Abstract
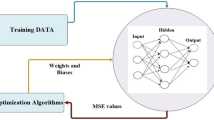
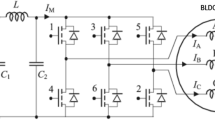
In this study, in order to determine the dynamic response of a four-pole permanent magnet three-phase brushless DC (BLDC) motor, parametric simulation studies are carried out with finite element analysis Rmxprt software depending on three specific input variables (excitation voltage, pulse width, and motor power). The rotor speed is defined as the output parameter to determine the dynamic response, and 600 parametric data are obtained according to the simulation studies. In order to estimate the rotor speed of the BLDC motor modeled using artificial intelligence (AI), an advanced recurrent neural network architecture known as bidirectional long short-term memory has been designed. Rotor speed is successfully estimated with the proposed architecture, and as a result, the mean absolute percentage error value is calculated as 3.25%. These results show that the analysis of BLDC motor parameters can be determined quickly with the proposed AI method without long-running simulations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kandiban, R.; Arulmozhiyal, R.: Design of adaptive fuzzy PID controller for speed control of BLDC motor. Int. J. Soft Comput. Eng. 2, 386–391 (2012)
Gouda, G.E.; Jyothi, N.: Analysis and co-simulation of BLDC motor drive with fault detection by FEA method. Int. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 5, 199–202 (2017)
Govindaraj, D.T.; Vishnu, S.: Simulation modelling of sensor less speed control of BLDC motor using artificial neural network. Int. J. Emerg. Trends Electr. Electron. 10, 7–15 (2014)
Leena, N.; Shanmugasundaram, R.: Artificial neural network controller for improved performance of brushless DC motor. In: 2014 International Conference on Power Signals Control and Computations (EPSCICON), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2014)
Tipsuwanporn, V.; Piyarat, W.; Tarasantisuk, C., Identification and control of brushless DC motors using on-line trained artificial neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Power Conversion Conference-Osaka 2002 (Cat. No. 02TH8579), pp. 1290–1294. IEEE (2002).
Solanki, S.: Brushless DC motor drive during speed regulation with artificial neural network controller. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 6, 01–05 (2016)
Rubaai, A.; Ricketts, D.; Kankam, M.D.: Development and implementation of an adaptive fuzzy-neural-network controller for brushless drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 38, 441–447 (2002)
Ganesh, C.; Prabhu, M.; Rajalakshmi, M.; Sumathi, G.; Bhola, V.; Patnaik, S.: ANN based PID controlled brushless DC drive system. In: Proceedings of the International Conference. on Advances in Electrical &\quad Electronics (2011)
Mamadapur, A.; Mahadev, G.U.: Speed control of BLDC motor using neural network controller and PID controller. In: 2019 2nd International Conference on Power and Embedded Drive Control (ICPEDC), pp. 146–151. IEEE (2019).
Belov, M.P.; Khoa, T.D.; Truong, D.D.: BLDC of robotic manipulators with neural torque compensator based optimal robust control. In: 2019 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), pp. 437–441. IEEE (2019)
Utomo, D.S.B.; Rizal, A.; Gaffar, A.F.O.: Model reference neural adaptive control based BLDC motor speed control. In: 2017 5th International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Information Engineering (ICEEIE) , pp. 49–54. IEEE (2017)
Singh, P.; Rai, P.: An ANN based X-PC target controller for speed control of permanent magnet brushless DC motor. In: Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Conference on Control Applications, 2005. CCA 2005, pp. 1027–1032. IEEE (2005)
Xia, C.-L.; Chen, W.: Sensorless control of brushless DC motors at low speed using neural networks. In: 2005 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, pp. 1099–1103. IEEE (2005).
Yi, Y.; Vilathgamuwa, D.M.; Rahman, M.A.: Implementation of an artificial-neural-network-based real-time adaptive controller for an interior permanent-magnet motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 39, 96–104 (2003)
Anshory, I.; Robandi, I.: Monitoring and optimization of speed settings for Brushless Direct Current (BLDC) using particle swarm optimization (PSO). In: 2016 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), pp. 243–248. IEEE (2016)
Sabanci, K.: Artificial intelligence based power consumption estimation of two-phase brushless DC motor according to FEA parametric simulation. Measurement 155, 107553 (2020)
Toha, S.F.; Tokhi, M.O.: MLP and Elman recurrent neural network modelling for the TRMS. In: 2008 7th IEEE International Conference on Cybernetic Intelligent Systems, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2008).
Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.: LSTM-based pitch range estimation from spectral information of brief speech input. In: 2018 11th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), pp. 349–353. IEEE (2018)
Akkaya, R.; Kulaksız, A.; Aydoğdu, Ö.: DSP implementation of a PV system with GA-MLP-NN based MPPT controller supplying BLDC motor drive. Energy Convers. Manag. 48, 210–218 (2007)
Kumar, R.; Gupta, R.; Bhangale, S.; Gothwal, H.: ANN based control and estimation of direct torque controlled induction motor drive. Asian Power Electron. J. 2, 115–122 (2008)
Nekoubin, A.: Design a single-phase BLDC motor and finite-element analysis of stator slots structure effects on the efficiency. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 5, 685–692 (2011)
Yu, R.; Gao, J.; Yu, M.; Lu, W.; Xu, T.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.: LSTM-EFG for wind power forecasting based on sequential correlation features. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 93, 33–42 (2019)
Kim, J.-G.; Lee, B.: Appliance classification by power signal analysis based on multi-feature combination multi-layer LSTM. Energies 12, 2804 (2019)
Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P.: Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 5, 157–166 (1994)
Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9, 1735–1780 (1997)
Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F.: Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 12, 2451–2471 (2000)
Gers, F.A.; Schraudolph, N.N.; Schmidhuber, J.: Learning precise timing with LSTM recurrent networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 115–143 (2002)
Chen, G.: A gentle tutorial of recurrent neural network with error backpropagation. arXiv preprint arXiv:0258 (2016)
Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Jin, B.; Ye, C.: Short-term traffic flow intensity prediction based on CHS-LSTM. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 45, 10845–10857 (2020)
Mehrani, M.; Attarzadeh, I.; Hosseinzadeh, M.: Sampling rate prediction of biosensors in wireless body area networks using deep-learning methods. In: Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, p. 102101 (2020)
Liu, G.; Guo, J.: Bidirectional LSTM with attention mechanism and convolutional layer for text classification. Neurocomputing 337, 325–338 (2019)
Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15, 1929–1958 (2014)
Warde-Farley, D.; Goodfellow, I.J.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.: An empirical analysis of dropout in piecewise linear networks, arXiv preprint arXiv: 0258 (2013)
Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980(2014)
Feng, S.; Zhou, H.; Dong, H.: Using deep neural network with small dataset to predict material defects. Mater. Des. 162, 300–310 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unlersen, M.F., Balci, S., Aslan, M.F. et al. The Speed Estimation via BiLSTM-Based Network of a BLDC Motor Drive for Fan Applications. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 2639–2648 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05700-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05700-w