Abstract
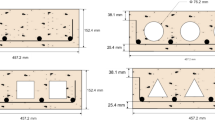
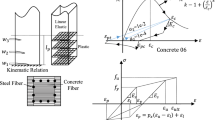
Due to the presence of composite action between steel and concrete, applications of concrete-filled tubular structures have increased rapidly in bridges, high-rise buildings and other infrastructures. In this study, a total of 15 square concrete-filled welded cold-formed steel columns were tested under concentric loading. Failure modes, ultimate strength and ductility of test specimens were analyzed on several parameters, including concrete compressive strength (f ′c = 27, 35 and 44 MPa), cross-sectional slenderness ratio (B/t = 25, 31 and 42) and global slenderness ratio (L/B = 3, 5 and 10). The results show that increasing the concrete compressive strength improved the ultimate strength, but decreased ductility of the test specimens. On the other hand, columns with higher slenderness ratio (B/t or L/B) showed lower ultimate strength and less ductile behavior. Failure appearances of the test columns include: outward buckling of the steel tube, crushing of in-fill concrete and welding failure at the joint. Meanwhile, no cracks were found at the corners of the test specimens due to the use of round corner cold-formed built-up steel sections. Finally, the design approaches adopted in (Eurocode-4, AISC-360-10 and Wang et al. 2017) are compared with the ultimate strength of the test columns, which shows satisfactory agreement between the predicted and experimental capacities.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AISC:
-
American Institute of Steel Construction
- EC4:
-
Eurocode 4
- AS:
-
Australian code
- CSA:
-
Canadian Standards Association
- BNBC:
-
Bangladesh National Building Code
- SCFST:
-
Square concrete-filled steel tubular column
- CFST:
-
Concrete-filled steel tubular column
- SCFWCFS:
-
Square concrete-filled welded cold-formed steel
- B :
-
Width of column
- D :
-
Depth of column
- L :
-
Length of column
- t :
-
Thickness of steel
- B/t :
-
Column cross-sectional slenderness ratio
- L/B :
-
Column global slenderness ratio
- A s :
-
Area of steel
- A c :
-
Area of concrete
- LVDT:
-
Linear variable differential transformer
- Af y :
-
Yield strength of structural steel
- f u :
-
Ultimate stress of steel
- E s :
-
Elastic modulus of steel
- E c :
-
Elastic modulus of concrete
- ε y :
-
Yield strain of steel
- ε su :
-
Ultimate strain of steel at peak load
- P ut,exp :
-
Ultimate load of the tested column
- ε u :
-
Peak axial strain at ultimate load
- DI:
-
Ductility index
- SI:
-
Strength index
- EIeff :
-
Effective stiffness of composite section
- P e :
-
Elastic critical buckling load
- K :
-
Effective length factor
- L :
-
Laterally unbraced length of the member
- W c :
-
Weight of concrete per unit volume
- f ′c :
-
Compressive cylinder strength (4 inch × 8 inch) Concrete
- ε 85% :
-
Axial displacement at 85% of the maximum load at the decay branch
References
Han, L.-H.; Li, W.; Bjorhovde, R.: Developments and advanced applications of concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) structures: Members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 100, 211–228 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2014.04.016
Liew, J.Y.R.; Xiong, M.; Xiong, D.: Design of concrete-filled tubular beam-columns with high strength steel and concrete. Structures 8, 213–226 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2016.05.005
Romero, M.L.; Ibañez, C.; Espinos, A.; Portolés, J.M.; Hospitaler, A.: Influence of ultra-high strength concrete on circular concrete-filled dual steel columns. Structures 9, 13–20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2016.07.001
Hassanein, M.F.; Elchalakani, M.; Karrech, A.; Patel, V.I.; Yang, B.: Behaviour of concrete-filled double-skin short columns under compression Through Finite Element Modelling: SHS Outer and SHS Inner Tubes. Structures 14, 358–375 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2018.04.006
Ekmekyapar, T.: Experimental performance of concrete filled welded steel tube columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 117, 175–184 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2015.10.013
Chan, T.-M.; Huai, Y.-M.; Wang, W.: Experimental investigation on lightweight concrete-filled cold-formed elliptical hollow section stub columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 115, 434–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2015.08.029
Serras, D.N.; Skalomenos, K.A.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.D.; Beskos, D.E.: Modeling of circular concrete-filled steel tubes subjected to cyclic lateral loading. Structures. 8, 75–93 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2016.08.008
Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.: Seismic behavior of blind bolted CFST frames with semi-rigid connections. Structures 9, 91–104 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2016.10.001
de Oliveira, W.L.A.; De Nardin, S.; de Cresce El Debs, A.L.H.; El Debs, M.K.: Influence of concrete strength and length/diameter on the axial capacity of CFT columns. J. Constr. Steel. Res. 65, 2103–2110 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2009.07.004
Ekmekyapar, T.; AL-Eliwi, B.J.M.: Experimental behaviour of circular concrete filled steel tube columns and design specifications. Thin-Walled Struct. 105, 220–230 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2016.04.004
Chen, C.-C.; Ko, J.-W.; Huang, G.-L.; Chang, Y.-M.: Local buckling and concrete confinement of concrete-filled box columns under axial load. J. Constr. Steel Res. 78, 8–21 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2012.06.006
Uy, B.: Strength of concrete-filled steel box columns incorporating local buckling. J. Struct. Eng. 126, 341–352 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2000)126:3(341)
Uy, B.: Local and post-local buckling of concrete filled steel welded box columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 47, 47–72 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-974X(98)80102-8
Ge, H.; Usami, T.: Strength of concrete-filled thin-walled steel box columns: experiment. J. Struct. Eng. 118, 3036–3054 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1992)118:11(3036)
Kitada, T.: Ultimate strength and ductility of state-of-the-art concrete-filled steel bridge piers in Japan. Eng. Struct. 20, 347–354 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0296(97)00026-6
Roeder, C.W.; Cameron, B.; Brown, C.B.: Composite action in concrete-filled tubes. J. Struct. Eng. 125, 477–484 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1999)125:5(477)
Petrus, C.; Abdul Hamid, H.; Ibrahim, A.; Parke, G.: Experimental behaviour of concrete filled thin walled steel tubes with tab stiffeners. J. Constr. Steel Res. 66, 915–922 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2010.02.006
Sani, M.S.H.M.; Muftah, F.; Muda, M.F.; Tan, C.S.: Resistance of built-up cold-formed steel channel columns filled with concrete. J. Teknol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v78.8498
Schneider, S.P.: Axially loaded concrete-filled steel tubes. J. Struct. Eng. 124, 1125–1138 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1998)124:10(1125)
Uy, B.: Strength of short concrete filled high strength steel box columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 57, 113–134 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-974X(00)00014-6
Han, L.-H.: Tests on stub columns of concrete-filled RHS sections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 58, 353–372 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-974X(01)00059-1
Lam, D.; Williams, C.A.: Experimental study on concrete filled square hollow sections. Steel Compos. Struct. 4, 95–112 (2004). https://doi.org/10.12989/scs.2004.4.2.095
Tao, Z.; Han, L.-H.; Wang, D.-Y.: Strength and ductility of stiffened thin-walled hollow steel structural stub columns filled with concrete. Thin-Walled Struct. 46, 1113–1128 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2008.01.007
Ellobody, E.; Young, B.; Lam, D.: Behaviour of normal and high strength concrete-filled compact steel tube circular stub columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 62, 706–715 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2005.11.002
Liang, Q.Q.; Uy, B.; Richard Liew, J.Y.: Nonlinear analysis of concrete-filled thin-walled steel box columns with local buckling effects. J. Constr. Steel Res. 62, 581–591 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2005.09.007
Richard Liew, J.Y.; Xiong, D.X.: Effect of preload on the axial capacity of concrete-filled composite columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 65, 709–722 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2008.03.023
Zhao, X.L.; Packer, J.A.: Tests and design of concrete-filled elliptical hollow section stub columns. Thin-Walled Struct. 47, 617–628 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2008.11.004
Han, L.-H.; Ren, Q.-X.; Li, W.: Tests on inclined, tapered and STS concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) stub columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 66, 1186–1195 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2010.03.014
Ren, Q.-X.; Han, L.-H.; Lam, D.; Hou, C.: Experiments on special-shaped CFST stub columns under axial compression. J. Constr. Steel Res. 98, 123–133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2014.03.002
Lai, M.H.; Ho, J.C.M.: Axial strengthening of thin-walled concrete-filled-steel-tube columns by circular steel jackets. Thin-Walled. Struct. 97, 11–21 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2015.09.002
EN 1994-1-1: Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures. Eurocode 4, Brussels, Belgium (2004)
AISC-360-10: Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction, Chicago, USA (2010)
CSA Standard S16: Design of steel structures. Canadian Standards Association, Ontario, Canada (2009)
DBJ13-51-2010: Technical Specification for Concrete-filled Steel Tubular Structures. The Construction Department of Fujian Province, Fuzhou, China (2010)
AS5100: Bridge Design-steel and Composite Construction. Australian Standard, Australia (2004)
BNBC: Bangladesh National Building Code. Dhaka, Draft version (2016)
Wang, Z.-B.; Tao, Z.; Han, L.-H.; Uy, B.; Lam, D.; Kang, W.-H.: Strength, stiffness and ductility of concrete-filled steel columns under axial compression. Eng. Struct. 135, 209–221 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.12.049
Standards Australia, AS/NZS 1391–2007 Metallic Materials: Tensile Testing at Ambient Temperature (2007)
Ren, Q.-X.; Zhou, K.; Hou, C.; Tao, Z.; Han, L.-H.: Dune sand concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) stub columns under axial compression: experiments. Thin-Walled. Struct. 124, 291–302 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2017.12.006
Han, L.-H.; Ren, Q.-X.; Li, W.: Tests on stub stainless steel–concrete–carbon steel double-skin tubular (DST) columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 67, 437–452 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2010.09.010
Acknowledgements
All assistance including laboratory, computing and financial supports from Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET) (Grant No. 0417042355), Dhaka, Bangladesh, is gratefully acknowledged. In addition, the authors would like to thank McDonalds Steel Building Products Ltd. for the supply of the tubular built-up steel sections for the CFST specimens.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.M., Ali, R.B., Begum, M. et al. Experimental Study of Square Concrete-Filled Welded Cold-Formed Steel Columns Under Concentric Loading. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 4225–4237 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04797-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04797-9