Abstract
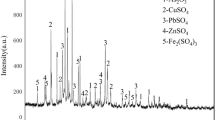
In this study, the Ag and Cu evolution in the sintering dust was extracted by chlorination roasting process, and the mechanism of the process was analyzed by atomic absorption spectroscopy, X-ray fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry. In addition, in order to better understand the chlorination roasting process, the mechanism and thermodynamics of roasting reaction were analyzed. The recovery of Ag and Cu reached 99.05% and 59.32%, respectively, under the conditions of roasting temperature of 1423 K, holding time of 60 min, and the air flow rate of 400 L/h. Thermodynamic analysis showed that MgO and SiO2 could promote the production of Cl2 and HCl and that CuO could be chlorinated by Cl2 at 1421 K, but it was not amenable for HCl. Compared with CuO, Ag was more easily chlorinated at high temperatures. Experimental results indicate that silver and copper can be efficiently extracted, indicating that the chlorination roasting is a promising pyrometallurgical treatment for the recycling of sintering dust.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tao, H.C.; Gao, Z.Y.; Ding, H., et al.: Recovery of silver from silver(I)-containing solutions in bioelectrochemical reactors. Biores. Technol. 111, 92–97 (2012)
Li, H.Y.; Li, S.W.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Zhang, L.B.; Yin, S.H.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.M.: Efficient cleaning extraction of silver from spent symbiosis lead-zinc mine assisted by ultrasound in sodium thiosulfate system. Ultrason. Sonochem. 49, 118–127 (2018)
Das, N.: Recovery of precious metals through biosorption—a review. Hydrometallurgy 103, 180–189 (2010)
Kołodzziej, B.; Adamski, Z.: A ferric chloride hydrometallurgical process for recovery of silver from electronic scrap materials. Hydrometallurgy 12, 117–127 (1984)
Li, H.Y.; Zhang, L.B.; Xie, H.M.; Yin, S.H.; Peng, J.H.; Li, S.W.; Yang, K.; Zhu, F.: Ultrasound-assisted silver leaching process for cleaner production. JOM-US 72, 766–773 (2019)
Koseoglu, H.; Kitis, M.: The recovery of silver from mining wastewaters using hybrid cyanidation and high-pressure membrane process. Miner. Eng. 22, 440–444 (2009)
Baláž, P.; Ficeriová, J.; Leon, C.V.: Silver leaching from a mechanochemically pretreated complex sulfide concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 70, 113–119 (2003)
Zhang, E.D.; Chang, J.; Zhou, J.W. et al.: Optimization of silver leaching using ultrasonic technology from sintering dust by response surface methodology. Chin. J. Process Eng. 16, 758–766 (2016)
Cui, P.; Guo, Z.C.; Zhang, F.L.: Existing state of potassium chloride in agglomerated sintering dust and its water leaching kinetics. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 21, 1847–1854 (2011)
Fu, Z.; Mei, Z.; Na, L., et al.: Recovery of lead in sintering electric dust from steel metallurgical and prepartion of lead oxide. J. Cent. South. Univ. Sci. Technol. 10, 3 (2016)
Zhan, G.; Guo, Z.C.: Water leaching kinetics and recovery of potassium salt from sintering dust. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 23, 3770–3779 (2013)
Wu, B.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Z., et al.: Recovery of silver, copper and zinc in sintering filtrated dust from iron and steel metallurgical process. Chin. J. Rare. Metal. 39, 1109–1114 (2015)
Guo, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wan, D. et al.: New progress in resources utilization of sintering dust. Sinter. Pellet. 39, 56–59 (2014)
Zhan, G.; Guo, Z.C.: Preparation of potassium salt with joint production of spherical calcium carbonate from sintering dust. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 25, 628–639 (2015)
Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, H., et al.: Separation and recovery of potassium chloride from sinter dust of a steel plant. Ironmak. Steelmak. 46, 193–198 (2019)
Peng, C.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.: Separation and recovery of potassium chloride from sintering dust of ironmaking works. ISIJ. Int. 49, 735–742 (2009)
Zhan, G.; Guo, Z.: Basic properties of sintering dust from iron and steel plant and potassium recovery. J. Environ. Sci (China) 25, 1226–1234 (2013)
Brocchi, E.A.; Moura, F.J.: Chlorination methods applied to recover refractory metals from tin slags. Miner. Eng. 21, 150–156 (2018)
Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Koppala, S., et al.: Extraction of gold and silver in the selective chlorination roasting process of cyanidation tailing. Sep. Sci. Technol. 53, 458–466 (2018)
Li, H.; Ma, A.; Srinivasakannan, C., et al.: Investigation on the recovery of gold and silver from cyanide tailings using chlorination roasting process. J. Alloys Compd. 763, 241–249 (2018)
Zhu, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, H., et al.: Gold extraction from cyanidation tailing using microwave chlorination roasting method. Metals-basel. 8, 1025 (2018)
Hao, Z.: Industrial test of spraying the solution of calcium chloride to sinter at Shaoguan Steel. Iron Mak. 18, 20–22 (1999)
Zhao, Y.; Stucki, S.; Ludwig, C., et al.: Impact of moisture on volatility of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incinerated in a laboratory scale simulated incinerator. Waste Manag. 24, 581–587 (2004)
Fraißler, G.; Jöller, M.; Brunner, T., et al.: Influence of dry and humid gaseous atmosphere on the thermal decomposition of calcium chloride and its impact on the remove of heavy metals by chlorination. Chem. Eng. Process. (Process Intensification) 48, 380–388 (2009)
Lin, G.; Hu, T.; Liu, C., et al.: Dielectric characterizations and microwave heating behavior of zinc compound in microwave field. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 2329–2338 (2018)
Liu, C.; Peng, J.; Li, Z., et al.: Removal of F and Cl from zinc oxide fume from fuming furnace by microwave roasting. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 42, 1413–1418 (2017)
Li, Z.Y.; Wang, W.W.; Yue, K., et al.: High-temperature chlorination of gold with transformation of iron phase. Rare Met. 35, 881–886 (2016)
Li, H.Y.; Long, H.L.; Zhang, L.B.; Yin, S.H.; Li, S.W.; Zhu, F.; Xie, H.M.: Effectiveness of microwave-assisted thermal treatment in the extraction of gold in cyanide tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 384, 121456 (2019)
Liu, J.; Wen, S.; Chen, Y., et al.: Process optimization and reaction mechanism of removing copper from an Fe-rich pyrite cinder using chlorination roasting. J. Iron. Steel. Res. Int. 20, 20–26 (2013)
Li, S.; Ren, X.; Srinivasakannan, C., et al.: Hydrogen sulfide removal from copper smelting contaminated acid using rotating packed bed. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 3557–3564 (2018)
Li, K.; Chen, G.; Chen, J., et al.: Microwave pyrolysis of walnut shell for reduction process of low-grade pyrolusite. Bioresour. Technol. 291, 121838 (2019)
Long, H.; Li, H.; Pei, J.; Srinivasakannan, C., et al.: Cleaner recovery of multiple valuable metals from cyanide tailings via chlorination roasting. Sep. Sci. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2020.1812650
Navarro, R.C.S.; Vasconcellos, E.T.; Brocchi, E.A.: Study on the thermodynamic viability of NiO and CuO chlorination with C2Cl4 at high temperatures. Thermochim. Acta 647, 22–29 (2017)
Liu, W.R.; Li, X.H.; Hu, Q.Y., et al.: Pretreatment study on chloridizing segregation and magnetic separation of low-grade nickel laterites. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 20, s82–s86 (2010)
Broqueville, A.D.; Wilde, J.D.: Numerical investigation of gas-solid heat transfer in rotating fluidized beds in a static geometry. Chem. Eng. Sci. 64, 1232–1248 (2009)
Li, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y., et al.: Chlorination roasting of laterite using salt chloride. Int. J. Miner. Process. 148, 23–31 (2016)
Acknowledgements
Financial aid from the following programs is gratefully acknowledged: Yunan Ten Thousand Talents Plan Young & Elite Talents Project (Grant Number YNWR-QNBJ-2018-112), the Liupanshui Key Laboratory of Metallurgical Energy Saving, Environmental Protection and Recycling Economy (52020-2018-0304), and the Science and Technology Innovation Group of Liupanshui Normol University (LPSSYKJTD201801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, H., Chen, K., Xu, C. et al. Efficient Recycling of Silver and Copper from Sintering Dust by Chlorination Roasting Process. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 6663–6672 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05291-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05291-y