Abstract
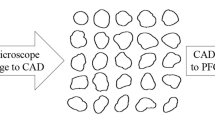
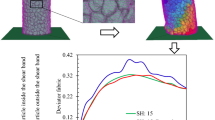
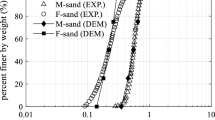
The particle shape contributes significantly to sand mechanical properties but is difficult to study in laboratory experiments. In this study, microscopy experiments were used to classify sand particle morphologies as spherical, non-spherical and ball-shaped. Particles with these three morphologies were modeled using the discrete element method to analyze the effect of the particle shape on the shear strength in a direct shear test simulation. The simulation results showed that the non-spherical particles and balls exhibited the highest and lowest peak shear strengths, respectively, under a low vertical stress. The highest and lowest contact force numbers were observed for the non-spherical particles and balls, respectively. The sand particles exhibited a higher resistance to motion with increasing contact force numbers, resulting in a higher shear strength. For particles with low sphericity (S) and roundness (R) values, a high number of contacts and interlocking structures can form, increasing resistance to external forces. As the S decreased, the anisotropy in the contact force increased during the test, and the contact number distribution of the spherical particles tended to remain isotropic during the entire process.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, J.; Gao, R. ; Liu, Y.: Numerical study of particle morphology effect on the angle of repose for coarse assemblies using DEM. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1–15 (2019)
Santamarina, J. ; Cho, G.-C.: Soil behaviour: The role of particle shape. In: Advances in geotechnical engineering: The Skempton conference: Proceedings of a three day conference on advances in geotechnical engineering, organised by the Institution of Civil Engineers and held at the Royal Geographical Society, London, UK, on 29–31 March 2004, pp. 604–617. Thomas Telford Publishing (2004)
Ren, X.W.; Santamarina, J.C.: The hydraulic conductivity of sediments: a pore size perspective. Eng. Geol. 233, 48–54 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.022
de Bono, J.P.; McDowell, G.R.: Investigating the effects of particle shape on normal compression and overconsolidation using DEM. Granul. Matter (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0605-5
Nasir, M.; Johari, M.A.M.; Yusuf, M.O.; Maslehuddin, M.; Al-Harthi, M.A.; Dafalla, H.: Impact of slag content and curing methods on the strength of alkaline-activated silico-manganese fume/blast furnace slag mortars. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(10), 8325–8335 (2019)
Härtl, J.; Ooi, J.Y.: Numerical investigation of particle shape and particle friction on limiting bulk friction in direct shear tests and comparison with experiments. Powder Technol. 212(1), (2011)
Bono, J.P.d.; McDowell, G.R.: Investigating the effects of particle shape on normal compression and overconsolidation using DEM. Granul. Matter 18(3), (2016)
Terzaghi, K.: Principles of soil mechanics. Engineering News Record, 5–832 (1925)
Wadell, H.: Volume, shape, and roundness of rock particles. J. Geol. 40(5), 443–451 (1932)
Li, D.; Minner, D.D.; Christians, N.E.: Quantitative evaluation of sand shape and roundness and their potential effect on stability of sand-based athletic fields. In: I International Conference on Turfgrass Management and Science for Sports Fields 661 2003, pp. 159–170
Ferellec, J.-F.; McDowell, G.R.: A method to model realistic particle shape and inertia in DEM. Granul. Matter 12(5), 459–467 (2010)
Cundall, P.A.: A computer model for simulating progressive, large-scale movement in blocky rock system. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Rock Mechanics (1971)
Cundall, P.A.: A Computer model for rock mass behavior using interactive graphics for the input and output of geometrical data. In: Minnesota Univ Minneapolis Dept of Civil and Mining Engineering, (1974)
Strack, O.; Cundall, P.A.: The distinct element method as a tool for research in granular media. University of Minnesota, Department of Civil and Mineral Engineering (1978)
Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D.: A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Geotechnique 29(1), 47–65 (1979)
Bowa, V.M.; Xia, Y.: Stability analyses of jointed rock slopes with counter-tilted failure surface subjected to block toppling failure mechanisms. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(10), 5315–5331 (2018)
Lu, Z.; Yao, A.; Su, A.; Ren, X.; Liu, Q.; Dong, S.: Re-recognizing the impact of particle shape on physical and mechanical properties of sandy soils: a numerical study. Eng. Geol. 253, 36–46 (2019)
Gong, J.; Nie, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, X.: Exploring the effects of particle shape and content of fines on the shear behavior of sand-fines mixtures via the DEM. Comput. Geotech. 106, 161–176 (2019)
Cho, G.-C.; Dodds, J.; Santamarina, J.C.: Particle shape effects on packing density, stiffness, and strength: natural and crushed sands. Geotech. Geoenviron. 132(5), 591–602 (2006)
Zhou, W.; Yang, L.; Ma, G.; Xu, K.; Lai, Z.; Chang, X.: DEM modeling of shear bands in crushable and irregularly shaped granular materials. Granul. Matter 19(2), 25 (2017)
Azéma, E.; Estrada, N.; Radjai, F.: Nonlinear effects of particle shape angularity in sheared granular media. Phys. Rev. E 86(4), 041301 (2012)
Ng, T.T.: Particle shape effect on macro-and micro-behaviors of monodisperse ellipsoids. Powder Technol. 33(4), 511–527 (2009)
Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Chan, D.H.; Taslagyan, K.A.: DEM simulation of shear vibrational fluidization of granular material. Granul. Matter 20(4), (2018)
Xu, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Du, J.; Hu, D.: 2D DEM simulation of particle mixing in rotating drum: a parametric study. Particuology. 8(02), 141–149 (2010)
Wang, X.; Tian, K.; Su, D.; Zhao, J.: Superellipsoid-based study on reproducing 3D particle geometry from 2D projections. Comput. Geotech. 114 (2019)
Owen, P.J.; Cleary, P.W.; Meriaux, C.: Quasi-static fall of planar granular columns: comparison of 2D and 3D discrete element modelling with laboratory experiments. Geomechanics and Geoengineering. 4(1) (2009)
Z Zhou, L.; Chu, X.; Xu, Y.: DEM investigation on characteristics of rolling resistance for modelling particle shape. In: EPJ Web of Conferences 2017, p. 05005. EDP Sciences
Wensrich, C.M.; Katterfeld, A.: Rolling friction as a technique for modelling particle shape in DEM. Powder Technol. 217, 409–417 (2012)
Cox, M.R.; Budhu, M.: A practical approach to grain shape quantification. Eng. Geol. 96(1–2), 1–16 (2008)
Liu, Q.; Lehane, B.: The influence of particle shape on the (centrifuge) cone penetration test (CPT) end resistance in uniformly graded granular soils. Geotechnique 62(11), 973–984 (2012)
Krumbein, W.C.; Sloss, L.L.: Stratigraphy and sedimentation, vol. 71. vol. 5. LWW, (1951)
Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Mechanics, S.: Discrete element analysis for size effects of coarse-grained soils. Rock. Soil. Mech 30(s1), 287–292 (2009)
Palmeira, E.M.; Mechanics, G.W.E.: Scale effects in direct shear tests on sand : Proc 12th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Rio de Janeiro, 13–18 August 1989 V1, P739–742. Publ Rotterdam: A A Balkema, 1989. (1991)
Li, Y.: Effects of particle shape and size distribution on the shear strength behavior of composite soils. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 72(3), 371–381 (2013)
Islam, M.N.; Siddika, A.; Hossain, B.; Rahman, A.; Asad, A.: Effect of particle size on the shear strengthen behaviour of sands. Aust. Geomech. J. (2011)
Vangla, P.; Latha, G.M.: Influence of particle size on the friction and interfacial shear strength of sands of similar morphology. Int. J. Geosynthetics Ground Eng 1(1), 1–12 (2015)
Xiaohui, C.: Discrete element analysis for size effects of coarse-grained soils. Rock. Soil. Mech. (2009)
Wang, J.; Gutierrez, M.: Discrete element simulations of direct shear specimen scale effects. Géotechnique 60(5), 395–409 (2010)
Winters, K.E.; Taylor, O.-D.S.; Berry, W.W.; Rowland, W.R.; Antwine, M.D.: Cohesionless soil fabric and shear strength at low confining pressures. Geo-Chicago 2016, 212–221 (2016)
Lehane, B.; Liu, Q.: Measurement of shearing characteristics of granular materials at low stress levels in a shear box. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 31(1), 329–336 (2013)
Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Kang, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.: Estimation of surface shear strength of undisturbed soils in the eastern part of northern China’s wind erosion area. Soil Tillage Res. 178, 1–10 (2018)
Taylor, O.D.S.; Cunningham, A.L.; Walker, R.E.; McKenna, M.H.; Martin, K.E.; Kinnebrew, P.G.: The behaviour of near-surface soils through ultrasonic near-surface inundation testing. Near Surf. Geophys. 17(4), 331–344 (2019)
Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Harbottle, M.J.: Exploring the effect of biopolymers in near-surface soils using xanthan gum-modified sand under shear. Can. Geotech. J. (2019)
Kim, J.; Dai, S.; Jang, J.; Waite, W.F.; Collett, T.S.; Kumar, P.: Compressibility and particle crushing of Krishna-Godavari Basin sediments from offshore India: Implications for gas production from deep-water gas hydrate deposits. Mar. Pet. Geol. 108, 697–704 (2019)
Danesh, A.; Mirghasemi, A.A.; Palassi, M.: Evaluation of particle shape on direct shear mechanical behavior of ballast assembly using discrete element method (DEM). Transp. Geotech. 100357 (2020)
Han, B.; Ling, J.; Shu, X.; Gong, H.; Huang, B.: Laboratory investigation of particle size effects on the shear behavior of aggregate-geogrid interface. Constr. Build Mater. 158, 1015–1025 (2018)
C.P. A, S.O.D.L.: Particle Flow Code in 2 Dimensions, Itasca Consult. Group, Inc (1999). http://www.itascag.com
Oda, M.; Konishi, J.; Nemat-Nasser, S.: Experimental micromechanical evaluation of strength of granular materials: effects of particle rolling. Mech. Mater. 1(4), 269–283 (1982)
Nie, Z.; Fang, C.; Gong, J.; Liang, Z.: DEM study on the effect of roundness on the shear behaviour of granular materials. Comput. Geotech. 121, 103457 (2020)
Alhashemi, H.M.B.; Alamoudi, O.S.B.: A review on the angle of repose of granular materials. Powder Technol. 330, 397–417 (2018)
Thornton, C.: Numerical simulations of deviatoric shear deformation of granular media. Géotechnique 50(1), 43–53 (2000)
Barnett, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Karim, M.R.; Nguyen, H.B.K.: Influence of Particle Rolling and Rotation on the Shearing Response of Clean Sand. In: Geo-Congress 2019: Geotechnical Materials, Modeling, and Testing 2019, pp. 30–39. American Society of Civil Engineers Reston, VA
Arthur, J.R.F.; Menzies, B.K.: Inherent anisotropy in a sand. Géotechnique 22(1), 115–128 (1972)
Hosseininia, E.S.: Discrete element modeling of inherently anisotropic granular assemblies with polygonal particles. Particuology 10(5), 542–552 (2012)
Zhao, S.; Zhou, X.: Effects of particle asphericity on the macro- and micro-mechanical behaviors of granular assemblies. Granul. Matter 19(2), 38 (2017)
Fu, P.; Dafalias, Y.F.: Relationship between void- and contact normal-based fabric tensors for 2D idealized granular materials. Int J Solids Struct 63(15), 68–81 (2015)
Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, X.: DEM investigation of angle of repose for super-ellipsoidal particles. Particuology (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 41402260) and by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (No.2020019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Z., Chen, C. & Wu, L. Numerical Investigation of Particle Shape Effect on Sand Shear Strength. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 10585–10595 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05430-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05430-z