Abstract
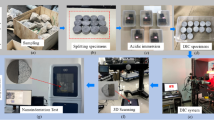
The investigation into the effects of acidizing treatment on the mechanical property of hot dry rocks (HDR) is beneficial for our understanding of the fracturing and stimulation mechanisms in HDR reservoirs. In this article, Brazilian disk tests were first carried out for hollow hot dry rocks with different internal diameters after acidizing treatments. The influences of acidizing treatments on the physical properties, tensile strength, and failure patterns of hot dry rock specimens were presented. Besides, the effects of the diameter of the internal hole on the peak load and failure patterns of the hot dry rock specimens were also investigated. The peak load decreases with the increase in the internal diameter. The results indicated that the acidizing treatments can dissolute the minerals, decrease rock mass, and tensile strength. The investigation of failure patterns demonstrated that the acidizing treatment is beneficial for the fracturing of hot dry rocks. The present study can provide some basic and theoretical data for the development of geothermal reservoir.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Portier, S.; Vuataza, F.; Namib, P.; Sanjuanc, B.; Gérard, A.: Chemical stimulation techniques for geothermal wells: experiments on the three-well EGS system at Soultz-sous-Forêts. France. Geothermics. 38, 349–359 (2009)
Williams, B.B. Acidizing fundamentals. New York and Dallas Society of Petroleum Engineers, European Formation Damage Control Conference, May 15–16, The Hague, The Netherlands. SPE Monograph. 1979, No. 6, pp 124
Strawn, J.A.: Results of acid treatment in hydrothermal direct heat experiment wells. Geotherm Resour Counc Trans. 4, 427–430 (1980)
Epperson, I.J.: Beowawe acid stimulation. Geotherm Resour Counc Trans. 7, 409–411 (1983)
Barrios, L.A.; Quijano, J.E.; Romero, R.E.; Mayorga, H.; Castro, M.; Caldera, J.: Enhanced permeability by chemical stimulation at the Berlin Geothermal Field. El Salvador. Geotherm Resour Counc Trans 26, 73–78 (2002)
Serpen, U.; Türeyen, O.I.: Acidizing geothermal wells. Geotherm Resour Counc Trans. 24, 683–688 (2000)
Yang, X.; Jiang, A.; Li, M.: Experimental investigation of the time-dependent behavior of quartz sandstone and quartzite under the combined effects of chemical erosion and freeze–thaw cycles. Cold Reg. Sci. Tech. 161, 51–62 (2019)
Li, S.; Huo, R.; Yoshiake, F.; Ren, D.; Song, Z.: Effect of acid-temperature-pressure on the damage characteristics of sandstone. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 122, 104079 (2019)
Miao, S.; Cai, M.; Guo, Q.; Wang, P.; Liang, M.: Damage effects and mechanisms in granite treated with acidic chemical solutions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 122, 77–86 (2016)
Feng, X.W.; Wang, W.; Yuan, S.S.; Wang, R.B.; Zhu, Q.Z.; Yu, J.: A coupled elastoplastic damage model for sandstone considering chemical corrosion. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 22(sup1), s302–s315 (2018)
Liu, T.G.; Wang, W.; Zeng, T.: A numerical study of chemical degradation effects on elastic-plastic behavior of sandstone. Eur J Environ Civ Eng (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2018.1490667
Feng, X.T.; Ding, W.: Coupled chemical stress processes in rock fracturing. Mater. Res. Innov. 15(sup1), s547–s550 (2011)
Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Man, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Su, R.: Characterizing the mechanical tensile behavior of Beishan granite with different experimental methods. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 69, 50–58 (2014)
Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G.: Dynamic Brazilian tests of granite under coupled static and dynamic loads. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 47(2), 495–505 (2014)
Yin, T.; Li, X.; Cao, W.; Xia, K.: Effects of thermal treatment on tensile strength of laurentian granite using Brazilian test. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 48(6), 2213–2223 (2015)
Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, D.; Braun, A.; Han, Z.: Investigation of the quasi-brittle failure of alashan granite viewed from laboratory experiments and grain-based discrete element modeling. Materials. 10(7), 835 (2017)
Jin, P.; Hu, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, X.; Li, C.: Influence of different thermal cycling treatments on the physical, mechanical and transport properties of granite. Geothermics 78, 118–128 (2019)
Wu, Q.; Weng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, B.; Luo, T.: On the tensile mechanical characteristics of fine-grained granite after heating/cooling treatments with different cooling rates. Eng. Geol. 253, 94–110 (2019)
Alsayed, M.I.: Utilising the Hoek triaxial cell for multiaxial testing of hollow rock cylinders. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 39, 355–366 (2002)
Labiouse, V.; Sauthier, C.; You, S.: Hollow cylinder simulation experiments of galleries in Boom clay formation. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 47, 43–55 (2014)
Monfared, M.; Sulem, J.; Delage, P.; Mohajerani, M.: A laboratory investigation on thermal properties of the Opalinus claystone. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 44(6), 735–747 (2011)
Haimson, B.; Kovacich, J.: Borehole instability in high-porosity Berea sandstone and factors affecting dimensions and shape of fracture-like breakouts. J. Eng. Geol. 69, 219–231 (2003)
Lee, D.H.; Juang, C.H.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, H.M.; Shieh, W.H.: Stress paths and mechanical behavior of a sandstone in hollow cylinder tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 36, 857–870 (1999)
Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Tao, M.; Weng, L.; Dong, L.; Zou, Y.: Dynamic Brazilian splitting test of ring-shaped specimens with different hole diameters. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 49(10), 4143–4151 (2016)
Wang, S.; Li, X.; Du, K.; Wang, S.; Tao, M.: Experimental study of the triaxial strength properties of hollow cylindrical granite specimens under coupled external and internal confining stresses. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018(51), 2015–2031 (2018)
Weng, L.; Li, X.; Shang, X.; Xie, X.: Fracturing Behavior and Failure in Hollowed Granite Rock with Static Compression and Coupled Static-Dynamic Loads. Int. J. Geomech. 18(6), 04018045 (2018)
Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xi, B.; Wan, Z.; Yang, D.; Liang, W.: Deformation and instability failure of borehole at high temperature and high pressure in Hot Dry Rock exploitation. Renew. Energ. 77, 159–165 (2015)
Wang, S.; Sloan, S.; Tang, C.: Three-dimensional numerical investigations of the failure mechanism of a rock disc with a central or eccentric hole. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 47(6), 2117–2137 (2013)
Yang, S.: Experimental study on deformation, peak strength and crack damage behavior of hollow sandstone under conventional triaxial compression. Eng. Geol. 213, 11–24 (2016)
Yang, S.: Fracturing mechanism of compressed hollow-cylinder sandstone evaluated by X-ray micro-CT scanning. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 53, 2033–2053 (2016)
Deichmann, N.; Giardini, D.: Earthquakes induced by the stimulation of an enhanced geothermal system below basel (Switzerland). Seismol. Res. Lett. 80(5), 784–798 (2009)
Ellsworth, W.L.: Injection-induced earthquakes. Science 341(6142), 142–142 (2013)
Kim, K.H.; Ree, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.Y.; Seo, W.: Assessing whether the 2017 Mw 5.4 Pohang earthquake in South Korea was an induced event. Science 360(6392), 1007–1009 (2018)
Chen, C.; Peng, S.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.: The effect of chemical erosion on mechanical properties and fracture of sandstone under shear loading: an experimental study. Sci. rep. 9, 19886 (2019)
Asadollahpour, E.; Hashemolhosseini, H.; Baghbanan, A., et al.: Redistribution of local fracture aperture and flow patterns by acidizing. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 117, 20–30 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41902303), Sichuan Youth Science & Technology Foundation (2017JQ0010), National High Technology Research & Development (2016ZX05053), Key Fund Project of Educational Commission of Sichuan Province (16CZ0008), and Explorative Project Fund (G201601) of State Key laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation (Southwest Petroleum University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C. Lin was involved in conceptualization and writing—original draft preparation; C. Lin and J.C. Mao helped in methodology; J.H. Mao contributed to data curation; X. Yang helped in investigation; A. Chen was involved in writing—review & editing. J. Zhao helped in supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C., Mao, J., Mao, J. et al. Experimental Study on the Strength and Failure Mechanism of Hollow Hot Dry Rocks Under Brazilian Splitting Tests. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 11125–11134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05704-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05704-6