Abstract
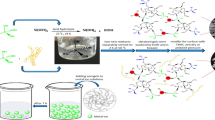
Silica-based aerogel composite was prepared adopting sol–gel technique combined with atmospheric drying method utilizing waste environmentally hazardous iron tailings. High-temperature alkali fusion was applied to extract the Si, Al and Fe in the tailings so as to maximize recovery of valuable elements. The SiO2-Al2O3 (SA) and SiO2-Al2O3-Fe2O3 (SAF) aerogel composites were subjected to assess its adsorption capacity for macromolecules, utilizing methylene blue (MB) as the adsorbate. The specific surface areas of the SA and SAF aerogel were estimated to be 922.03 m2/g and 683.84 m2/g. The equilibrium adsorption capacity for MB was estimated to be 318.47 mg/g and 334.44 mg/g, respectively. Although the specific surface area of SAF was lower than SA, it offered higher MB adsorption capacity which could be attributed to the presence of iron oxide. The results promised utilization of iron tailing generated aerogel composite as a potential adsorbent for separation of high molecular weight compounds.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao, A.P.; Rao, A.V.; Pajonk, G.M.: Hydrophobic and physical properties of the ambient pressure dried silica aerogels with sodium silicate precursor using various surface modification agents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 6032–6040 (2007)
Gurav, J.L.; Jung, I.-K.; Park, H.-H.; Kang, E.S.; Nadargi, D.Y.: Silica aerogel: synthesis and applications. J. Nanomater. 2010, 1–11 (2010)
Berestok, T.; Guardia, P.; Du, R.; Portals, J.B.; Colombo, M.; Estrade, S.; Peiro, F.; Brock, S.L.; Cabot, A.: Metal oxide aerogels with controlled crystallinity and faceting from the epoxide-driven cross-linking of colloidal nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 16041–16048 (2018)
Kistler, S.S.: Coherent expanded-aerogels. J. Phys. Chem. 36, 52–64 (1931)
García-González, C.A.; Alnaief, M.; Smirnova, I.: Polysaccharide-based aerogels—promising biodegradable carriers for drug delivery systems. Carbohyd. Polym. 86, 1425–1438 (2011)
Wiehn, M.; Levario, T.J.; Staggs, K.; Linneen, N.; Wang, Y.; Pfeffer, R.; Lin, Y.S.; Nielsen, D.R.: Adsorption of short-chain alcohols by hydrophobic silica aerogels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 18379–18385 (2013)
Perdigoto, M.L.; Martins, R.C.; Rocha, N.; Quina, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.; Patricio, R.; Duraes, L.: Application of hydrophobic silica based aerogels and xerogels for removal of toxic organic compounds from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 380, 134–140 (2012)
Abolghasemi Mahani, A.; Motahari, S.; Mohebbi, A.: Sol-gel derived flexible silica aerogel as selective adsorbent for water decontamination from crude oil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 129, 438–447 (2018)
Liu, H.; Sha, W.; Cooper, A.T.; Fan, M.: Preparation and characterization of a novel silica aerogel as adsorbent for toxic organic compounds. Colloid Surf. A. 347, 38–44 (2009)
Gurav, J.L.; Rao, A.V.; Nadargi, D.Y.; Park, H.-H.: Ambient pressure dried TEOS-based silica aerogels: good absorbents of organic liquids. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 503–510 (2010)
Bi, H.; Yin, Z.; Cao, X.; Xie, X.; Tan, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Bu, X.; Lu, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.: Carbon fiber aerogel made from raw cotton: a novel, efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Adv. Mater. 25, 5916–5921 (2013)
Li, Y.-Q.; Samad, Y.A.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Alhassan, S.M.; Liao, K.: Carbon aerogel from winter melon for highly efficient and recyclable oils and organic solvents absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2, 1492–1497 (2014)
Alatalo, S.M.; Pileidis, F.; Makila, E.; Sevilla, M.; Repo, E.; Salonen, J.; Sillanpaa, M.; Titirici, M.M.: Versatile cellulose-based carbon aerogel for the removal of both cationic and anionic metal contaminants from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 25875–25883 (2015)
Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, F.; You, L.; Shen, X.; Li, S.: Removal of organic solvents/oils using carbon aerogels derived from waste durian shell. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E. 78, 351–358 (2017)
Tian, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Shan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.: Adsorption of antibiotics from aqueous solution by different aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 505, 72–78 (2019)
Nagapriya, S.; Ajith, M.R.; Sreemoolanadhan, H.; Mathew, M.; Sharma, S.C.: Hydrophobic silica aerogels by ambient pressure drying. Mater. Sci. Forum. 830–831, 476–479 (2015)
Parale, V.G.; Han, W.; Jung, H.N.R.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, H.H.: Ambient pressure dried tetrapropoxysilane-based silica aerogels with high specific surface area. Solid State Sci. 75, 63–70 (2018)
Rao, A.V.; Bhagat, S.D.; Hirashima, H.; Pajonk, G.M.: Synthesis of flexible silica aerogels using methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) precursor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 300, 279–285 (2006)
Feng, Q.G.; Chen, K.; Ma, D.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, Z.; Qin, S.; Luo, Y.: Synthesis of high specific surface area silica aerogel from rice husk ash via ambient pressure drying. Colloid Surf. A. 539, 399–406 (2018)
Liu, S.W.; Wei, Q.; Cui, S.P.; Nie, Z.R.; Du, M.H.; Li, Q.-Y.: Hydrophobic silica aerogel derived from wheat husk ash by ambient pressure drying. J. Sol-gel Sci. Technol. 78, 60–67 (2016)
Li, T.; Wang, T.: Preparation of silica aerogel from rice hull ash by drying at atmospheric pressure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 398–401 (2008)
Parvathy, R.A.; Venkateswara, R.A.; Pajonk, G.M.; Shewale, P.M.: Effect of solvent exchanging process on the preparation of the hydrophobic silica aerogels by ambient pressure drying method using sodium silicate precursor. J Mater Sci. 42, 8418–8425 (2007)
De Pooter, S.; Latré, S.; Desplentere, F.; Seveno, D.: Optimized synthesis of ambient pressure dried thermal insulating silica aerogel powder from non-ion exchanged water glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 499, 217–226 (2018)
Omranpour, H.; Motahari, S.: Effects of processing conditions on silica aerogel during aging: role of solvent, time and temperature. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 379, 7–11 (2013)
Iswar, S.; Malfait, W.J.; Balog, S.; Winnefeld, F.; Lattuada, M.; Koebel, M.M.: Effect of aging on silica aerogel properties. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 241, 293–302 (2017)
Shimizu, T.; Kanamori, K.; Maeno, A.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K.: Transparent, highly insulating polyethyl- and polyvinylsilsesquioxane aerogels: mechanical improvements by vulcanization for ambient pressure drying. Chem. Mater. 28, 6860–6868 (2016)
Shimizu, T.; Kanamori, K.; Maeno, A.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K.: Transparent ethylene-bridged polymethylsiloxane aerogels and xerogels with improved bending flexibility. Langmuir 32, 13427–13434 (2016)
Zhang, S.; Xue, X.; Liu, X.; Duan, P.; Yang, H.; Jiang, T.; Wang, D.; Liu, R.: Current situation and comprehensive utilization of iron ore tailing resources. J. Min. Sci. 42, 403–408 (2006)
Yang, C.; Chong, C.; Qin, J.; Cui, X.: Characteristics of the fired bricks with low-silicon iron tailings. Constr. Build Mater. 70, 36–42 (2014)
Ma, B.-G.; Cai, L.-X.; Li, X.-G.; Jian, S.-W.: Utilization of iron tailings as substitute in autoclaved aerated concrete: physico-mechanical and microstructure of hydration products. J. Clean. Prod. 127, 162–171 (2016)
Xiong, C.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.: Use of grounded iron ore tailings (GIOTs) and BaCO3 to improve sulfate resistance of pastes. Constr. Build Mater. 150, 66–76 (2017)
Mendes, B.C.; Pedroti, L.G.; Fontes, M.P.F.; Ribeiro, J.C.L.; Vieira, C.M.F.; Pacheco, A.A.; Azevedo, A.R.G.D.: Technical and environmental assessment of the incorporation of iron ore tailings in construction clay bricks. Constr. Build Mater. 227, 116669 (2019)
Das, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Ramachandrarao, P.: Exploitation of iron ore tailing for the development of ceramic tiles. Waste Manag. 20, 725–729 (2000)
Yao, R.; Liao, S.Y.; Dai, C.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, X.Y.; Zheng, F.: Preparation and characterization of novel glass-ceramic tile with microwave absorption properties from iron ore tailings. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 367–375 (2015)
La Parola, V.; Deganello, G.; Scirè, S.; Venezia, A.M.: Effect of the Al/Si atomic ratio on surface and structural properties of sol–gel prepared aluminosilicates. J. Solid State Chem. 174, 482–488 (2003)
Szczygieł, I.; Matraszek, A.; Chęcmanowski, J.; Szczygieł, B.: Thermal behaviour of mixed alumina–silica gels obtained from alkoxides: phase formation and morphology of powders. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 356, 2824–2830 (2010)
Aravind, P.R.; Mukundan, P.; Krishna, P.P.; Warrier, K.G.K.: Mesoporous silica–alumina aerogels with high thermal pore stability through hybrid sol–gel route followed by subcritical drying. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 96, 14–20 (2006)
Wu, X.; Shao, G.; Cui, S.; Wang, L.; Shen, X.: Synthesis of a novel Al2O3–SiO2 composite aerogel with high specific surface area at elevated temperatures using inexpensive inorganic salt of aluminum. Ceram. Int. 42, 874–882 (2016)
Sehlleier, Y.H.; Hardt, S.; Schulz, C.; Wiggers, H.: A novel magnetically-separable porous iron-oxide nanocomposite as an adsorbent for methylene blue (MB) dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 3779–3787 (2016)
Zhang, P.; O’Connor, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Hou, D.: A green biochar/iron oxide composite for methylene blue removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 384, 121286 (2019)
Zhang, C.Q.; Li, S.Q.: Utilization of iron ore tailing for the synthesis of zeolite A by hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Cycles Waste. 20, 1605–1614 (2018)
Hu, W.B.; Li, M.M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Z.: Preparation of hydrophobic silica aerogel with kaolin dried at ambient pressure. Colloid Surf. A. 501, 83–91 (2016)
Yoo, J.K.; Kong, H.J.; Wagle, R.; Shon, B.H.; Kim, I.K.; Kim, T.H.: A study on the methods for making iron oxide aerogel. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 72, 332–337 (2019)
Ji, X.F.; Zhou, Q.; Qiu, G.B.; Peng, B.; Guo, M.; Zhang, M.: Synthesis of an alumina enriched Al2O3-SiO2 aerogel: reinforcement and ambient pressure drying. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 471, 160–168 (2017)
Abdelrahman, E.A.; Hegazey, R.M.; El-Azabawy, R.E.: Efficient removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous media using Fe/Si, Cr/Si, Ni/Si, and Zn/Si amorphous novel adsorbents. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 5301–5313 (2019)
Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W.: Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 87, 1051–1069 (2015)
Sangwichien, C.; Aranovich, G.L.; Donohue, M.D.: Density functional theory predictions of adsorption isotherms with hysteresis loops. Colloid Surf. A. 206, 313–320 (2002)
Gan, L.H.; Xu, Z.J.; Feng, Y.; Chen, L.W.: Synthesis of alumina aerogels by ambient drying method and control of their structures. J. Porous Mat. 12, 317–321 (2005)
Orlović, A.; Janaćković, D.; Skala, D.: Alumina/silica aerogel with zinc chloride alkylation catalyst: Influence of supercritical drying conditions and aerogel structure on alkylation catalytic activity. Catal. Commun. 3, 119–123 (2002)
Zu, G.; Shen, J.; Wei, X.; Ni, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.: Preparation and characterization of monolithic alumina aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 357, 2903–2906 (2011)
Yu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Ji, Y.; Wang, M.: Quartz fiber reinforced Al2O3-SiO2 aerogel composite with highly thermal stability by ambient pressure drying. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 505, 79–86 (2019)
Horiuchi, T.; Chen, L.; Osaki, T.; Mori, T.: Thermally stable alumina–gallia aerogel as a catalyst for NO reduction with C3H6 in the presence of excess oxygen. Catal. Lett. 72, 77–81 (2001)
Zhu, H.Y.; Jiang, R.; Xiao, L.; Li, W.: A novel magnetically separable gamma-Fe2O3/crosslinked chitosan adsorbent: preparation, characterization and adsorption application for removal of hazardous azo dye. J. Hazard. Mater. 179, 251–257 (2010)
Dong, G.; Tian, G.; Gong, L.; Tang, Q.; Li, M.; Meng, J.; Liang, J.: Mesoporous zinc silicate composites derived from iron ore tailings for highly efficient dye removal: structure and morphology evolution. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 305, 110352 (2020)
Silva, L.A.D.; Borges, S.M.S.; Paulino, P.N.; Fraga, M.A.; Oliva, S.T.D.; Marchetti, S.G.; Rangel, M.D.C.: Methylene blue oxidation over iron oxide supported on activated carbon derived from peanut hulls. Catal. Today. 289, 237–248 (2017)
Sun, L.; Wan, S.; Yuan, D.; Yu, Z.: Adsorption of nitroimidazole antibiotics from aqueous solutions on self-shaping porous biomass carbon foam pellets derived from Vallisneria natans waste as a new adsorbent. Sci. Total Environ. 664, 24–36 (2019)
Amini, T.F.; Nabizadeh, R.; Nasseri, S.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Khorsandi, H.; Mahvi, A.H.; Gholibegloo, E.; Alimohammadi, M.; Khoobi, M.: Endotoxin removal from aqueous solutions with dimethylamine-functionalized graphene oxide: modeling study and optimization of adsorption parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 368, 163–177 (2019)
Han, H.K.; Wei, W.; Jiang, Z.F.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xie, J.: Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto hydrophobic/hydrophilic silica aerogel. Colloid Surf. A. 509, 539–549 (2016)
Liu, G.Q.; Yang, R.; Li, M.: Liquid adsorption of basic dye using silica aerogels with different textural properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 356, 250–257 (2010)
Duman, O.; Polat, T.G.; Diker, C.O.; Tunc, S.: Agar/kappa-carrageenan composite hydrogel adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 160, 823–835 (2020)
Yan, B.; Chen, Z.; Cai, L.; Chen, Z.; Fu, J.; Xu, Q.: Fabrication of polyaniline hydrogel: synthesis, characterization and adsorption of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 356, 39–47 (2015)
Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, A.; Jiang, W.: Lead(II) and methylene blue removal using a fully biodegradable hydrogel based on starch immobilized humic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 268, 348–355 (2015)
Beh, J.H.; Lim, T.H.; Lew, J.H.; Lai, J.C.: Cellulose nanofibril-based aerogel derived from sago pith waste and its application on methylene blue removal. Int J Biol Macromol. 160, 836–845 (2020)
Chan, C.H.; Chia, C.H.; Zakaria, S.; Sajab, M.S.; Chin, S.X.: Cellulose nanofibrils: a rapid adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue. Rsc Adv. 5, 18204–18212 (2015)
Ho, Y.-S.: Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 136, 681–689 (2006)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the National Key Research and Development Project (2019YFC1904601) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, W., Liu, X., Srinivasakannan, C. et al. Novel Aerogel Absorbent Derived from Iron Tailings Via Atmospheric Drying. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 6901–6914 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05973-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05973-1