Abstract
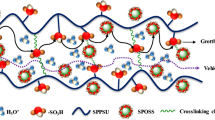
A Composite proton exchange membrane consists of octaphenyl polyhedral silsesquioxane (POSS) has been incorporated into a highly sulfonated polyphenylsulfone (SPPSU) for potential use in fuel cell applications. The effect of modified POSS by functionalization with sulfonic acid groups (SPOSS) addition on physicochemical properties, mechanical strength, and proton conductivity of the SPPSU is examined. Results revealed that the incorporation of POSS and SPOSS has significantly improved the mechanical strength and conductivity of the SPPSU composite membranes. SPPSU-POSS composite membrane shows tough and ductile features. Meanwhile, the SPPSU-SPOSS composite membrane exhibits mechanically lower strength but greater in flexibility as compared to SPPSU-POSS composite membrane. As per expectation, the proton conductivity of the SPPSU-SPOSS composite membrane is significantly improved compared to SPPSU-POSS composite membrane according to its relatively higher water uptake value. Based on the obtained results, it has been suggested that POSS has enhanced the proton conductivity and mechanical strength of the highly sulfonated PPSU based membrane desirable to be served as a proton exchange membrane in fuel cell application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kyu, T.; Nazir, N.A.: Supramolecules impregnated proton electrolyte membranes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2(1), 132–138, 2013
Dodds, P.E.; Staffell, L.; Hawkes, A.D.; Li, F.; Grunewald, P.; McDowall, W.; Ekins, P.: Hydrogen and fuel cell technologies for heating: a review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 40(5), 2065–2083, 2015
Kahraman, H.; Coban, A.: Performance improvement of a single pem fuel cell using an innovative flow field design methodology. Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04368-y.
Sun, X.; Simonsen, S.C.; Norby, T.; Chatzitakis, A.: Composite membranes for high temperature PEM fuel cells and electrolysers: a critical review. Membranes 9(7), 83, 2019
Meemuk, C.; Chirachanchai, S.: Stable and effective proton exchange membrane formation via cross-linking the polymeric proton donor and proton acceptorin layer-by-layer structure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43(13), 6701–6710, 2018
Assumma, L.; Iojoiu, C.; Ari, A.; Cointeaux, L.; Sanchez, J.-Y.: Polyethersulfone containing sulfonimide groups as proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39, 2740–2750, 2014
Muthumeenal, A.; Rethinam, A.J.; Nagendran, A.: Sulfonated polyethersulfone based composite membranes containing heteropolyacids laminated with polypyrrole for electrochemical energy. Solid State Ionics 296, 106–113, 2016
Shin, D.W.; Kang, N.R.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, Y.M.: Proton conducting, composite sulfonated polymer membrane for medium temperature and low relative humidity fuel cells. J. Power Sources 262, 162–168, 2014
Ahmadian-Alam, L.; Mahdavi, H.: A novel polysulfone-based ternary nanocomposite membrane consisting of metal organic framework and silica nanoparticles: as proton exchange membrane for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Renew Energy 126, 630–639, 2018
Kim, J.-D.; Ghil, L.-J.: Annealing Effect of Highly Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone Polymer. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41(27), 11794–11800, 2016
Elakkiya, S.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Venkatesh, K.; Kweon, J.: Enhancement of fuel cell properties in polyethersulfone and sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membranes using metal oxide nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43(47), 21750–21759, 2018
Hamedani, M.P.; Ataei, S.M.: Effect of sulfonation degree on molecular weight, thermal stability, and proton conductivity of poly(arylene ether sulfone)s membrane. Des. Monomers Polym. 20(1), 54–65, 2016
Ru, C.; Gu, Y.; Na, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.: Preparation of a cross-linked sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) proton exchange membrane with enhanced proton conductivity and methanol resistance by introducing an ionic liquid-impregnated metal organic framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 11(35), 31899–31908, 2019
Dhanapal, D.; Xiao, M.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y.: A review on sulfonated polymer composite/organic-inorganic hybrid membranes to address methanol barrier issue for methanol fuel cells. Nanomaterials 9(5), 668, 2019
Janeta, M.; Szafert, S.: Synthesis, characterization and thermal properties of T8 type amido-POSS with p-halophenyl end-group. J. Organomet. Chem. 847, 173–183, 2017
Kim, S.-W.; Choi, S.-Y.; Rhee, H.-W.: Sulfonated poly(etheretherketone) based nanocomposite membranes containing POSS-SA for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFC). J. Membr. Sci. 566, 69–76, 2018
Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Gong, C.; Ding, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Bu, W.: Polydopamine-modified sulfonated polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane: an appealing nanofiller to address the trade-off between conductivity and stabilities for proton exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 596, 117734, 2020
Liu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Ni, N.; Luo, F.; Zhang, R.; Hu, S.; Bao, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, F.; Li, X.: Novel octopus shaped organic-inorganic composite membranes for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41(36), 16160–16166, 2016
Kaneko, Y.; Toyodome, H.; Mizumo, T.; Shikinaka, K.; Iyi, N.: Preparation of a sulfo-group-containing rod-like polysilsesquioxane with a hexagonally stacked structure and its proton conductivity. Chem. A Eur. J. 20, 9394–9399, 2014
Liu, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhao, J.; Lu, L.; Muhammad, Y.; Lan, P.; He, R.; Zou, Y.; Tong, Z.: Synthesis and application of PDMS/OP-POSS membrane for the pervaporative recovery of n-butyl acetate and ethyl acetate from aqueous media. J. Membr. Sci. 591, 117324, 2019
Ye, Y.S.; Rick, J.; Hwang, B.-J.: Water soluble polymers as proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. Polymers 4, 913–963, 2012
Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N.: Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: a critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 1, 2–30, 2019
Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Khan, A.A.: Solid polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications-a review. J. Membr. Sci. 259, 10–26, 2005
Rhim, J.W.; Park, B.; Lee, C.S.; Jun, J.H.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, Y.M.: Crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes containing sulfonic acid group: proton and methanol transport through membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 238, 143–151, 2014
Kumari, M.; Sodaye, H.S.; Sen, D.; Bindal, R.C.: Properties and morphology studies of proton exchange membranes based on cross-linked sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) for electrochemical application: effect of cross-linker chain length. Solid State Ion. 316, 75–84, 2018
Yen, Y.C.; Ye, Y.S.; Cheng, C.C.; Lu, C.H.; Tsai, L.D.; Huang, J.M.; Chang, F.C.: The effect of sulfonic acid groups within a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane containing cross-linked proton exchange membrane. Polymer 51, 84–91, 2010
Subianto, S.; Mistry, M.K.; Choudhury, N.T.; Dutta, N.K.; Knott, R.: Composite polymer electrolyte containing ionic liquid and functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes for anhydrous PEM applications. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1(6), 1173–1182, 2009
Wong, C.Y.; Wong, W.Y.; Loh, K.S.; Daud, W.R.W.; Lim, K.L.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R.: Development of poly(vinyl alcohol)-based polymers as proton exchange membranes and challenges in fuel cell application: a review. Polym. Rev., 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2019.1641514.
Zhang, Y.; Kim, J.-D.; Miyatake, K.: Effect of thermal crosslinking on the properties of sulfonated poly(phenylene sulfone)s as proton conductive membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 44218, 1–8, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.44218.
Zhai, S.; Dai, W.; Lin, J.; He, S.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.: Enhanced proton conductivity in sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membranes by incorporating sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. Polymers 11(203), 1–11, 2019
Martos, A.M.; Biasizzo, M.; Trotta, F.; del Rio, C.; Varez, A.; Levenfeld, B.: Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated PEEK-WC-PES copolymers for fuel cell proton exchange membrane application. Eur. Polymer J. 93, 390–402, 2017
Gupta, D.; Madhukar, A.; Choudhary, V.: Effect of functionality of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) on the properties of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) based hybrid nanocomposite proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 38, 12817–12829, 2013
Brijmohan, S.B.; Swier, S.; Weiss, R.A.; Shaw, M.T.: Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked sulfonated polystyrene nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44, 8039–8045, 2005
Xu, C.; Cao, Y.; Kumar, R.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Scott, K.: A Polybenzimidazole/sulfonated graphite oxide composite membrane for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 11359, 2011
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express gratitude to the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) and Research Management Centre (RMC), UTM for supporting the research management activities specifically under project Grant of R. J130000.7851.4L880 MRUN 4.4: Integrated Energy and Water Generation System from Direct Ethanol Fuel Cell (DEFC) Technology. The authors would also like to acknowledge supported by the International Cooperative Graduate School (ICGS) Fellowship under the “Universiti Teknologi Malaysia-NIMS Cooperative Graduate School Program” to conduct research in National Institute of Materials Science (NIMS), Tsukuba, Japan. This work also was supported by the MEXT Program for Development of Environmental Technology using Nanotechnology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamad Nor, N.A., Jaafar, J., Kim, JD. et al. Effect of Polyhedral Silsesquioxane Functionalized Sulfonic Acid Groups Incorporated Into Highly Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone as Proton-Conducting Membrane. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 6399–6407 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05088-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05088-z