Abstract
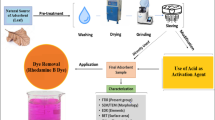
The present work reports a combination approach involving adsorption followed by ultrasonic degradation for the treatment of Rhodamine 6G (R6G) containing wastewater. The main benefit of the combination treatment approach is that adsorption concentrates the effluent which is treated in the subsequent step of ultrasonic degradation in a cost-effective manner based on lower treatment volumes. In the adsorptive removal, INDION 225Na Resin has been used as adsorbent. A study into the effect of different adsorption parameters revealed that the optimum contact time required for the equilibrium was 20 min. It was also established that the optimum values of pH and resin loading for maximum dye removal as 77.6% were 12 and 6 g L−1, respectively. Analysis of different adsorption isotherm models for equilibrium established that the Langmuir model is the best-fitted model with the correlation coefficient value (R2) as 0.99. Similarly, kinetic data analysis revealed that pseudo-second-order model explained the system precisely based on a higher value of R2. For the case of ultrasonic degradation, it was established that a pH of 12 and a temperature of 50 °C were the best treatment conditions. Overall, it was demonstrated that the proposed combination of adsorption and sonication is an efficient approach for the treatment of R6G containing wastewater.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Senturk, H.B.; Ozdes, D.; Duran, C.: Biosorption of Rhodamine 6G from aqueous solutions onto almond shell (Prunusdulcis) as a low cost biosorbent. Desalination 252, 81–87 (2010)
Laasri, L.; Elamrani, M.K.; Cherkaoui, O.: Removal of two cationic dyes from a textile effluent by filtration–adsorption on wood sawdust. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 14(4), 237–240 (2007)
McKay, G.; Otterburn, M.S.; Aga, D.A.: Fullers earth and fired clay as adsorbent for dye stuffs, equilibrium and rate constants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 24(3), 307–322 (1985)
Hameed, B.H.; Din, A.T.M.; Ahmad, A.L.: Adsorption of methylene blue onto bamboo based activated carbon: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 14(3), 819–825 (2007)
Hamdaoui, O.: Dynamic sorption of methylene blue by cedar sawdust and crushed brick in fixed bed columns. J. Hazard. Mater. 38(2), 293–303 (2006)
Hameed, B.H.; El-Khaiary, M.I.: Removal of basic dye from aqueous medium using a novel agricultural waste material: pumpkin seed hull. J. Hazard. Mater. 155(3), 601–609 (2008)
Vilar, V.J.P.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Boaventura, R.A.R.: Methylene blue adsorption by algal biomass based materials: biosorbents characterization and process behavior. J. Hazard. Mater. 147(1–2), 120–132 (2007)
Gemeay, A.H.: Adsorption characteristics and the kinetics of the cation exchange of rhodamine-6G with Na+-montmorillonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 251(2), 235–241 (2002)
Pakhale, V.D.; Gogate, P.R.: Removal of Calcium and Magnesium from Wastewater Using ion Exchange Resins. Novel Water Treatment and Separation Methods, pp. 125–140. Apple Academic Press Inc., Waretown (2017)
Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B.: A review of imperative technologies for waste water treatment II. Hybrid methods. Adv. Environ. Res. 8, 553–597 (2004)
Banerjee, B.; Khode, A.; Patil, A.; Mohod, A.V.; Gogate, P.R.: Sonochemical decolorization of wastewaters containing rhodamine 6G using ultrasonic bath at an operating capacity of 2L. Desalin. Water Treat. J. 52, 1378–1387 (2013)
Han, R.; Wang, Y.; Han, P.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.: Removal ofmethylene blue fromaqueous solution by chaff in batch mode. J. Hazard. Mater. 137(1), 550–557 (2006)
Daware, G.B.; Gogate, P.R.: Adsorption of 3-Aminopyridine (3AP) from aqueous solution using sugarcane bagasse activated carbon (SBAC). Environ. Technol. Innov. 19, 100921 (2020)
Singare, P.U.; Lokhande, R.S.; Madyal, R.S.: Thermal degradation studies of some strongly acidic cation exchange resins. Open J. Phys. Chem. 1, 45–54 (2011)
Vishwanathan, N.; Meenakshi, S.: Role of metal ion concentration in ion exchange resin on the selectivity of fluoride. J. Hazard. Mater. 162, 920–930 (2009)
Bashir, M., Aziz, H., Yusoff, M.: Recycling of the exhausted cation exchange resin for stabilized landfill leaching treatment. In: The 4th International Engineering Conference-Towards Engineering of 21st Century, 1–11 (2012)
Mane, V.S.; Babu, P.V.: Studies on the adsorption of Brilliant green dye from aqueous solution onto low-cost NaOH treated saw Dust. Desalination 273, 321–329 (2011)
Jain, S.N.; Gogate, P.R.: Acid Blue 113 removal from aqueous solution using novel biosorbent based on NaOH treated and surfactant modified fallen leaves of Prunus Dulcis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 3384–3394 (2017)
Chowdhury, S.; Saha, P.: Sea shell powder as a new adsorbent to remove Basic Green 4 (Malachite green) from aqueous solutions: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 164, 168–177 (2010)
Tsai, W.T.; Hsub, H.C.; Su, T.Y.; Lin, K.Y.; Lin, C.M.: Removal of basic dye (methylene blue) from wastewaters utilizing beer brewery waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 154(1–3), 73–78 (2008)
Han, R.; Zou, W.; Yu, W.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.: Biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by fallen phoenix tree’s leaves. J. Hazard. Mater. 141(1), 156–162 (2007)
Langmuir, I.: The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40, 1361–1403 (1918)
Ahmad, A.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Aziz, N.: Adsorption of direct dye on palm ash: kinetic and equilibrium modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 141(1), 70–76 (2007)
Hameed, B.H.; El-Khaiary, M.I.: Sorption kinetics and isotherm studies of a cationic dye using agricultural waste: broad bean peels. J. Hazard. Mater. 154(1–3), 639–648 (2008)
Khattri, S.D.; Singh, M.K.: Color removal from synthetic dye wastewater using a biosorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut. 120(3–4), 283–294 (2000)
Freundlich, H.; Uber, M.F.: Dye adsorption in losungen. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 57, 385–470 (1906)
Ju, D.J.; Byun, I.G.; Park, J.J.; Lee, C.H.; Ahn, G.H.; Park, T.J.: Biosorption of a reactive dye (Rhodamine-B) from an aqueous solution using dried biomass of activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 7971–7975 (2008)
Lagergren, S.: About the theory of so called adsorption of soluble substances. Ksver Veterskapsakad Hadl. 24, 1–6 (1898)
Demirbas, E.; Kobya, M.M.; Sulak, T.: Adsorption kinetics of a basic dye from aqueous solutions onto apricot stone activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 99(13), 5368–5373 (2008)
Alkan, M.; Dogan, M.; Turhan, Y.; Demirbas, O.; Turan, P.: Adsorption kinetics and mechanism of maxilon blue 5G dye on sepiolite from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 139, 213–223 (2008)
Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G.: Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 76(4), 183–191 (1998)
Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G.: Pseudo Second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Bulut, E.; Ozacar, M.; Şengil, I.A.: Adsorption of malachite green onto bentonite: equilibrium and kinetic studies and process design. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 115(3), 234–246 (2008)
Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C.: Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 89, 31–60 (1963)
Menendez, A.; Lombrana, J.I.; Rodriguez, C.; Contreras, S.; Esplugas, S.: Oxidant dosage and pH effect in the decolorizationby ozone model (Rhodamine 6G) dye wastewaters. Univ. Delpaisvasco J. 4, 1–10 (2005)
Kansal, S.K.; Singh, M.; Sud, D.: Studies on photodegradation of two commercial dyes in aqueous phase using different photocatalysts. J. Hazard. Mat. 141, 581–590 (2007)
Vichare, N.P.; Senthilkumar, P.; Moholkar, V.S.; Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B.: Energyanalysis in acoustic cavitation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 39, 1480–1486 (2000)
Golash, N.; Gogate, P.R.: Degradation of dichlorvos containing wastewaters using sonochemical reactors. Ultrason. Sonochem. 19, 1051–1060 (2012)
Elsayed, M.A.: Successive advanced oxidation of pyridine by ultrasonic irradiation: effect of additives and kinetic study, Desal. Water Treat. 53, 57–65 (2015)
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to University Grants Commission, India for the facilities under the scheme of UGC Networking Resource Centre at ICT Mumbai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pakhale, V.D., Gogate, P.R. Removal of Rhodamine 6G from Industrial Wastewater Using Combination Approach of Adsorption Followed by Sonication. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 6473–6484 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05074-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05074-5