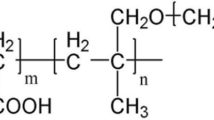
Abstract
To solve the problem that the low temperature leads to the slow development of cement strength in deepwater cementing, we prepared low-temperature early strength material of nano-C-S-H gel seed with sodium silicate nonahydrate and calcium nitrate tetrahydrate as raw materials. The chemical structure and elemental composition of nanometer C-S-H gel seed were characterized by FT-IR, EDS, XRD, SEM, and TEM. The effect of nanometer C-S-H gel seed on the early strength of cement at 5 °C was evaluated. The results showed that the nano-C-S-H gel seed is nanoscale and semi-crystalline form. Compared with blank cement, nano-C-S-H gel seed increased the compressive strength of cement by 2.6 MPa (8 h), which could significantly improve the early strength of cement. Finally, mechanistic analysis by XRD and SEM showed the nucleation effect and the adsorption effect of nano-C-S-H gel seed stimulated the reactivity of cement clinker at the low temperature, accelerating the hydration process of the cement slurry. The low-temperature early strength material of nano-C-S-H gel seed may have promising application in deepwater cementing.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huo, J.-H.; Peng, Z.-G.; Feng, Q.: Fly ash and slag cement slurry containing microencapsulated phase change materials: characterization and application. Int. J. Energy Res. 43, 4459–4472 (2019)
Pettingill, H.S., YPF, R., Weimer, P.: World-wide deepwater exploration and production: past, present and future % J Offshore Technology Conference (2002)
Rehder, S.; Franke, D.: How to include ignorance into hydrocarbon-resource assessments? A case study applied to the presence of source rock at the argentine deep water margin(article). Nat. Resour. Res. 21, 301–309 (2012)
Zou, C.; Zhai, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wen, Z.; Ma, F.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Liang, K.: Formation, distribution, potential and prediction of global conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon resources. Pet. Explor. Dev. 42, 14–28 (2015)
Vengosh, A.; Jackson, R.B.; Warner, N.; Darrah, T.H.; Kondash, A.: A critical review of the risks to water resources from unconventional shale gas development and hydraulic fracturing in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 8334–8348 (2014)
Elshahawi, H.: Deepwater exploration and production in the gulf of mexico-challenges and opportunities. Petrophysics 55, 81–87 (2014)
Feng, Q.; Liu, X.J.; Peng, Z.G.; Zheng, Y.; Huo, J.H.; Liu, H.: Preparation of low hydration heat cement slurry with micro- encapsulated thermal control material. Energy. 187, 116000 (2019)
Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Bu, Y.; Zhou, W.: Design and performance evaluation of a unique deepwater cement slurry. SPE Drill. Complet. 26, 220–226 (2011)
Ward, M.; Granberry, V.; Campos, G.; Rausis, M.; Sledz, M.; Weber, L.; Guillot, D.; Naziri, I.; Romero, J.: A joint industry project to assess circulating temperatures in deepwater wells %J SPE drilling and completion. SPE Drill. Complet. 18, 133–137 (2003)
Wang, C., Peng, Z., Wang, R.: Study on a new cement for deepwater well cementing. In Advanced building materials and sustainable architecture, Pts 1–4, Y. Shao, S. Hao, Y. Luo, J. Xing, Z. Liu, Eds. (Applied mechanics and materials, 2012), vol. 174–177, pp. 1321–1325
Sun, C., Zhang, X., Zhao, H., Gao, Q.: Early strength agent on the properties of reinforcement materials research. In Applied mechanics and materials Ii, Pts 1 and 2, S. B. Choi, Y. H. Kim, P. Yarlagadda, Eds. (Applied mechanics and materials, 2014), vol. 477–478, pp. 936-+
Choi, S.Y.; Yang, E.I.: An experimental study on alkali silica reaction of concrete specimen using steel slag as aggregate. Appl. Sci. Basel. 10, 6699 (2020)
Ferche, A.C.; Gautam, B.; Habibi, F.; Panesar, D.K.; Sheikh, S.A.; Vecchio, F.J.; Orbovic, N.: Material, structural and modelling aspects of alkali aggregate reaction in concrete. Nucl. Eng. Des. 351, 87–93 (2019)
Lee, B.Y.; Kurtis, K.E.: Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles on early C3S hydration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 3399–3405 (2010)
Land, G.; Stephan, D.: Controlling cement hydration with nanoparticles. Cement Concr. Compos. 57, 64–67 (2015)
Lavergne, F.; Belhadi, R.; Carriat, J.; Ben Fraj, A.: Effect of nano-silica particles on the hydration, the rheology and the strength development of a blended cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 95, 42–55 (2019)
Liu, R.; Han, F.; Yan, P.: Characteristics of two types of C-S-H gel in hardened complex binder pastes blended with slag. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 56, 1395–1402 (2013)
Hou, D.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.: Mechanical properties of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) at nano-scale: a molecular dynamics study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 146, 503–511 (2014)
Matsuyama, H.; Young, J.F.: Intercalation of polymers in calcium silicate hydrate: a new synthetic approach to biocomposites? . Mater. Chem. 11, 16–19 (1998)
Thomas, J.J.; Jennings, H.M.; Chen, J.J.: Influence of nucleation seeding on the hydration mechanisms of tricalcium silicate and cement. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 4327–4334 (2009)
Nicoleau, L.: Accelerated growth of calcium silicate hydrates: experiments and simulations. Cem. Concr. Res. 41, 1339–1348 (2011)
Plank, J.; Schoenlein, M.; Kanchanason, V.: Study on the early crystallization of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) in the presence of polycarboxylate superplasticizers. J. Organomet. Chem. 869, 227–232 (2018)
Land, G.; Stephan, D.: The effect of synthesis conditions on the efficiency of C-S-H seeds to accelerate cement hydration. Cement Concr. Compos. 87, 73–78 (2018)
Chen, J.J.; Thomas, J.J.; Taylor, H.F.W.; Jennings, H.M.: Solubility and structure of calcium silicate hydrate. Cem. Concr. Res. 34, 1499–1519 (2004)
Taylor, H.F.W.: Nanostructure of CSH: Current status. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1, 38–46 (1993)
Jennings, H.M.: A model for the microstructure of calcium silicate hydrate in cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 30, 101–116 (2000)
Moghaddam, S.E.; Hejazi, V.; Hwang, S.H.; Sreenivasan, S.; Miller, J.; Shi, B.H.; Zhao, S.; Rusakova, I.; Alizadeh, A.R.; Whitmire, K.H.; Shahsavari, R.: Morphogenesis of cement hydrate. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 3798–3811 (2017)
Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, G.; Yang, Q.: Nucleation thermodynamics inside micro/nanocavity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 24, 183–186 (2008)
Wang, Z.H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Liu, Y.: Investigation on gelation nucleation kinetics of waxy crude oil emulsions by their thermal behavior. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 181, 106230 (2019)
John, E.; Matschei, T.; Stephan, D.: Nucleation seeding with calcium silicate hydrate - a review. Cem. Concr. Res. 113, 74–85 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Q., Mao, Y., Peng, Z. et al. Preparation and Properties of Low-Temperature Early Strength Material for Nano-C-S-H Gel Seed. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 5567–5575 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05558-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05558-y