Abstract
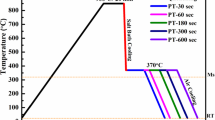
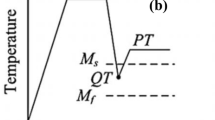
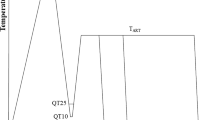
Herein, an attempt has been made to investigate effect of C and Mn partitioning during quenching and partitioning heat-treatment process on microstructure, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of experimental 3 wt% Mn steel. The quenching and partitioning heat-treatment process was applied to the experimental steel with varying partitioning time periods ranging from 15 to 120 s at a constant partitioning temperature of 425 °C. The partitioning time period of 15 s resulted in a high volume fraction of supersaturated lath martensite with a small volume fraction of retained austenite. With increasing partitioning time period to 45–60 s, diffusion of C and Mn from martensite to retained austenite occurred resulting in the formation of decreased volume fraction of martensite phase with a reduced carbon and increased volume fraction of retained austenite phase with increased carbon. Partitioning for 90 s produced a moderate volume fraction of both lath martensite and retained austenite phases with nucleation of secondary phase, epsilon carbides. This phase transformation provided an optimum combination of 21% improved Vickers hardness and threefold improved impact toughness compared to as-received steel. Electrochemical properties of quenched and partitioned 3 wt% Mn steel were also evaluated in a 3 wt% NaCl solution. The highest corrosion resistance was achieved after prolonged partitioning of 120 s, whereas slightly low corrosion resistance was achieved after partitioning of 90 s.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seo, E.J.; Cho, L.; Kim, J.K.; Mola, J.; Zhao, L.; Lee, S.; Cooman, B.C.D.: Focused ion beam-induced displacive phase transformation from austenite to martensite during fabrication of quenched and partitioned steel micro-pillar. J. Alloys Compd. 812, 152061 (2020)
Ariza-Echeverri, E.A.; Masoumi, M.; Nishikawa, A.S.; Mesa, D.H.; Marquez-Rossy, A.E.; Tschiptschin, A.P.: Development of a new generation of quench and partitioning steels: influence of processing parameters on texture, nanoindentation, and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 186, 108329 (2020)
Peng, F.; Xu, Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.: The relationships of microstructure mechanical properties in quenching and partitioning (Q & P) steel accompanied with microalloyed carbide precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 728, 247–258 (2018)
Dai, Z.; Ding, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.: Elucidating the effect of Mn partitioning on interface migration and carbon partitioning during quenching and partitioning of the Fe–C–Mn–Si steels: modeling and experiments. Acta Mater. 144, 666–678 (2018)
Allain, S.Y.P.; Geandier, G.; Hell, J.C.; Soler, M.; Danoix, F.; Gouné, M.: In-situ investigation of quenching and partitioning by high energy X-ray diffraction experiments. Scr. Mater. 131, 15–18 (2017)
Inam, A.; Ishtiaq, M.; Hafeez, A.; Nawaz, M.; Rizwan, M.; Hassan, M.H.: Quenching and partitioning of AISI 4340 steel. J. Fac. Eng. Technol. 24, 47–56 (2017)
Akbary, F.H.; Sietsma, J.; Petrov, R.H.; Miyamoto, G.; Furuhara, T.; Santofimia, M.J.: A quantitative investigation of the effect of Mn segregation on microstructural properties of quenching and partitioning steels. Scr. Mater. 137, 27–30 (2017)
Huyghe, P.; Malet, L.; Caruso, M.; Georges, C.; Godet, S.: On the relationship between the multiphase microstructure and mechanical properties of a 0.2 C quenched and partitioned steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 701, 254–263 (2017)
Wang, M.M.; Hell, J.C.; Tasan, C.C.: Martensite size effects on damage in quenching and partitioning steels. Scr. Mater. 138, 1–5 (2017)
Moor, E.D.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.B.: Effect of carbon and manganese on the quenching and partitioning response of CMnSi steels. ISIJ Int. 51, 137–144 (2011)
Yaqiang, T.; Wang, L.; Xiaoping, Z.; Yingli, W.; Jinying, S.; Liansheng, C.: Application of alloy elements in quenching and partitioning steel: an overview. Mater. Rep. 33, 1109–1118 (2019)
Cai, H.L.; Chen, P.; Oh, J.K.; Cho, Y.R.; Wu, D.; Yi, H.L.: Quenching and flash-partitioning enables austenite stabilization during press-hardening processing. Scr. Mater. 178, 77–81 (2020)
Wu, J.; Bao, L.; Gu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.: The strengthening and toughening mechanism of dual martensite in quenching-partitioning steels. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 772, 138765 (2020)
Pierce, D.T.; Coughlin, D.R.; Clarke, K.D.; Moor, E.D.; Poplawsky, J.; Williamson, D.L.; Mazumder, B.; Speer, J.G.; Hood, A.; Clarke, A.J.: Microstructural evolution during quenching and partitioning of 0.2C–1.5Mn–1.3Si steels with Cr or Ni additions. Acta Mater. 151, 454–469 (2018)
Wendler, M.; Ullrich, C.; Hauser, M.; Krger, L.; Volkova, O.; Wei, A.; Mola, J.: Quenching and partitioning (Q and P) processing of fully austenitic stainless steels. Acta Mater. 133, 346–355 (2017)
Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Gu, J.; Gu, C.: Corrosion behaviour of a quenched and partitioned medium carbon steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 130, 64–75 (2018)
Kimand, K.; Lee, S.J.: Effect of Ni addition on the mechanical behavior of quenching and partitioning (Q & P) steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 698, 183–190 (2017)
Moor, E.D.; Matlock, D.K.; Speer, J.G.; Merwin, M.J.: Austenite stabilization through manganese enrichment. Scr. Mater. 64, 185–188 (2011)
Ayenampudi, S.; Celada-Casero, C.; Sietsma, J.; Santofimia, M.J.: Microstructure evolution during high-temperature partitioning of a medium-Mn quenching and partitioning steel. Materialia 8, 100492 (2019)
Knijf, D.D.; Santofimia, M.J.; Shi, H.; Bliznuk, V.; Föjer, C.; Petrov, R.; Xu, W.: In situ austenite–martensite interface mobility study during annealing. Acta Mater. 90, 161–168 (2015)
Gouné, M.; Aoued, S.; Danoix, F.; Geandier, G.; Poulon, A.Q.; Hell, J.C.; Soler, M.; Allain, S.Y.P.: Alloying-element interactions with austenite/martensite interface during quenching and partitioning of a model Fe–C–Mn–Si alloy. Scr. Mater. 162, 181–184 (2019)
Seo, E.J.; Cho, L.; Cooman, B.C.D.: Kinetics of the partitioning carbon and substitutional alloying elements during quenching and partitioning (Q&P) processing of medium Mn steel. Acta Mater. 107, 354–365 (2016)
Toji, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Herbig, M.; Choi, P.P.; Raabe, D.: Atomic-scale analysis of carbon partitioning between martensite and austenite by atom probe tomography and correlative transmission electron microscopy. Acta Mater. 65, 215–228 (2014)
Lu, S.Y.; Yao, K.F.; Chen, Y.B.; Wang, M.H.; Chen, N.; Ge, X.Y.: Effect of quenching and partitioning on the microstructure evolution and electrochemical properties of a martensitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 103, 95–104 (2016)
Lu, S.Y.; Yao, K.F.; Chen, Y.B.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, X.; Ge, X.: The effect of tempering temperature on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of a 13 wt.% Cr-type martensitic stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta 165, 45–55 (2015)
Hafeez, M.A.; Farooq, A.: Microstructural, mechanical and tribological investigation of 30CrMnSiNi2A ultra-high strength steel under various tempering temperatures. Mater. Res. Express 5, 016505 (2018)
Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Northwood, D.O.; Liu, Y.: A new empirical formula for the calculation of MS in pure iron super low alloy steels. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 113, 556–562 (2011)
Hafeez, M.A.; Inam, A.; Farooq, A.: Mechanical and corrosion properties of medium carbon low alloy steel after cyclic quenching and tempering heat-treatments. Mater. Res. Express 7, 016553 (2020)
Hafeez, M.A.; Farooq, A.: Effect of quenching baths on microstructure and hardness of AISI1035 steel. Niger. J. Technol. Res. 13, 82–88 (2018)
Inam, A.; Imtiaz, Y.; Hafeez, M.A.; Munir, S.; Ali, Z.; Ishtiaq, M.; Hassan, M.H.; Maqbool, A.; Haider, W.: Effect of tempering time on microstructure, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of quenched–partitioned–tempered advanced high strength steel (AHSS). Mater. Res. Express 6, 126509 (2020)
Chen, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Xu, W.: Correlation of isothermal bainite transformation and austenite stability in quenching and partitioning steels. J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 24, 1095–1103 (2017)
Kong, H.; Chao, Q.; Cai, M.H.; Pavlina, E.J.; Rolfe, B.; Hodgson, P.D.; Beladi, H.: One-step quenching and partitioning treatment of a commercial low silicon boron steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 707, 538–547 (2017)
Nishikawa, A.S.; Santofimia, M.J.; Sietsma, J.; Goldenstein, H.: Influence of bainite reaction on the kinetics of carbon redistribution during the quenching and partitioning process. Acta Mater. 142, 142–151 (2018)
Hafeez, M.A.; Farooq, A.: Effect of heat treatments on the mechanical and electrochemical corrosion behavior of 38CrSi and AISI 4140 steels. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 8, 479–487 (2019)
Hafeez, M.A.; Inam, A.; Arshad, M.A.: Investigation on microstructural, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of water, brine quenched and tempered low carbon steel. Mater. Res. Express 6, 096524 (2019)
Hafeez, M.A.: Effect of microstructural transformation during tempering on mechanical properties of quenched and tempered 38CrSi steel. Mater. Res. Express 6, 086552 (2019)
Hidalgo, J.; Celada-Casero, C.; Santofimia, M.J.: Fracture mechanisms and microstructure in a medium Mn quenching and partitioning steel exhibiting macrosegregation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 754, 766–777 (2019)
Nayak, S.S.; Anumolu, R.; Misra, R.D.K.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.L.: Microstructure–hardness relationship in quenched and partitioned medium-carbon and high-carbon steels containing silicon. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 498, 442–456 (2008)
Roberge, P.R.: Handbook of Corrosion Engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York (2000)
Hafeez, M.A.; Usman, M.; Arshad, M.A.; Umer, M.A.: Nanoindentation-based micro-mechanical and electrochemical properties of quench-hardened, tempered low-carbon steel. Crystals 10, 508 (2020)
Hafeez, M.A.; Inam, A.; Hassan, M.U.; Umer, M.A.; Usman, M.; Hanif, A.: Optimized corrosion performance of AISI 1345 steel in hydrochloric acid through thermo-mechanical cyclic annealing processes. Crystals 10, 265 (2020)
Revie, R.W.; Uhlig, H.H.: Corrosion and Corrosion Control, 4th edn. Wiley, New York (2008)
Hafeez, M.A.: Investigation on mechanical properties and immersion corrosion performance of 0.35% C–10.5% Mn steel processed by austenite reverted transformation (ART) annealing process. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 9, 159–168 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inam, A., Hafeez, M.A., Atif, M. et al. Microstructural, Mechanical, and Electrochemical Properties of Quenched and Partitioned 3 wt% Mn Steel. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 417–423 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04867-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04867-y