Abstract
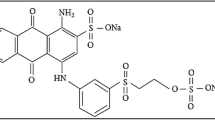
The adsorption study of anionic reactive blue 19 (RB19) and cationic methylene blue (MB) dyes from synthetic water was investigated using a new adsorbent. It was prepared from drinking water treatment sludge (DWTS) modified by iron nitrate. The surface area Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller BET increased from 15.58 to 106.12 m2/g after the iron incorporation. The adsorption of RB19 and MB on Fe-DWTS was carried out in a batch system to evaluate the effect of contact time (0–30 min), initial solution pH (2–8), Fe-DWTS dosage (0.5–2.5 g/L), and initial dye concentration (10–200 mg/L). The second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm model provided the best fit to the experimental data for RB 19 and MB. The maximum adsorption capacities were found to be 40.16 and 46.08 mg/g for RB19 and MB, respectively.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y.: Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 4676–4697 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.060
Temel, F.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Kucukcongar, S.: Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by silica gel supported calix[4]arene cage: Investigation of adsorption properties. Eur. Polym. J. 125, 109540 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109540
Mantasha, I.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, M.; Shahid, M.: Two dimensional (2D) molecular frameworks for rapid and selective adsorption of hazardous aromatic dyes from aqueous phase. Sep. Purif. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116413
Ayazi, Z.; Khoshhesab, Z.M.; Norouzi, S.: Modeling and optimizing of adsorption removal of Reactive Blue 19 on the magnetite/graphene oxide nanocomposite via response surface methodology. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 25301–25316 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1157705
Deng, D.; Guo, J.; Zeng, G.; Sun, G.; Red, C.: Decolorization of anthraquinone, triphenylmethane and azo dyes by a new isolated Bacillus cereus strain DC11*. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation. 62, 263–269 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2008.01.017
El-shishtawy, R.M.; El-zawahry, M.M.; Abdelghaffar, F.; Ahmed, N.S.E.: Nucleophilic addition of reactive dyes on amidoximated acrylic fabrics. Sci. world J. 2014, 1–11 (2014)
Ogunleye, D.T.; Akpotu, S.O.; Moodley, B.: Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and reactive blue 19 using graphene oxide modified with imidazolium based ionic liquid. Environ. Technol. Innov. 17, 100616 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100616
Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A.: Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 177, 70–80 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047
Jadhav, A.J.; Srivastava, V.C.: Adsorbed solution theory based modeling of binary adsorption of nitrobenzene, aniline and phenol onto granulated activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 229, 450–459 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.021
Boudechiche, N.; Fares, M.; Ouyahia, S.; Yazid, H.; Trari, M.: Comparative study on removal of two basic dyes in aqueous medium by adsorption using activated carbon from Ziziphus lotus stones. Microchem. J. 146, 1010–1018 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.02.010
Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.I.H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S.: Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 256, 395–407 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Marrakchi, F.; Hameed, B.H.; Hummadi, E.H.: Mesoporous biohybrid epichlorohydrin crosslinked chitosan/carbon—clay adsorbent for effective cationic and anionic dyes adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 163, 1079–1086 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.032
Brião, G.V.; Jahn, S.L.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L.: Highly efficient and reusable mesoporous zeolite synthetized from a biopolymer for cationic dyes adsorption. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 556, 43–50 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.08.019
Jiang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Tian, X.: Adsorption of CI reactive blue 19 from aqueous solutions by porous particles of the grafted chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 235, 151–157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.001
Gupta, V.K.: Suhas: application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. J. Environ. Manage. 90, 2313–2342 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017
Adeniyi, A.G.; Ighalo, J.O.: Biosorption of pollutants by plant leaves : an empirical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7, 103100 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103100
Dahhou, M.; El Moussaouiti, M.; Arshad, M.A.; Moustahsine, S.; Assafi, M.: Synthesis and characterization of drinking water treatment plant sludge-incorporated Portland cement. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 20, 891–901 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-017-0650-0
Dahhou, M.; Barbach, R.; El Moussaouiti, M.: Synthesis and characterization of belite-rich cement by exploiting alumina sludge. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 23, 1150–1158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0178-z
Benlalla, A.; Elmoussaouiti, M.; Dahhou, M.; Assafi, M.: Utilization of water treatment plant sludge in structural ceramics bricks. Appl. Clay Sci. 118, 171–177 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.09.012
Fan, J.; He, Z.; Ma, L.Q.; Yang, Y.; Stoffella, P.J.: Impacts of calcium water treatment residue on the soil-water-plant system in citrus production. Plant Soil. 374, 993–1004 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1881-z
Rashed, M.N.; El-Daim-El-Taher, M.A.; Fadlalla, S.M.M.: Adsorption of methylene blue using modified adsorbents from drinking water treatment sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 74, 1885–1898 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.377
Abo-El-Enein, S.A.; Shebl, A.; Abo El-Dahab, S.A.: Drinking water treatment sludge as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metals removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 146, 343–349 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.06.027
Cheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Xia, H.; Peng, J.; Shu, J.; Li, C.: Ultrasound and microwave-assisted preparation of Fe-activated carbon as an effective low-cost adsorbent for dyes wastewater treatment. RSC Adv. 6, 78936–78946 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra14082c
Xiao, W.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Garba, Z.N.; Lawan, I.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Z.: Adsorption of organic dyes from wastewater by metal-doped porous carbon materials. J. Clean. Prod. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124773
Cottet, L.; Almeida, C.A.P.; Naidek, N.; Viante, M.F.; Lopes, M.C.; Debacher, N.A.: Adsorption characteristics of montmorillonite clay modified with iron oxide with respect to methylene blue in aqueous media. Appl. Clay Sci. 95, 25–31 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.03.023
Čerović, L.S.; Milonjić, S.K.; Todorović, M.B.; Trtanj, M.I.; Pogozhev, Y.S.; Blagoveschenskii, Y.; Levashov, E.A.: Point of zero charge of different carbides. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 297, 1–6 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.10.012
Jamalluddin, N.A.; Abdullah, A.Z.: Fe incorporated mesocellular foam as an effective and stable catalyst: Effect of Fe concentration on the characteristics and activity in Fenton-like oxidation of acid red B. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 414, 94–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.01.006
Bedia, J.; Monsalvo, V.M.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Mohedano, A.F.: Iron catalysts by chemical activation of sewage sludge with FeCl3 for CWPO. Chem. Eng. J. 318, 224–230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.096
Ayodele, O.B.; Lim, J.K.; Hameed, B.H.: Degradation of phenol in photo-Fenton process by phosphoric acid modified kaolin supported ferric-oxalate catalyst: optimization and kinetic modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 197, 181–192 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.04.053
Yuan, P.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Tao, Q.; Fan, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; He, H.; Chen, T.: A combined study by XRD, FTIR, TG and HRTEM on the structure of delaminated Fe-intercalated/pillared clay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 324, 142–149 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.04.076
Silva, T.L.; Ronix, A.; Pezoti, O.; Souza, L.S.; Leandro, P.K.T.; Bedin, K.C.; Beltrame, K.K.; Cazetta, A.L.; Almeida, V.C.: Mesoporous activated carbon from industrial laundry sewage sludge: adsorption studies of reactive dye Remazol Brilliant Blue R. Chem. Eng. J. 303, 467–476 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.009
Ayodele, O.B.; Lim, J.K.; Hameed, B.H.: Pillared montmorillonite supported ferric oxalate as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for degradation of amoxicillin. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 413–414, 301–309 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.11.023
Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.: Adsorption of Reactive Blue 19 from aqueous solution by chitin nanofiber-/nanowhisker-based hydrogels. RSC Adv. 8, 15804–15812 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra01563e
Shanehsaz, M.; Seidi, S.; Ghorbani, Y.; Shoja, S.M.R.; Rouhani, S.: Polypyrrole-coated magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient adsorbent for RB19 synthetic textile dye: removal and kinetic study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 149, 481–486 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.04.114
Gök, Ö.; Özcan, A.S.; Özcan, A.: Adsorption behavior of a textile dye of Reactive Blue 19 from aqueous solutions onto modified bentonite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 5439–5443 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.12.134
Ismail, B.; Hussain, S.T.; Akram, S.: Adsorption of methylene blue onto spinel magnesium aluminate nanoparticles: adsorption isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 219, 395–402 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.034
Brar, S.K.; Wangoo, N.; Sharma, R.K.: Enhanced and selective adsorption of cationic dyes using novel biocompatible self-assembled peptide fibrils. J. Environ. Manage. 255, 109804 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109804
Chinoune, K.; Bentaleb, K.; Bouberka, Z.; Nadim, A.; Maschke, U.: Adsorption of reactive dyes from aqueous solution by dirty bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 123, 64–75 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.01.006
El-Bindary, A.A.; Abd El-Kawi, M.A.; Hafez, A.M.; Rashed, I.G.A.; Aboelnaga, E.E.: Removal of reactive blue 19 from aqueous solution using rice straw fly ash. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 7, 1023–1036 (2016)
Almeida, C.A.P.; Debacher, N.A.; Downs, A.J.; Cottet, L.; Mello, C.A.D.: Removal of methylene blue from colored effluents by adsorption on montmorillonite clay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 332, 46–53 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.12.012
Ding, L.; Zou, B.; Gao, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.: Adsorption of Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution using treated rice husk-based activated carbon. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 446, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.01.030
Ciobanu, G.; Barna, S.; Harja, M.: Kinetic and equilibrium studies on adsorption of Reactive Blue 19 dye from aqueous solutions by nanohydroxyapatite adsorbent. Arch. Environ. Prot. 42, 3–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/aep-2016-0014
Ergene, A.; Ada, K.; Tan, S.; Katircioǧlu, H.: Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto immobilized Scenedesmus quadricauda: equilibrium and kinetic modeling studies. Desalination 249, 1308–1314 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.06.027
Al-Qodah, Z.; Lafi, W.K.; Al-Anber, Z.; Al-Shannag, M.; Harahsheh, A.: Adsorption of methylene blue by acid and heat treated diatomaceous silica. Desalination 217, 212–224 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.03.003
Krishnan, G.R.; Radhika, R.; Jayalatha, T.; Jacob, S.; Rajeev, R.K.; George, B.; Anjali, B.R.: Removal of perchlorate from drinking water using granular activated carbon modified by acidic functional group: adsorption kinetics and equilibrium studies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 109, 158–171 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.03.014
Abdelwahab, O.: Evaluation of the use of loofa activated carbons as potential adsorbents for aqueous solutions containing dye. Desalination 222, 357–367 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.146
Abbas, M.; Trari, M.: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study on the removal of Congo Red from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto apricot stone. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 98, 424–436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.09.015
Yeddou Mezenner, N.; Lagha, H.; Kais, H.; Trari, M.: Biosorption of diazinon by a pre-treated alimentary industrial waste: equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Appl. Water Sci. 7, 4067–4076 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0563-z
Walker, G.M.; Hansen, L.; Hanna, J.A.; Allen, S.J.: Kinetics of a reactive dye adsorption onto dolomitic sorbents. Water Res. 37, 2081–2089 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00540-7
Wakkel, M.; Khiari, B.; Zagrouba, F.: Textile wastewater treatment by agro-industrial waste: equilibrium modelling, thermodynamics and mass transfer mechanisms of cationic dyes adsorption onto low-cost lignocellulosic adsorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 96, 439–452 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.12.014
Monsef Khoshhesab, Z.; Ahmadi, M.: Removal of reactive blue 19 from aqueous solutions using NiO nanoparticles: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 20037–20048 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1101713
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laib, S., Rezzaz-Yazid, H. & Sadaoui, Z. Comparative Study on Removal of Textile Dyes in Aqueous Medium by Adsorption Using Modified Drinking Water Treatment Sludge. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 6085–6098 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05950-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05950-8