; Tan H.: An effective length model for octet lattice. Int. J. Mech. Sci., pp. 279–287 (2018)
Sur, A.; Narkhede, S.V.; Darvekar, S.K.: Applications, manufacturing and thermal characteristics of micro-lattice structures: current state of the art. Eng. J. 23 (6), 419–431 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SakshiKokil-Shah, Sur, A., Darvekar, S. et al. Recent Advancements of Micro-Lattice Structures: Application, Manufacturing Methods, Mechanical Properties, Topologies and Challenges. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 11587–11600 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05992-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05992-y